IRIG AM synchronization of a device to its IRIG source is typically measured in the tens of
microseconds, while synchronization using a IRIG DCLS signal can typically provide around
100 nanoseconds or so (plus the cable delays between VersaSync and the other device, as
well as the processing delays of the other system itself).
IRIGAMfunctionality is available through an option card.
Note that all IRIG outputs has its own available ‘offset’ capability, which is configurable via
VersaSync’s WebUI, to help account for cabling and processing delays of the device each
output is connected with.
5.4.2 IRIG Carrier Frequencies
Each IRIG code specifies a carrier frequency that is modulated to encode date and time, as
well as control bits to time-stamp events. Initially, IRIG applications were primarily military
and government associated. Today, IRIG is commonly used to synchronize voice loggers,
recall recorders, and sequential event loggers found in emergency dispatch centers and
power utilities.
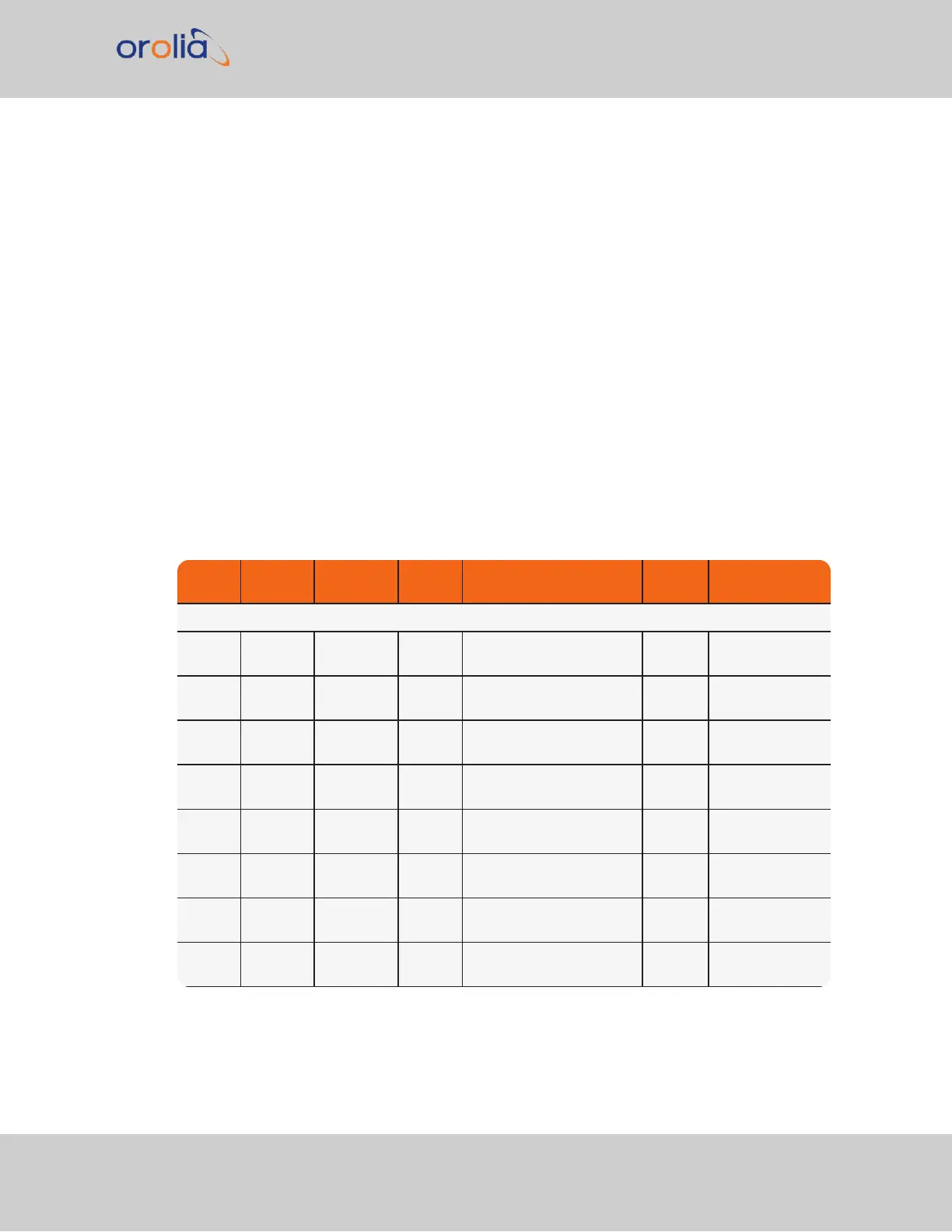
Table 5-32:
Available IRIG output signals
Format Encoding Modulation Carrier Coded Expressions Bit rate
Time Frame
Interval
IRIG-A
IRIG-A A000 DCLS N/A BCD
TOY
, CF and SBS 1000
pps
0.1 sec
IRIG-A A001 DCLS N/A BCD
TOY
, CF 1000
pps
0.1 sec
IRIG-A A002 DCLS N/A BCD
TOY
1000
pps
0.1 sec
IRIG-A A003 DCLS N/A BCD
TOY
, SBS 1000
pps
0.1 sec
IRIG-A A004 DCLS N/A BCD
TOY
, BCD
YEAR
, CF
and SBS
1000
pps
0.1 sec
IRIG-A A005 DCLS N/A BCD
TOY
, BCD
YEAR
, and
CF
1000
pps
0.1 sec
IRIG-A A006 DCLS N/A BCD
TOY
, BCD
YEAR
1000
pps
0.1 sec
IRIG-A A007 DCLS N/A BCD
TOY
, BCD
YEAR
, and
SBS
1000
pps
0.1 sec
VersaSync User Manual 329
APPENDIX
 Loading...
Loading...