14.2.1 PRELIMINARIES
1. Determine which output relays have been selected to operate when a DEF trip occurs, by viewing the
programmable scheme logic. If the trip outputs are phase segregated (a different output relay allocated for
each phase), the output relay assigned for tripping on ‘A’ phase faults should be used.
2. Connect the output relay so that its operation will trip the test set and stop the timer.
3. Connect the current output of the test set to the ‘A’ phase current transformer input
4. Connect, all three phase voltages Va, Vb, and Vc.
5. Depending on the test equipment used, make sure the timer is set to start when the current is applied.
14.2.2 PERFORM THE TEST
1. Ensure that the timer is reset and prepare the following test shot.
2. Simulate a forward fault on the A-phase. The A-phase voltage must be simulated to drop by 4 times the DEF
VNpol Set setting; Va = Vn - 4 (DEF Vpol)
3. Set the fault current on the A-phase should to 2 times the DEF Threshold setting, and in the forward
direction. For a forward fault, the current Ia should lag the voltage Va by the DEF Char Angle setting; Ia = 2
(IN DEF Threshold Ð q DEF)
4. Phases B and C should retain their healthy pref-ault voltage, and no current. The duration of the injection
should be in excess of the DEF Delay setting (typically Aid. 1 DEF Dly. and Aid. 2 DEF Dly. + 100 ms).
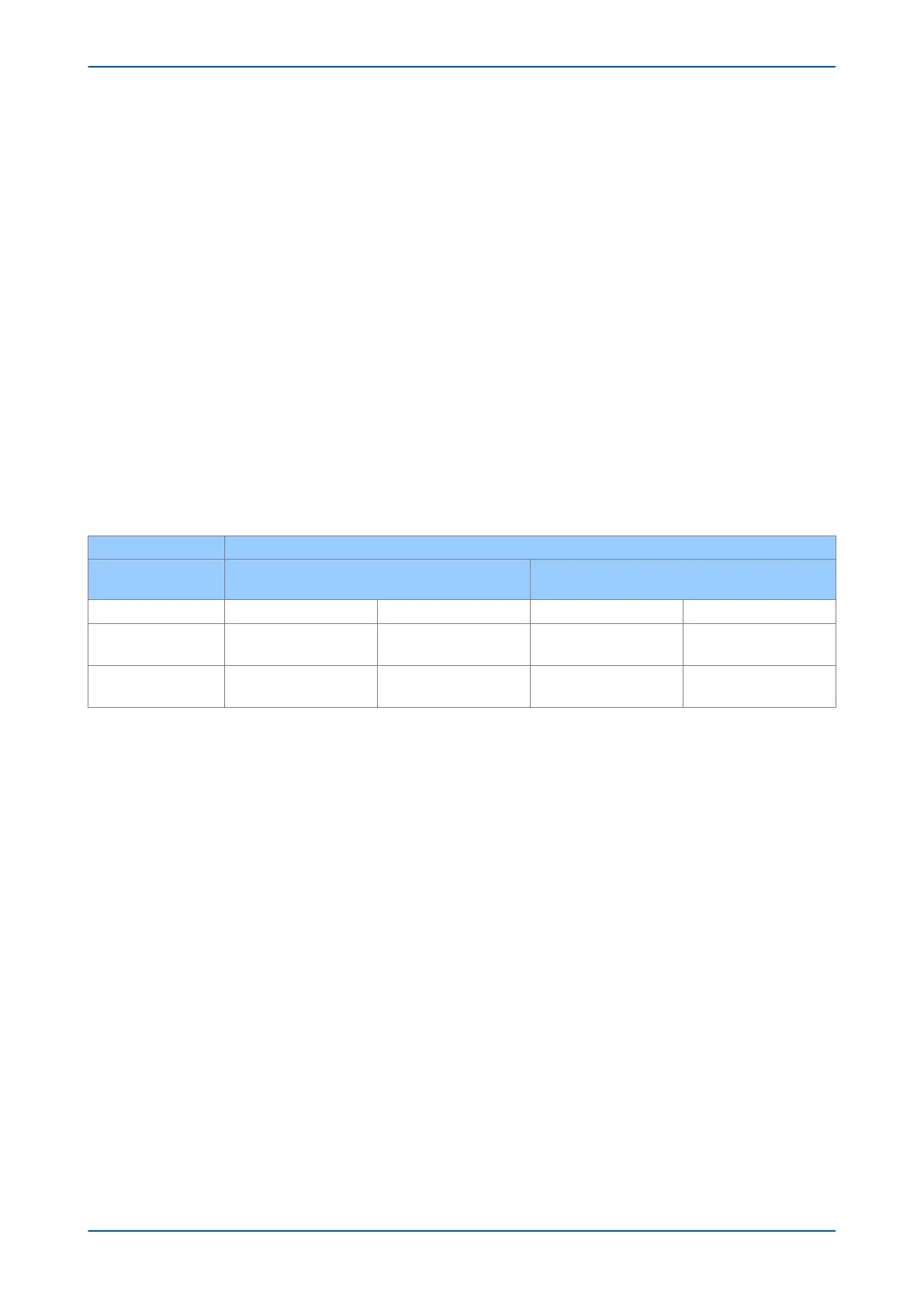
IED RESPONSE
Direction of fault
test injection
Forward fault Reverse fault
Signal Receive Opto ON OFF ON OFF
Blocking Scheme
No Trip,
No Signal Send
Trip,
No Signal Send
No Trip,
Signal Send
No Trip,
Signal Send
Permissive Scheme
(POR/POTT)
Trip,
Signal Send
No Trip,
Signal Send
No Trip,
No Signal Send
No Trip,
No Signal Send
14.2.3 FORWARD FAULT TRIP TEST
A forward fault is now injected as described, with the intention to cause a scheme trip.
For a permissive scheme, the Signal Receive opto-input should be energised. This is done by applying a
continuous DC voltage onto the required opto-input, either from the test set, station battery, or IED field voltage.
The commissioning engineer decides on the best method.
For a blocking scheme, the opto-input should remain de-energised (“OFF”).
1. Apply the fault and record the (phase A) trip time.
2. Switch OFF the AC supply and reset the alarms.
The aided earth fault (DEF) scheme trip time for POR schemes (permissive overreach) POR schemes should be less
than 40 ms.
For blocking schemes, where a non-zero DEF Dly time delay is set, the expected operating time is typically within
+/- 5% of the delay setting plus the “instantaneous” (40 ms) delay quoted above.
There is no need to repeat the test for phases B and C, as these trip assignments have already been proven by the
distance/delta trip tests.
Chapter 25 - Commissioning Instructions P543i/P545i
678 P54x1i-TM-EN-1

 Loading...
Loading...











