User's Manual 9. CLI-Based Management
Version 6.8 81 Mediant 500L MSBR
9.2.2 Enabling SSH with RSA Public Key for CLI
Unless configured for TLS, Telnet is not secure as it requires passwords to be transmitted
in clear text. To overcome this, Secure SHell (SSH) is used, which is the de-facto standard
for secure CLI. SSH 2.0 is a protocol built above TCP, providing methods for key
exchange, authentication, encryption, and authorization.
SSH requires appropriate client software for the management PC. Most Linux distributions
have OpenSSH pre-installed; Windows-based PCs require an SSH client software such as
PuTTY, which can be downloaded from
http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/.
By default, SSH uses the same username and password as the Telnet and Web server.
SSH supports 1024/2048-bit RSA public keys, providing carrier-grade security. Follow the
instructions below to configure the device with an administrator RSA key as a means of
strong authentication.
To enable SSH and configure RSA public keys for Windows (using PuTTY SSH
software):
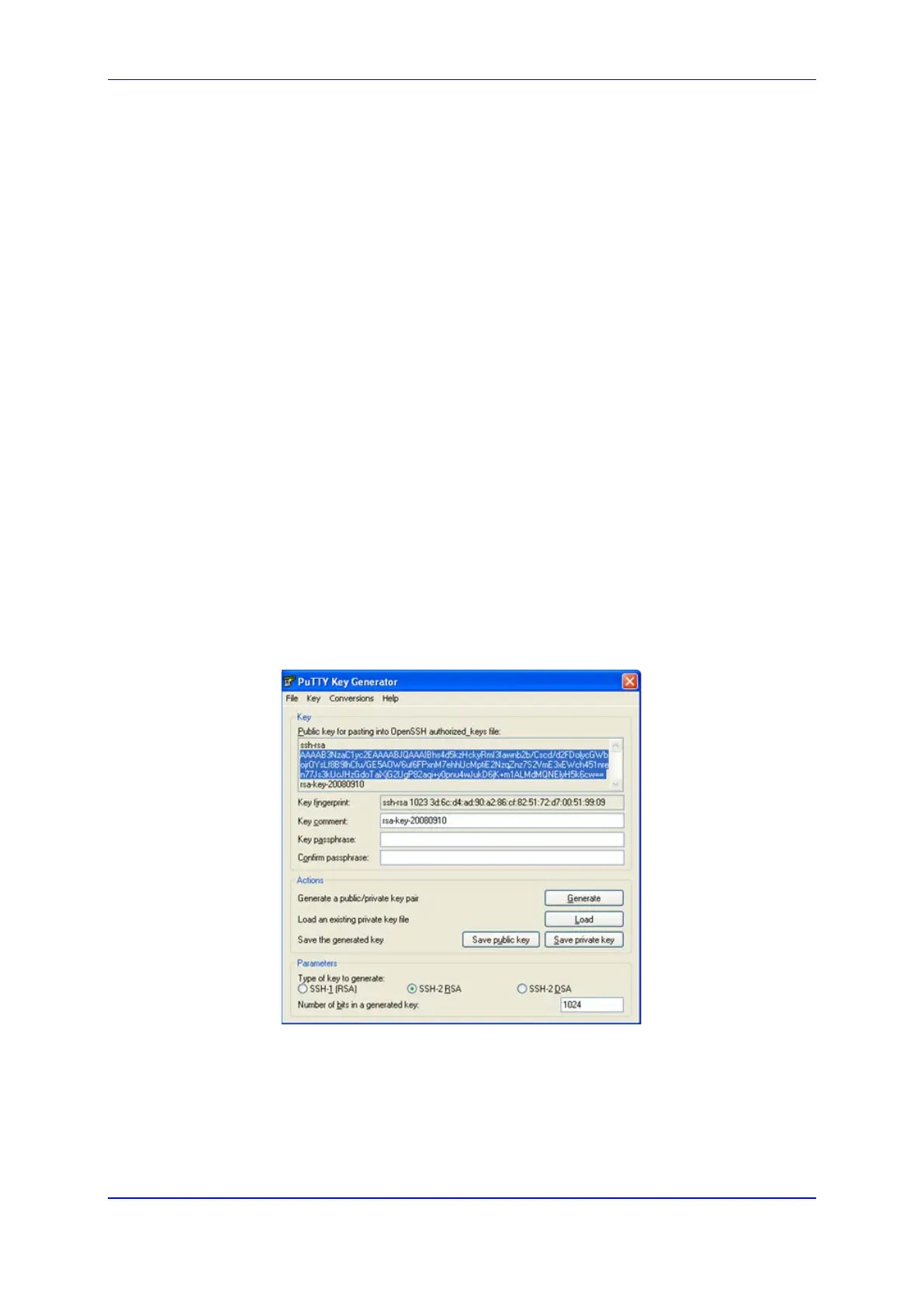
1. Start the PuTTY Key Generator program, and then do the following:
a. Under the 'Parameters' group, do the following:
♦ Select the SSH-2 RSA option.
♦ In the 'Number of bits in a generated key' field, enter "1024" bits.
b. Under the 'Actions' group, click Generate and then follow the on-screen
instructions.
c. Under the 'Actions' group, click Save private key to save the new private key to a
file (*.ppk) on your PC.
d. Under the 'Key' group, select the displayed encoded text between "ssh-rsa" and
"rsa-key-….", as shown in the example below:
Figure 9-2: Selecting Public RSA Key in PuTTY
2. Open the Telnet/SSH Settings page (Configuration tab > System menu >
Management > Telnet/SSH Settings), and then do the following:
a. Set the 'Enable SSH Server' parameter to Enable.

 Loading...
Loading...



