Chapter 7: Functional description
Fresenius Medical Care multiFiltrate IFU-EN-UK 15A-2015 7-15
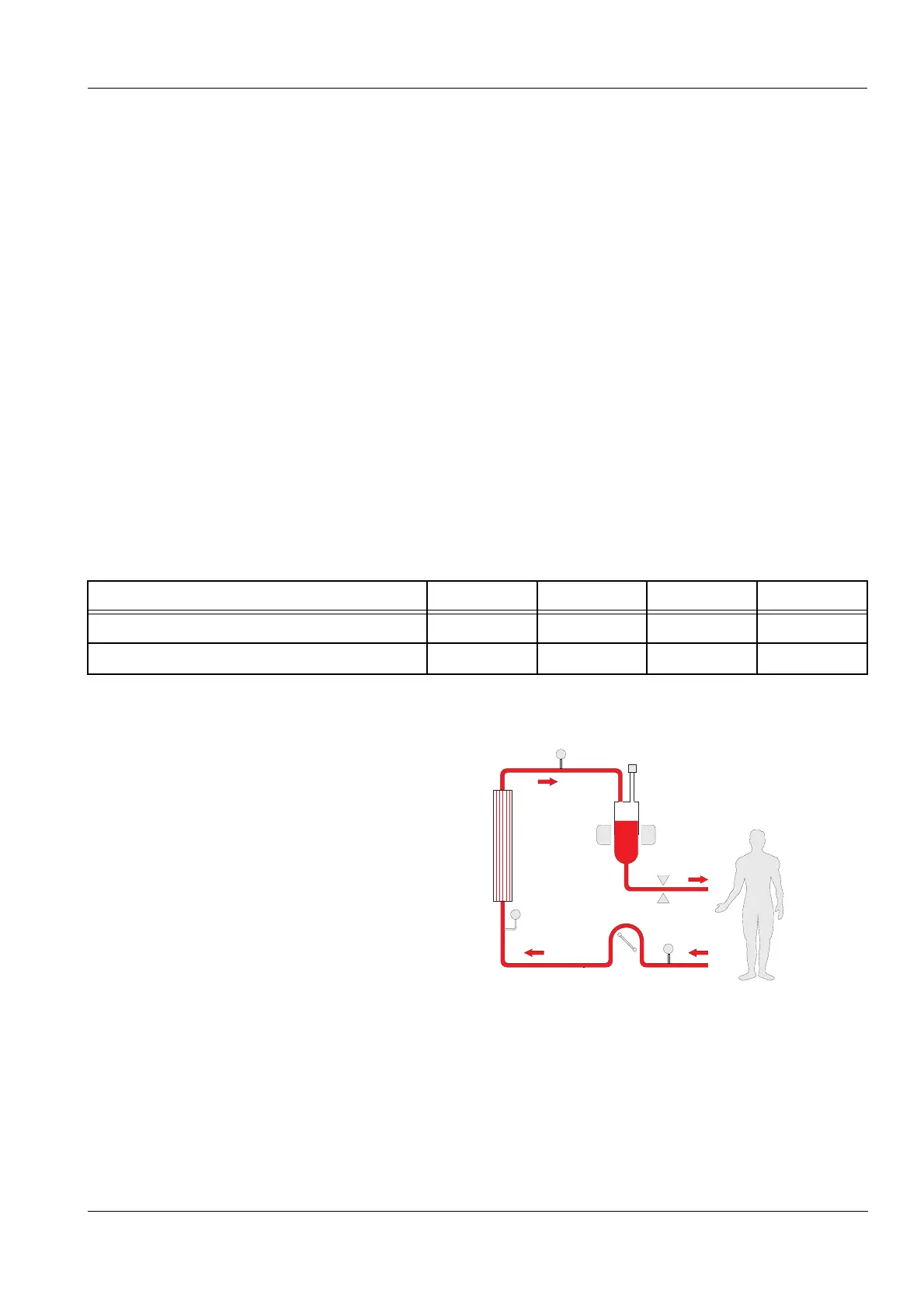
7.2.5 Haemoperfusion (HP)
Adsorption In haemoperfusion, toxins are removed by adsorption. It is employed to
remove toxic substances from the patient's blood which cannot be
removed by dialysis or haemofiltration due to proteopexy, for example.
It is a possible therapy following attempted suicide with certain drugs or
for the treatment of amanita poisoning. The extracorporeal blood circuit
is monitored as in conventional dialysis. Any possible clot formation in
the adsorber cartridge will be detected at an early stage by monitoring
the adsorber inlet pressure (pre-filter pressure) between the blood
pump and the adsorber cartridge.
Adsorber cartridge The patient is connected as usual to an extracorporeal circuit that is
driven by a blood pump. Instead of flowing through a dialyser, the blood
passes through an adsorber cartridge filled, for example, with small
sorbent particles. The arrangement of the sorbent material serves to
increase the adsorption surface. Inlet and outlet port of the adsorber
cartridge are closed by sieves of appropriate mesh size which permit
the passage of blood cells but prevent the comparatively large sorbent
particles from escaping.
Treatment parameters
Available settings
Fig.: Schematic of a haemoperfusion treatment (HP)
Legend 1 Blood pump
2 Adsorber cartridge
3Air detector
4 Venous clamp
HP Min. Max. Resolution Unit
Blood flow 10 500 10 ml/min
Cont. heparin adm. Off / 0.1 25 0.1 ml/h
 Loading...
Loading...