Appendix 7 Supplemental Technical Information
A19
Appendix
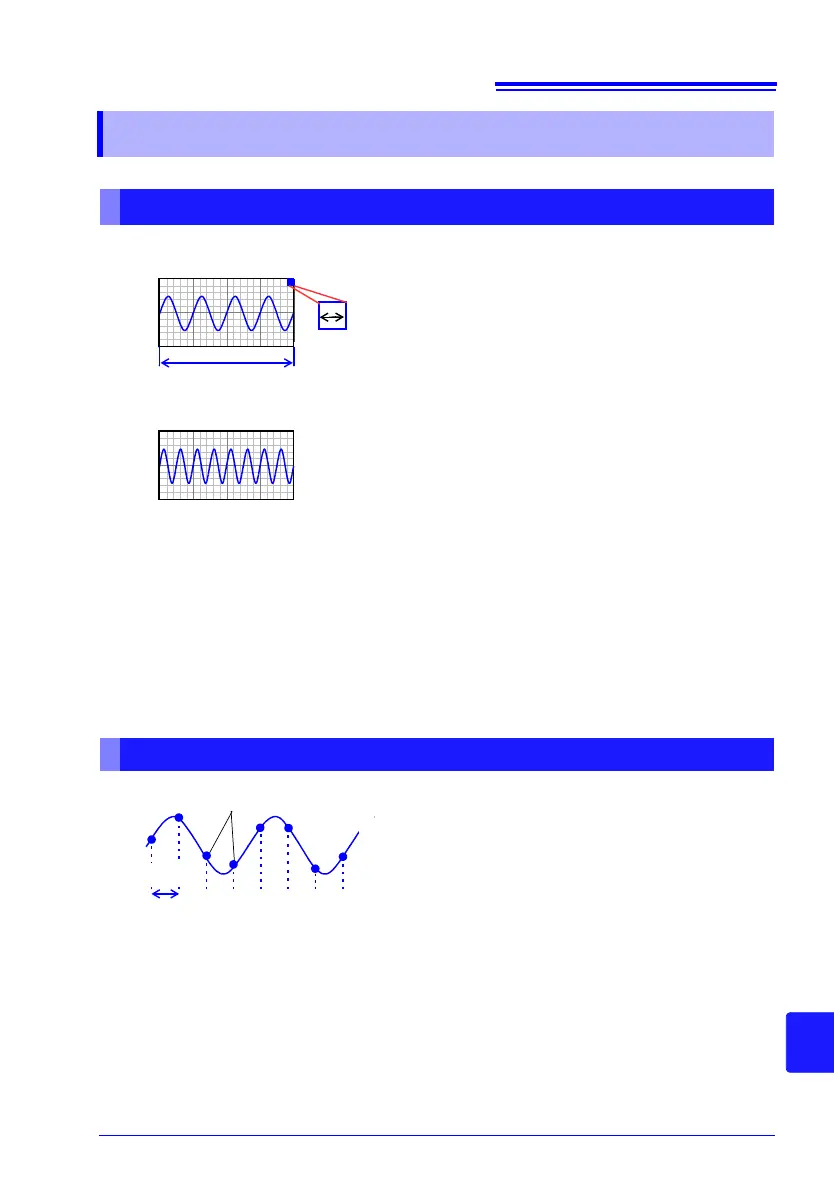
The input signal acquisition rate corresponds to time
per division on the horizontal axis.
Determining the timebase: Calculate from the fre-
quency and period.
f [Hz] = 1/t [s] (f: frequency, t: period)
Example: If the measurement frequency is 50 Hz
50 [Hz] = 1/t [s] t = 1/50 [s] = 0.02 [s] = 20 [ms]
To enable 1 period to be displayed with 10 divisions,
the timebase becomes 20 [ms]/10 [div]= 2 ms/div.
To display multiple periods, set a timebase range that
is slower than 2 ms/div.
From the selection ranges for the timebase range, se-
lect a range that is close to the calculated value.
To measure phenomena with relatively fast signals
such as instantaneous waveforms, we suggest setting
a small value (if the frequency is 50 Hz, the timebase
should be set faster than 5 ms/div).
During and after measurement, waveforms can be ex-
panded and compressed along the time axis.
This instrument converts analog input signals into
digital values which are then processed internally as
digital (numerical) values. This A/D conversion pro
-
cess is called sampling. Sampling repeatedly mea-
sures the size of the input signal at a specific interval
(the sampling period).
The rate of measurement is called the sampling rate.
Sampling units are [S/s] (read as samples-per-sec-
ond)
This is the number of samples taken each second,
and is the inverse of the sampling period. (1/T)
Appendix 7 Supplemental Technical Information
Selecting a Timebase (Horizontal Axis)
20 div
Timebase: with 1 div = 5 ms
Timebase: with 1 div = 10 ms
1 div
Timebase and Sampling
Sampling Period
Sampling Points
Measurement

 Loading...
Loading...