6-32 Using Explicit Messaging
PowerFlex® 755 Drive Embedded EtherNet/IP Adapter User Manual
Publication 750COM-UM001A-EN-P
MicroLogix 1100 Example
When using RSLogix 500 v7.10 or lower, explicit messaging must be
performed using the PCCC N-File method. For RSLogix 500 v7.20 or
higher, the CIP messaging method has been added along with the PCCC
N-File method. However, the CIP method is recommended because it is
easier to use and understand. For this reason, only instructions for the
CIP method are provided.
Important:Due to inherent limitations with the PCCC N-File method,
only contiguous multiple parameters can be read or written
in one explicit message.
For explicit messaging using the PCCC N-File method, the N150
N-Files must be used because they are already mapped to specific
parameters in the drive and its connected peripherals. This enables
direct access to any parameter.
For PCCC N150 N-File information, refer to page C-9
.
The CIP messaging method provides a Generic Get/Set Attribute
Service which can be used to perform single parameter read or write
and multiple parameter read or write explicit messages. Also, the
Generic Set Attribute Service offers the choice of writing the data to the
drive’s Non-Volatile Storage (NVS) or the drive’s Random Access
Memory (RAM). Note that when selecting the data to be written to
RAM, the data will be lost if the drive loses power.
For supported classes, instances, and attributes, refer to Appendix
C,
EtherNet/IP Objects
.
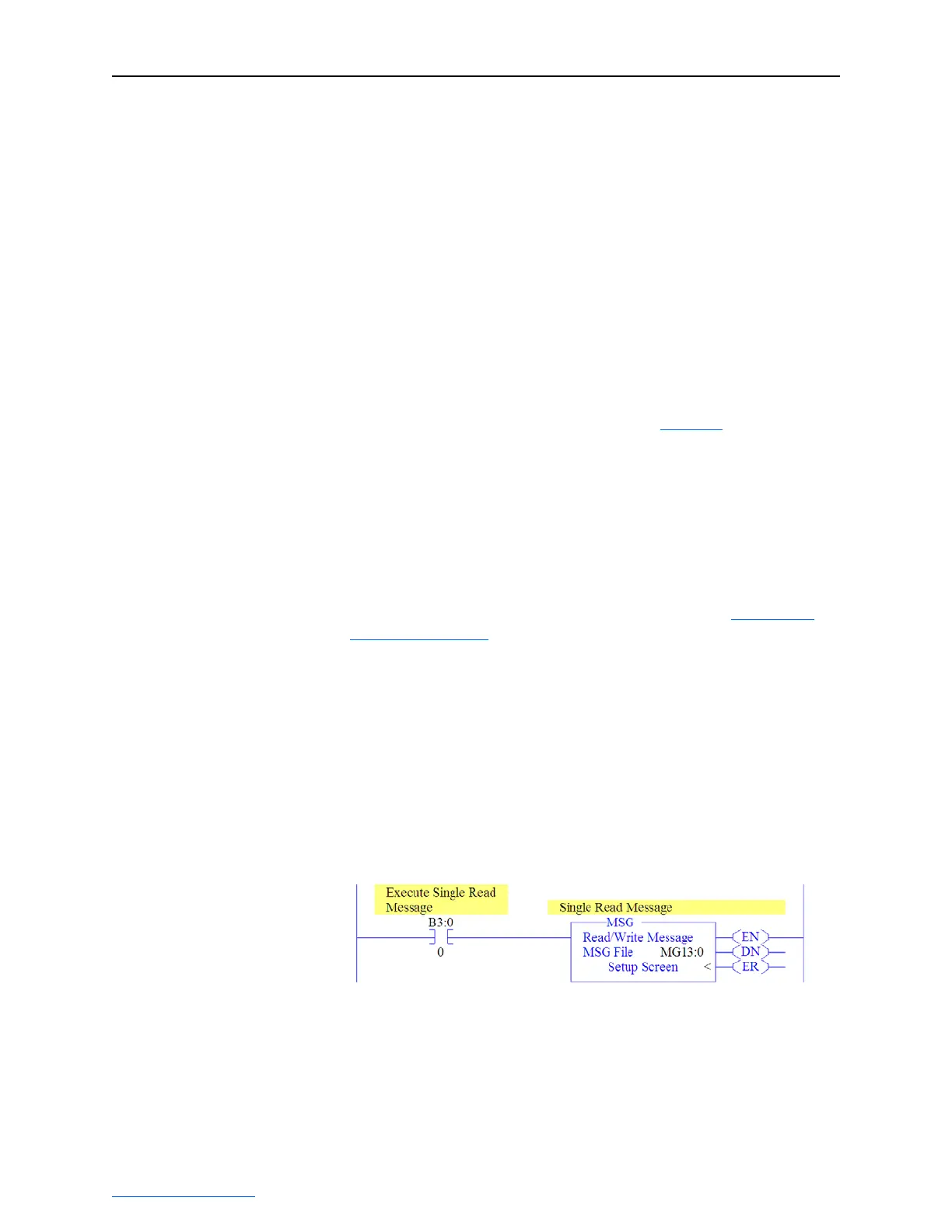
MicroLogix 1100 Example Ladder Logic Program to Read Single
Parameter
A Generic Get Attribute Single message is used to read a single
parameter. This read message example reads the value of the 32-bit
REAL (floating point) parameter 007 - [Output Current] in a PowerFlex
750-Series drive.
Figure 6.37 Example Ladder Logic Explicit Messaging Program for Read Single

 Loading...
Loading...