Publication 1752-UM001A-EN-P - October 2006
84 Create Your Application Program
You can password-protect your application program to prevent
unauthorized editing, verification, or printing of programs. To create a
password, follow these steps.
1. On the Logic tab of the Controller Properties dialog, check the
Enable Password checkbox.
2. On the Change Password dialog, type in the password in the
New Password field.
Passwords may contain up to six characters.
3. Re-type the password in the Confirm Password field.
4. Click OK.
The password will be requested whenever the Edit button is clicked
to open the Logic Editor. You can upload or download the program
without the password, but program edit, verification, print and report
functions are not available.
Programming Basics
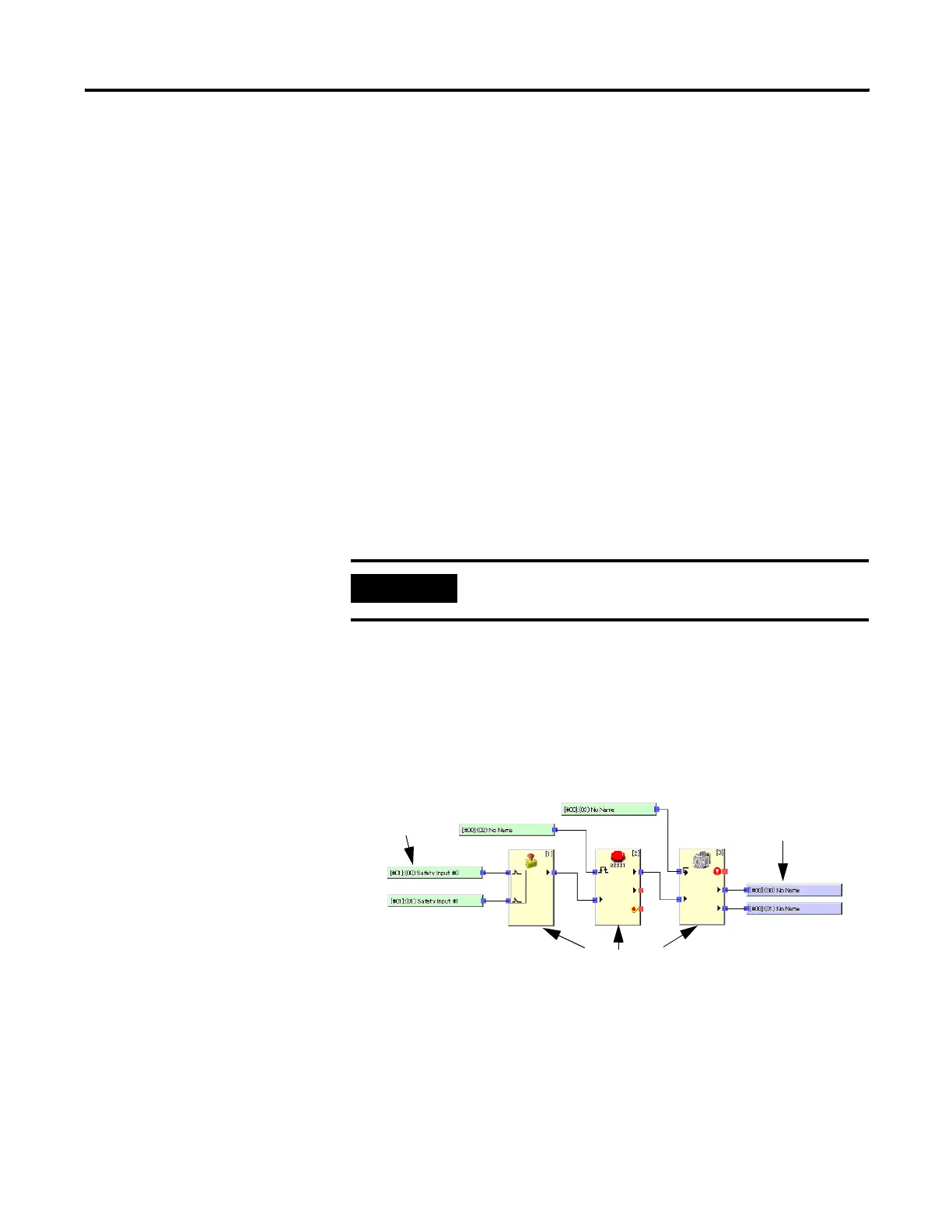
Programs are created from logic functions and function blocks that
indicate commands, from input tags that indicate data input sources,
and from output tags that indicate data output destinations. The I/O
are connected with connection lines.
I/O Connections
IMPORTANT
If you forget the password, it cannot be recovered.
Input Tags
Output Tags
Function Blocks

 Loading...
Loading...