V Series Operating Instructions 9 - 21
ECG – Arrhythmia Arrhythmia Algorithm
9.6 Arrhythmia Algorithm
The V 12/V 21 uses an arrhythmia algorithm to monitor ECG waveform data. During the learning
phase of the algorithm templates of beats including one for the patient’s dominant beats are created.
These templates are then used to analyze newly received data. The algorithm verifies that data is free
from noise and artifact, and that it does not deviate from the patient's normal ECG rhythms.
A normal ECG waveform typically includes consistent spacing between R waves, a sharp and well
defined QRS complex, and an ECG baseline that is free of noise and artifact.
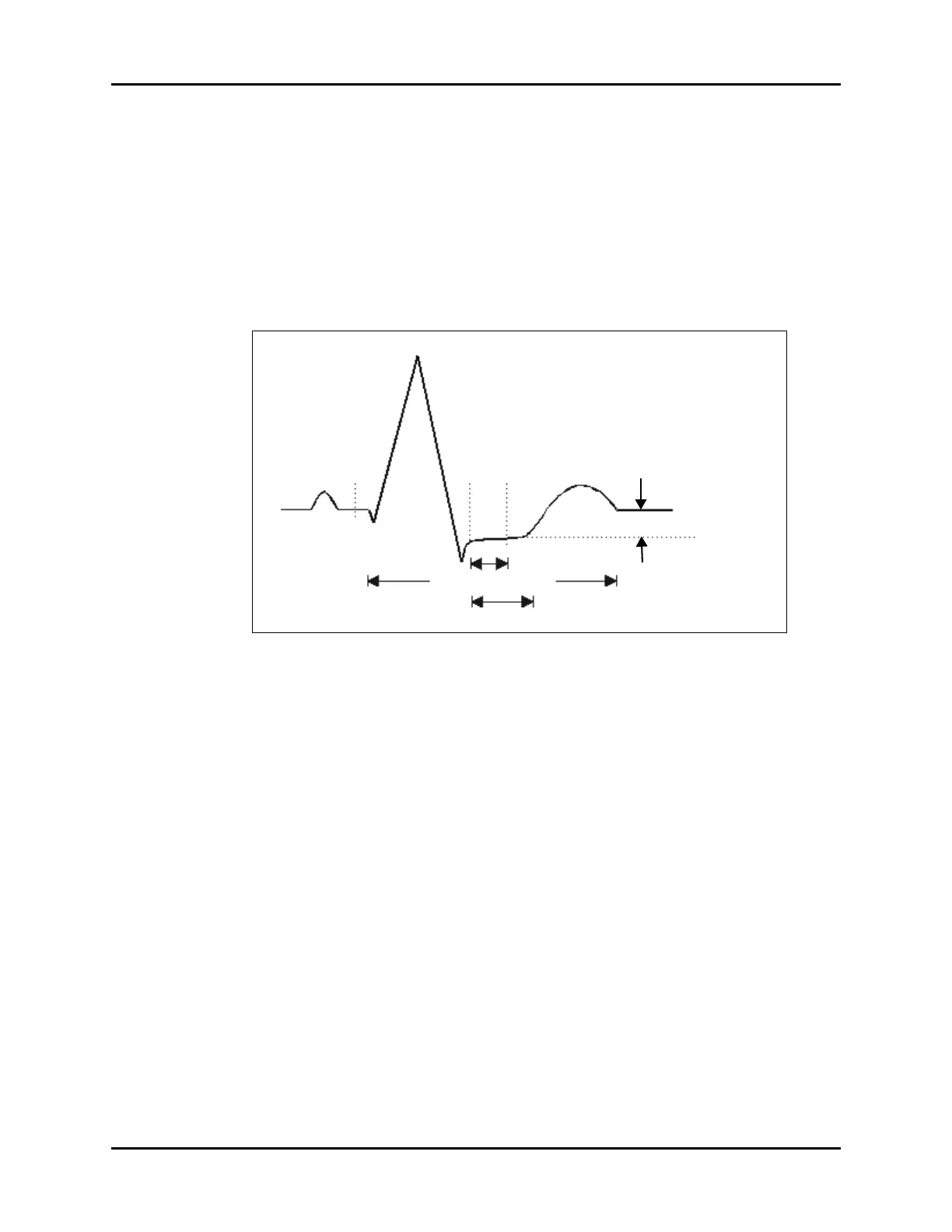
FIGURE 9-23 Example Waveform
9.6.1 Noise and Artifact
The presence of noise or artifact in an ECG waveform makes the accurate detection and classification
of heart beats difficult. To best optimize performance, all leads should be free of noise.
Some of the causes of ECG noise include poor skin preparation, improperly attached electrodes, dried
electrode gel, defective lead wires, and patient movement. The algorithm uses several techniques to
differentiate a patient’s QRS complexes from noise sources.
If noise levels are too high for a particular lead, a message is posted, and the data is dropped from
analysis until the signal quality is re-established.
If noise levels are too high, the following will occur until the signal quality is re-established:
• Beat detection is suspended
• All rhythm calls are suspended
•An ECG Noise message is displayed
ST Point
J Point
ST deviation
(Depression or Elevation)
ISO Point
40 to 80 msec
ST Segment
P
R
Q
S
T
QT Interval

 Loading...
Loading...