SV-DA200 series AC servo drive Running and operation
-77-
COM-. Then the servo enters into the locking state.
9. The motor shaft may rotate at a low speed if there is no upper command voltage. It is
necessary to adjust P3.20. Please refer to the detailed instruction of P3.20.
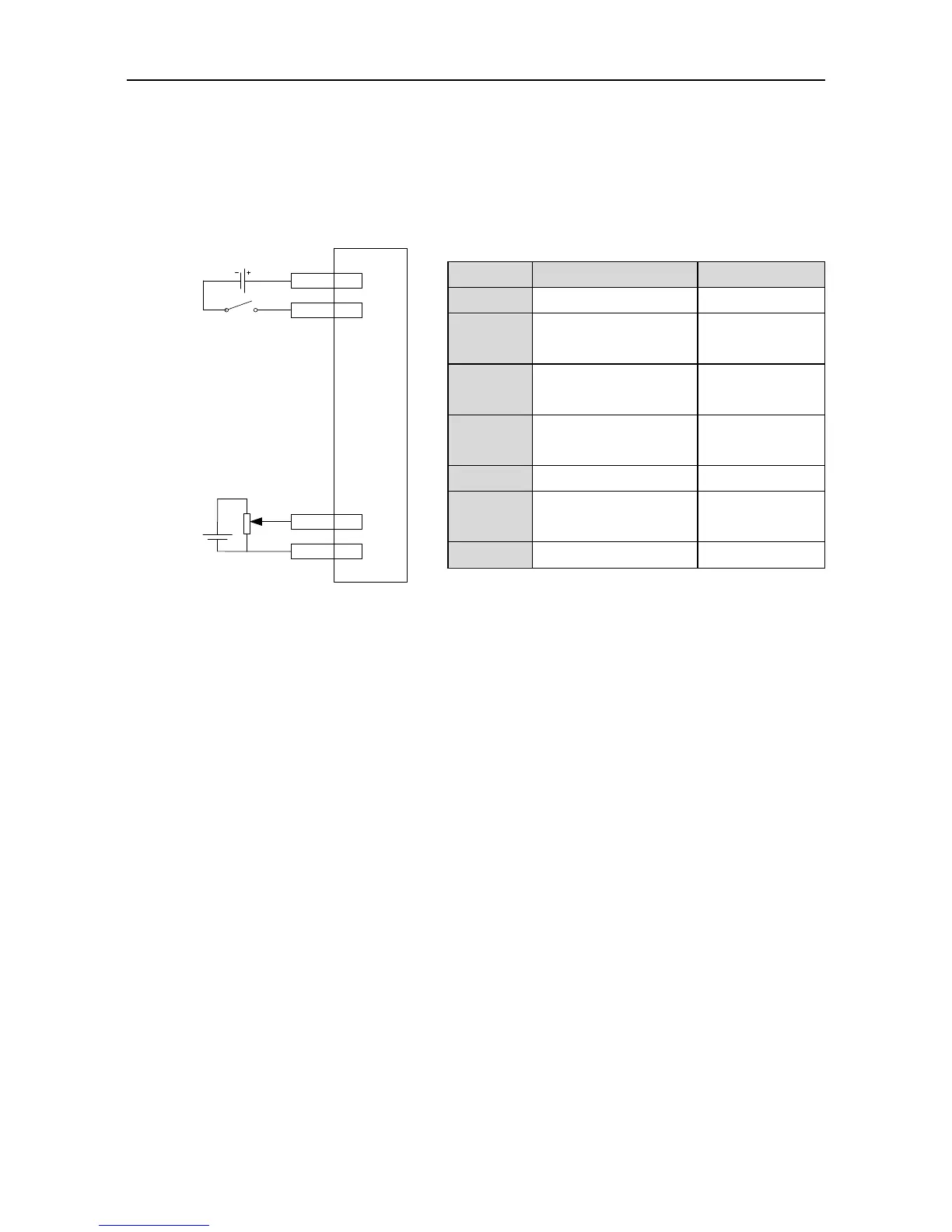
5.1.5 Running at the torque control mode
Simple connection:
Steps:
1. Complete the connection between the drive and the servo motor.
2. Set P0.03 to “2”, the torque control mode.
3. It is necessary to disconnect the control power supply after saving the modified value of
P0.03. And it will be valid after repowering on.
4. Set P0.60 to “1”, external analog torque command mode.
5. Set P0.61 to the required value. Please refer to the instruction of P0.61.
6. Set P3.26 to “4”, analog input 1 is torque command;
7. Set P0.62 to the required value. Please refer to the instruction of P0.62.
8. Connect the corresponding terminals of CN1.
9. Connect the CN1 to the drive and power on. Control the connection between SON and
COM-. Then the servo enters into the locking state.
10. The motor shaft may rotate at a low speed if there is no upper command voltage. It is
necessary to adjust P3.23. Please refer to the detailed instruction of P3.23.
11. In the torque mode, please adjust the speed limit and set P0.46 to the required value. Please
refer to the detailed instruction of P0.46.
5.1.6 Parameter setting before running the servo
Parameter setting must be conducted before running the servo. Relevant parameters can be set via
the panel, PC software or communication to meet the function and performance requirements of the
site application. See chapter 6 for the detailed description of all parameters of the servo drive. Some