because of modal dispersion, but their costs are also lower. They are used
for small-capacity, short-distance transmission.
Wavelength division multiplexing modules dier from other optical modules in
center wavelengths. A common optical module has a center wavelength of 850
nm, 1310 nm, or 1550 nm, whereas a wavelength division multiplexing module
transmits lights with
dierent center wavelengths. Wavelength division
multiplexing modules are classied into two types: coarse wavelength division
multiplexing (CWDM) and dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM).
Within the same band, DWDM modules are available in more types and use
wavelength resources more
eciently than CWDM modules. DWDM and CWDM
modules allow lights with
dierent center wavelengths to be transmitted on one
ber without interfering each other. Therefore, a passive multiplexer can be used
to combine the lights into one channel, which is then split into multiple channels
by a demultiplexer on the remote end. This reduces the optical
bers required.
DWDM and CWDM modules are used for long-distance transmission.
The transmit power of a long-distance optical module is often larger than its
overload power. Therefore, when using such optical modules, select optical
bers
of an appropriate length to ensure that the actual receive power is smaller than
the overload power. If the optical
bers connected to a long-distance optical
module are too short, use an optical attenuator to reduce the receive power on
the remote optical module. Otherwise, the remote optical module may be burnt.
3.4.1.3 Instruction
The following lists some common optical modules, which may not be supported
by this product. The gures are for reference only.
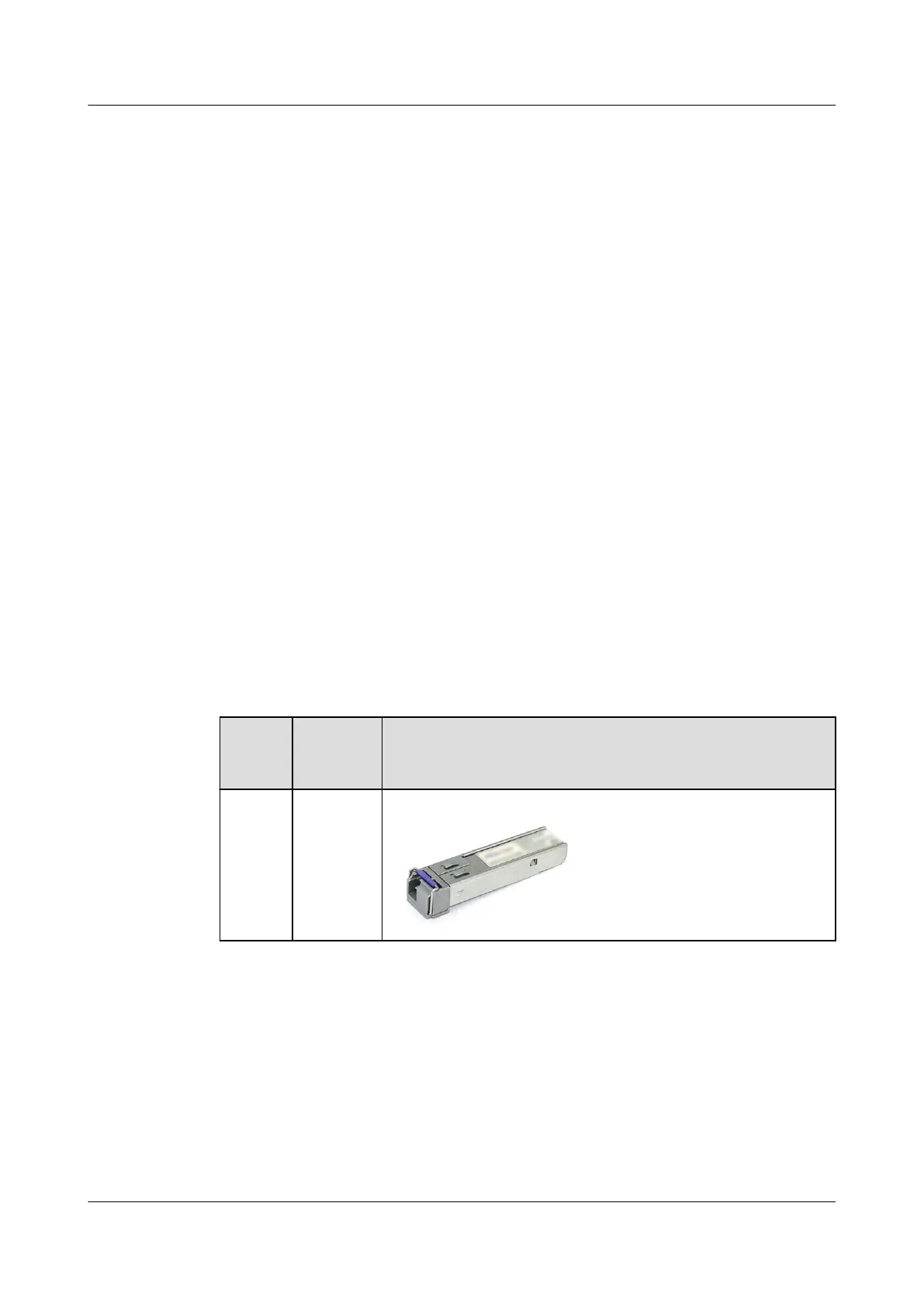
Table 3-86 Commonly used optical modules
Encaps
ulatio
n type
Interface
type
Appearance
SFP LC Single-ber-bidirectional transceiver
HUAWEI NetEngine 8000 F
Hardware Guide 3 Hardware Description
Issue 05 (2023-03-31) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 101

 Loading...
Loading...











