Endian Modes
MOTOROLA
MPC823e REFERENCE MANUAL
14-3
ENDIAN MODES
14
14.1 LITTLE-ENDIAN FEATURES
The following is a list of the little-endian system’s main features:
• System Memory Organization and E-Bus Format are Little-Endian
• U-Bus Data, Instruction and Data Caches, and Internal Memory Format are Big-Endian
• Data Access Constraints that Follow the PowerPC Little-Endian Rules
• Same Byte Order between the Media and System Memory
• For Core Accesses, Swap and Address Demunging are Performed by the System
Interface Unit on the U-Bus to the System Path
• The Core’s Load/Store Unit Swapper Uses Munged Addresses to Put the Data on the
Right Byte Lanes when Half-Word or Byte Accesses are Performed
• The Communication Processor Module Performs Data Swapping According to
Information in the Buffer Descriptors
The following tables describe how to handle the little-endian program or data in the
little-endian system that is built around the MPC823e for various port sizes.
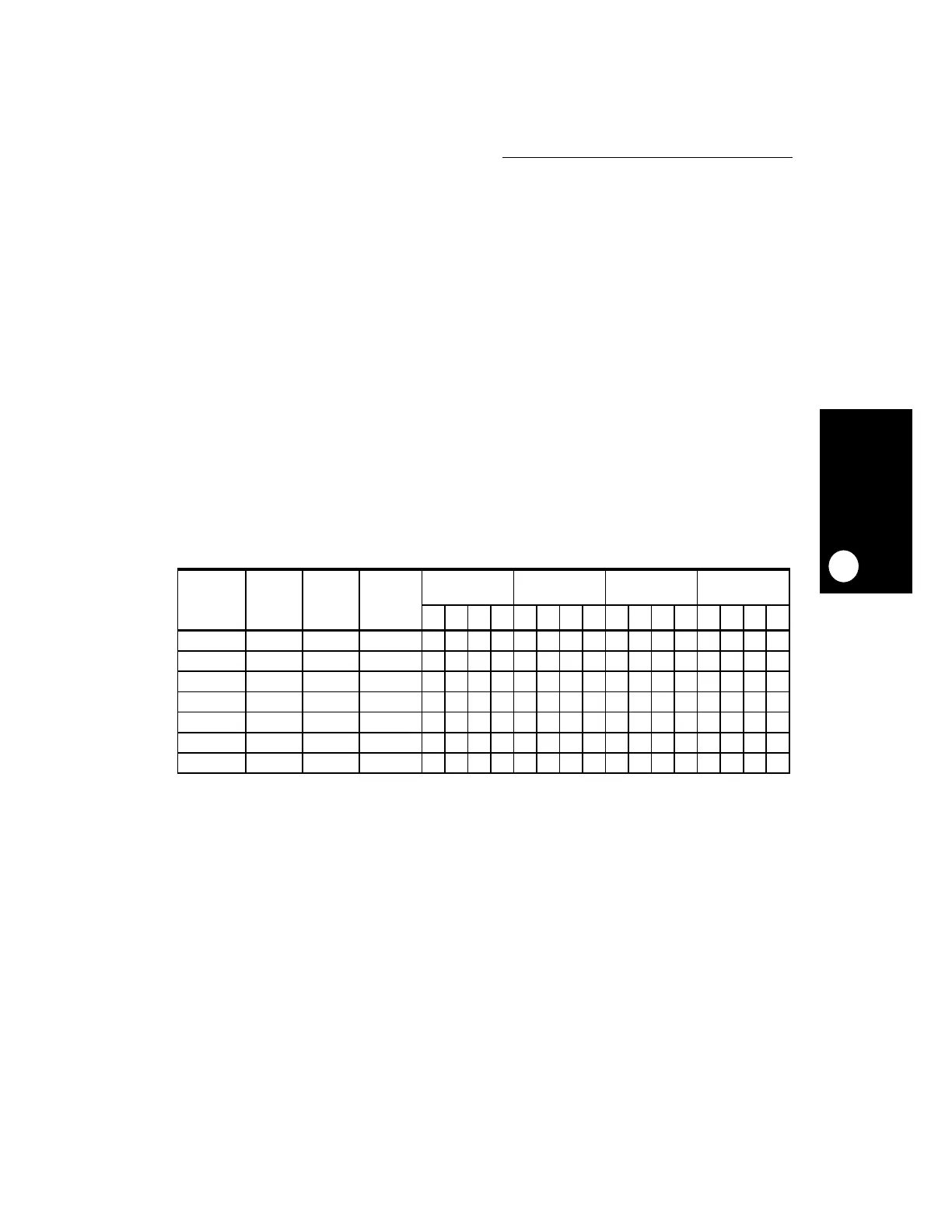
Table 14-3. Little-Endian Program/Data Path Between the
Register and 32-Bit Memory
FETCH/
LOAD
STORE
TYPE
LITTLE-
ENDIAN
ADDRESS
U-BUS
AND
CACHES
ADDRESS
EXTERNAL
BUS
ADDRESS
DATA IN THE
REGISTER
U-BUS AND
CACHES FORMAT
E-BUS FORMAT LITTLE-ENDIAN
PROGRAM/DATA
0123012301233210
Word 0 0 0 11 12 13 14 11 12 13 14 14 13 12 11 11 12 13 14
Half-word 0 2 0 21 22 21 22 22 21 21 22
Half-word 2 0 2 31 32 31 32 32 31 31 32
Byte 0 3 0 ‘a’ ‘a’ ‘a’ ‘a’
Byte 1 2 1 ‘b’ ‘b’ ‘b’ ‘b’
Byte 2 1 2 ‘c’ ‘c’ ‘c’ ‘c’
Byte 3 0 3 ‘d’ ‘d’ ‘d’ ‘d’

 Loading...
Loading...