9-2 Passport 12/Passport 8 Operator’s Manual
9.4 Placing Resp Electrodes
As the skin is a poor conductor of electricity, preparing the skin is necessary for a good respiration signal. You can refer to
the ECG section for how to prepare the skin. For details, refer to section 8.3.1 Preparing the Patient and Placing the
Electrodes.
As the respiration measurement adopts the standard ECG electrode placement, you can use different ECG cables (3-lead,
or 5-lead). Since the respiration signal is measured between two ECG electrodes, if a standard ECG electrode placement
is applied, the two electrodes should be RA and LA of ECG Lead I, or RA and LL of ECG Lead II.
NOTE
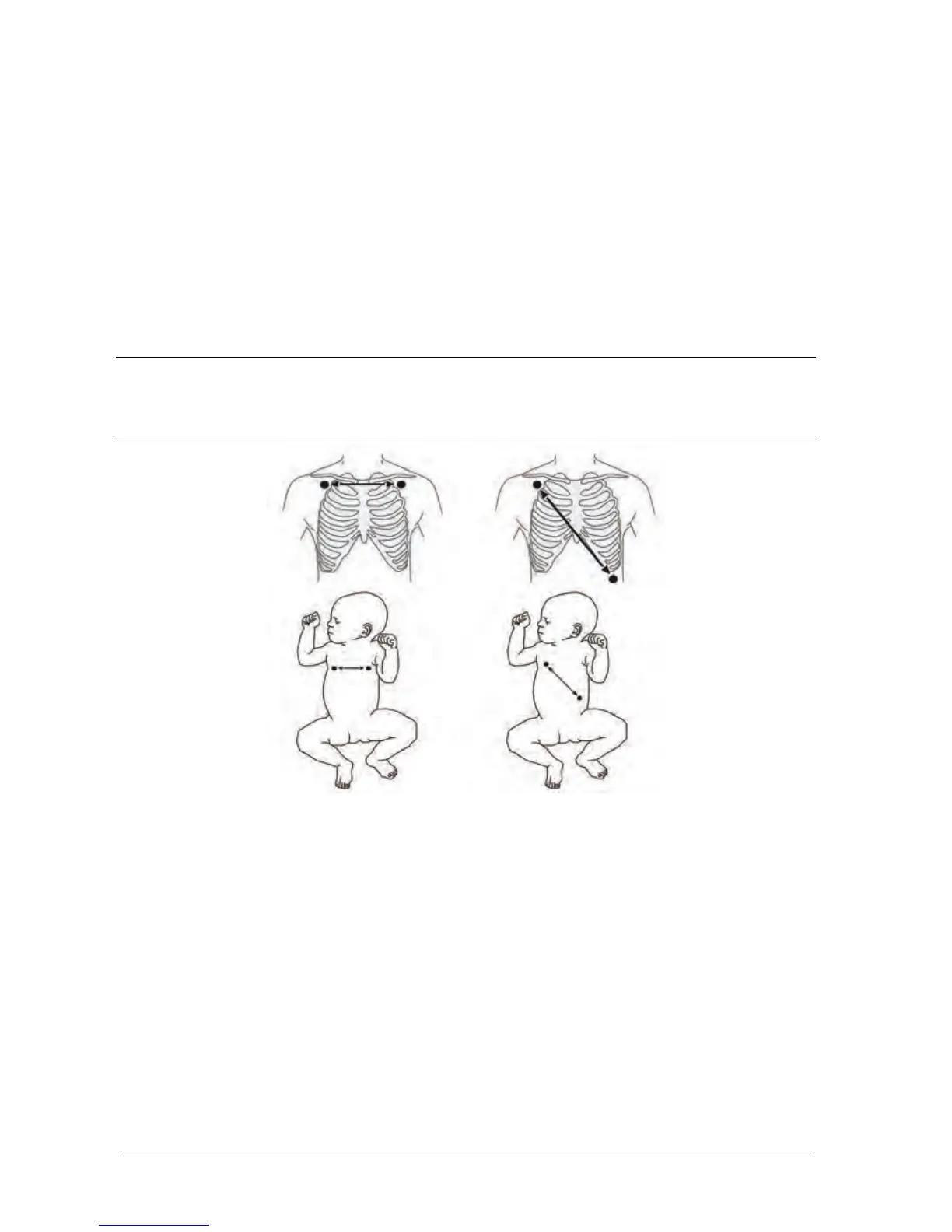
To optimize the respiration waveform, place the RA and LA electrodes horizontally when monitoring
respiration with ECG Lead I; place the RA and LL electrodes diagonally when monitoring respiration with
ECG Lead II.
Lead I Lead II
9.4.1 Optimizing Lead Placement for Resp
If you want to measure Resp and you are already measuring ECG, you may need to optimize the placement of the two
electrodes between which Resp will be measured. Repositioning ECG electrodes from standard positions results in
changes in the ECG waveform and may influence ST and arrhythmia interpretation.
9.4.2 Cardiac Overlay
Cardiac activity that affects the Resp waveform is called cardiac overlay. It happens when the Resp electrodes pick up
impedance changes caused by the rhythmic blood flow. Correct electrodes placement can help to reduce cardiac
overlay: avoid the liver area and the ventricles of the heart in the line between the respiratory electrodes. This is
particularly important for neonates.
 Loading...
Loading...