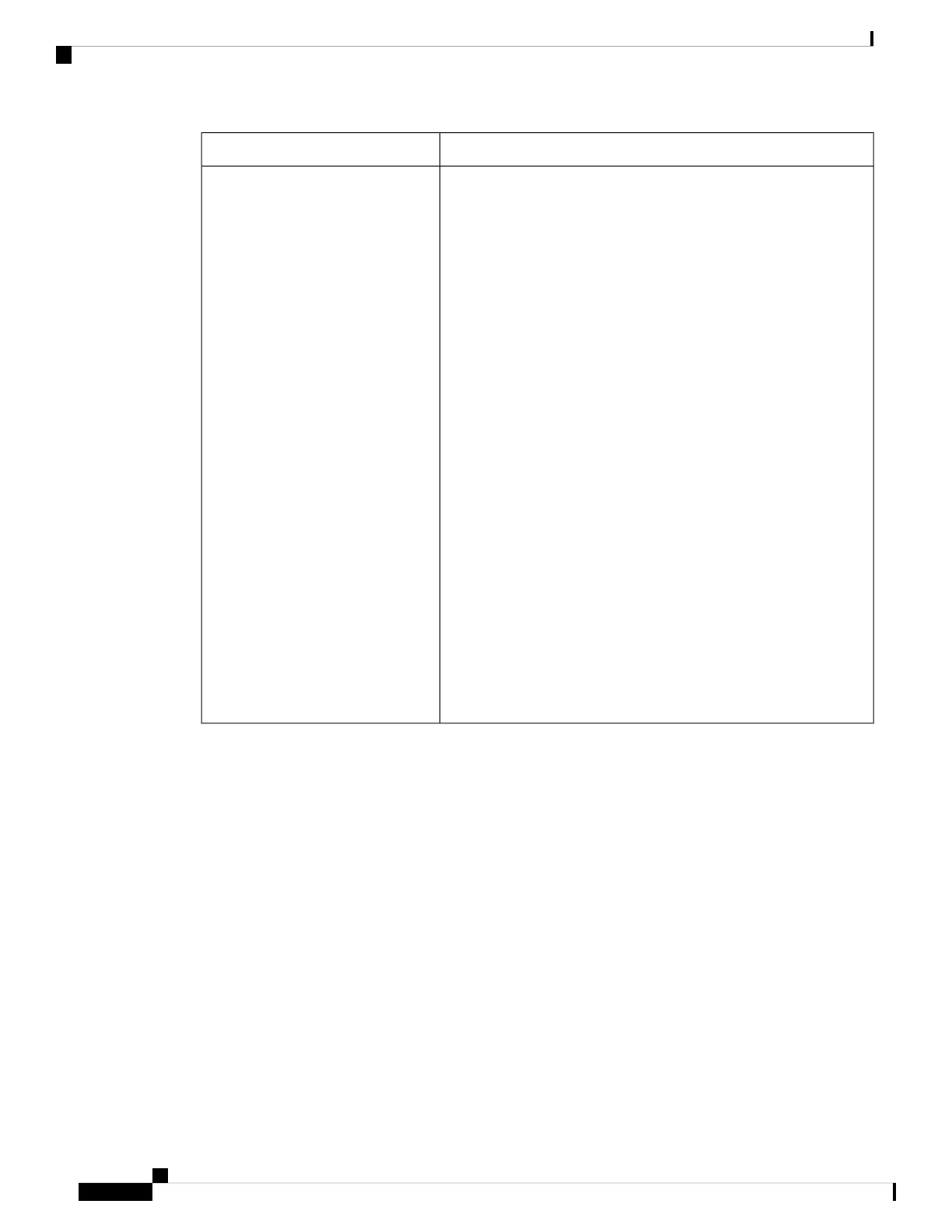
ValueField
Alias for file system.
crashinfo:—Crashinfo file.
disk0:—M2 SATA module.
flash:—Flash file system.
ftp:—FTP server.
http:—HTTP server.
https:—Secure HTTP server.
nvram:—NVRAM.
null:—Null destination for copies. You can copy a remote file to null
to find its size.
rcp:—Remote Copy Protocol (RCP) server.
scp:—Session Control Protocol (SCP) server.
system:—Contains the system memory, including the running
configuration.
tftp:—TFTP network server.
usbflash0:—USB flash memory.
usbflash1:—External USB flash memory.
xmodem:—Obtain the file from a network machine by using the
Xmodem protocol.
ymodem:—Obtain the file from a network machine by using the
Ymodem protocol.
Prefixes
Setting the Default File System
You can specify the file system or directory that the system uses as the default file system by using the cd
filesystem: privileged EXEC command. You can set the default file system to omit the filesystem: argument
from related commands. For example, for all privileged EXEC commands that have the optional filesystem:
argument, the system uses the file system specified by the cd command.
By default, the default file system is flash:.
You can display the current default file system as specified by the cd command by using the pwd privileged
EXEC command.
Displaying Information About Files on a File System
You can view a list of the contents of a file system before manipulating its contents. For example, before
copying a new configuration file to flash memory, you might want to verify that the file system does not
already contain a configuration file with the same name. Similarly, before copying a flash configuration file
System Management Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Bengaluru 17.4.x (Catalyst 9400 Switches)
368
Working with the Flash File System
Setting the Default File System
 Loading...
Loading...











