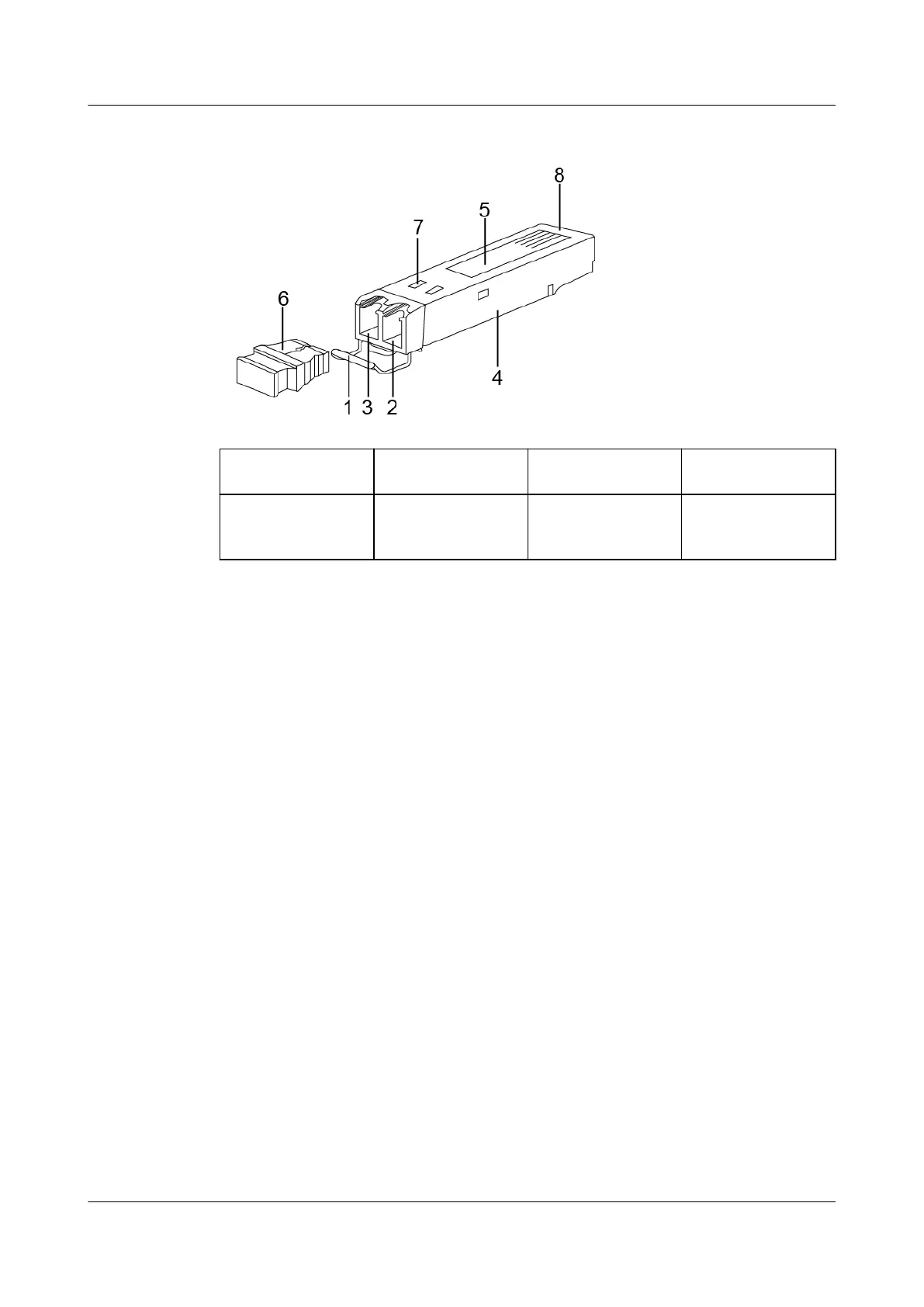
Figure 3-34 Optical module structure
1. Handle 2. Receiver 3. Transmitter 4. Shell
5. Label 6. Dust cap 7. Spring 8. Module
connector
3.4.1.2 Types of Optical Modules
Optical modules are available in various types to meet
diversied requirements.
● Classied by transmission rates
Currently, the transmission rates of optical modules cover a wide range.
According to
dierent transmission rates, optical modules can be classied
into 400 Gbit/s optical modules, 200 Gbit/s optical modules, 100 Gbit/s optical
modules, 40 Gbit/s optical modules, 25 Gbit/s optical modules, and 10 Gbit/s
optical modules, 2.5 Gbit/s optical modules, 1.25 Gbit/s optical modules, 1000
Mbit/s optical modules, 155 Mbit/s optical modules, and 100 Mbit/s optical
modules.
●
Classied by encapsulation types
The higher transmission rate an optical module provides, the more complex
structure it has. According to the encapsulation type, optical modules are
classied into SFP, eSFP, SFP+, XFP, SFP28, QSFP28, QSFP+, CXP, CFP,CSFP and
QSFP-DD.
– SFP: small form-factor pluggable.
– eSFP: enhanced small form-factor pluggable. An eSFP module is an SFP
module that supports monitoring of voltage, temperature, bias current,
transmit optical power, and receive optical power. Because all the SFP
optical modules support these monitoring functions, eSFP is also called
SFP.
– SFP+: small form-factor pluggable plus, SFP with a higher rate. SFP+
modules are more sensitive to electromagnetic interference (EMI)
because they have a higher rate. To reduce EMI, SFP+ modules have more
springs than SFP modules and the cages for SFP+ modules on a card are
tighter.
HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F
Hardware Guide 3 Hardware Description
Issue 05 (2023-03-31) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 99

 Loading...
Loading...











