Chapter 7: Functional description
7-14 Fresenius Medical Care multiFiltrate IFU-EN-UK 15A-2015
7.2.4 Slow continuous ultrafiltration (SCUF)
Indication A SCUF treatment can be indicated for the treatment of patients with
fluid overload, where the primary aim is the removal of fluid and the
elimination of urinary excreted solutes, or where the correction of
electrolyte disturbances is clinically not indicated.
Vascular access Just like CRRT treatments, SCUF also requires a venovenous vascular
access, i.e., blood is both removed from and, after treatment, reinfused
into a vein of the patient. Usually, a large-bore central venous
double-lumen catheter is used for the vascular access.
Extracorporeal blood
circuit
For SCUF, the blood pump maintains the extracorporeal blood circuit,
and the filtrate pump ensures the gravity-controlled removal of the
necessary ultrafiltration volume. No substituate is infused, nor is any
dialysate used.
Treatment parameters
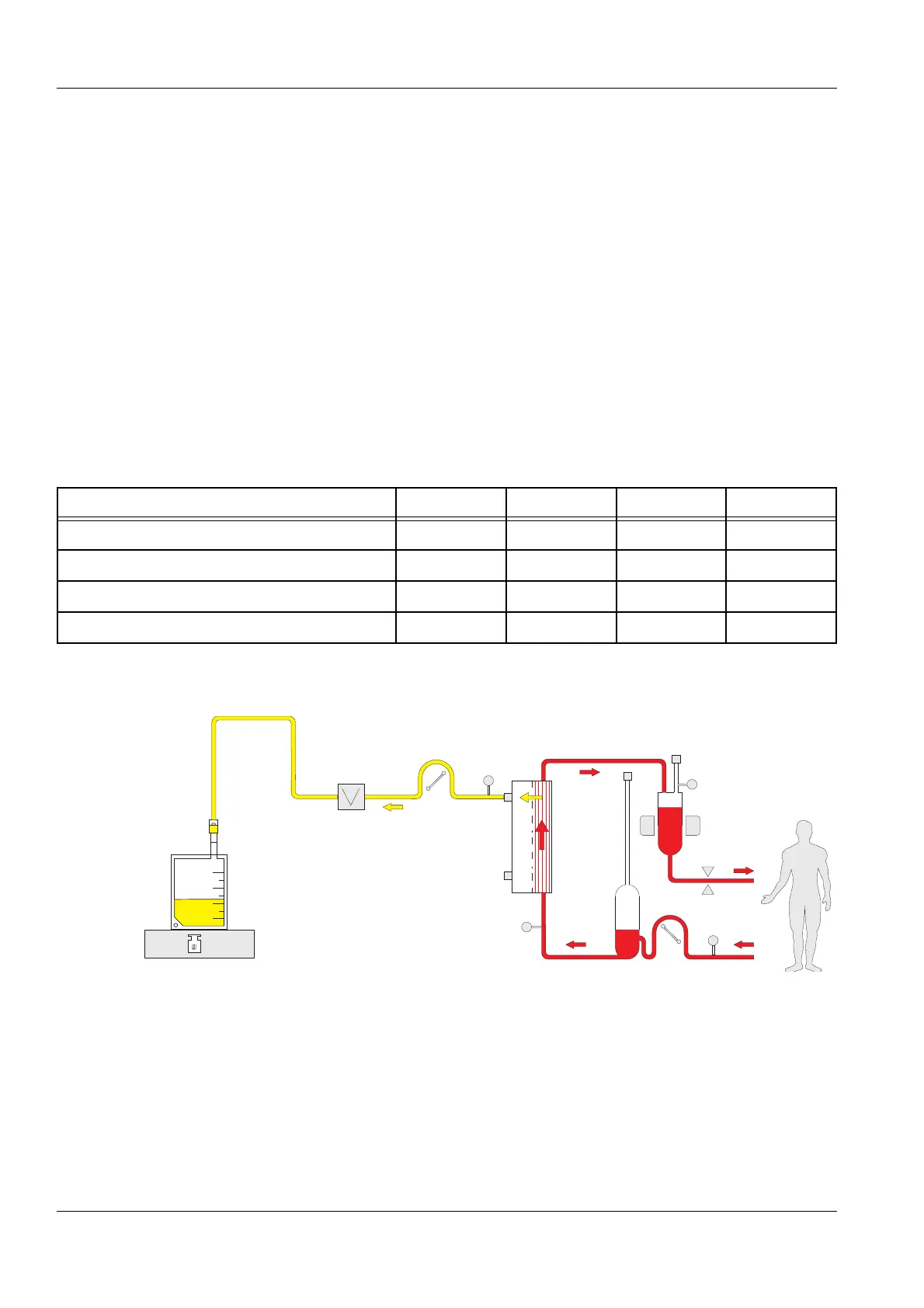
Fig.: SCUF flow diagram
Legend 1 Blood pump
2 Haemofilter
3 Air detector
4 Venous clamp
5 Filtrate pump
6 Blood leak detector
7 Filtrate
8 Scales 3 and 4
SCUF Min. Max. Resolution Unit
Blood flow 10 100 2 ml/min
Ultrafiltration 0 1200 10 ml/h
UF goal Off / 50 10,000 50 ml
Cont. heparin adm. Off / 0.1 25 0.1 ml/h
 Loading...
Loading...