ATTENTION
This test requires a minimum of one NIM and one server (other UCN nodes). With only two
nodes, the NIM talks point-to-point. Three nodes are required for true triangulation.
Introduction
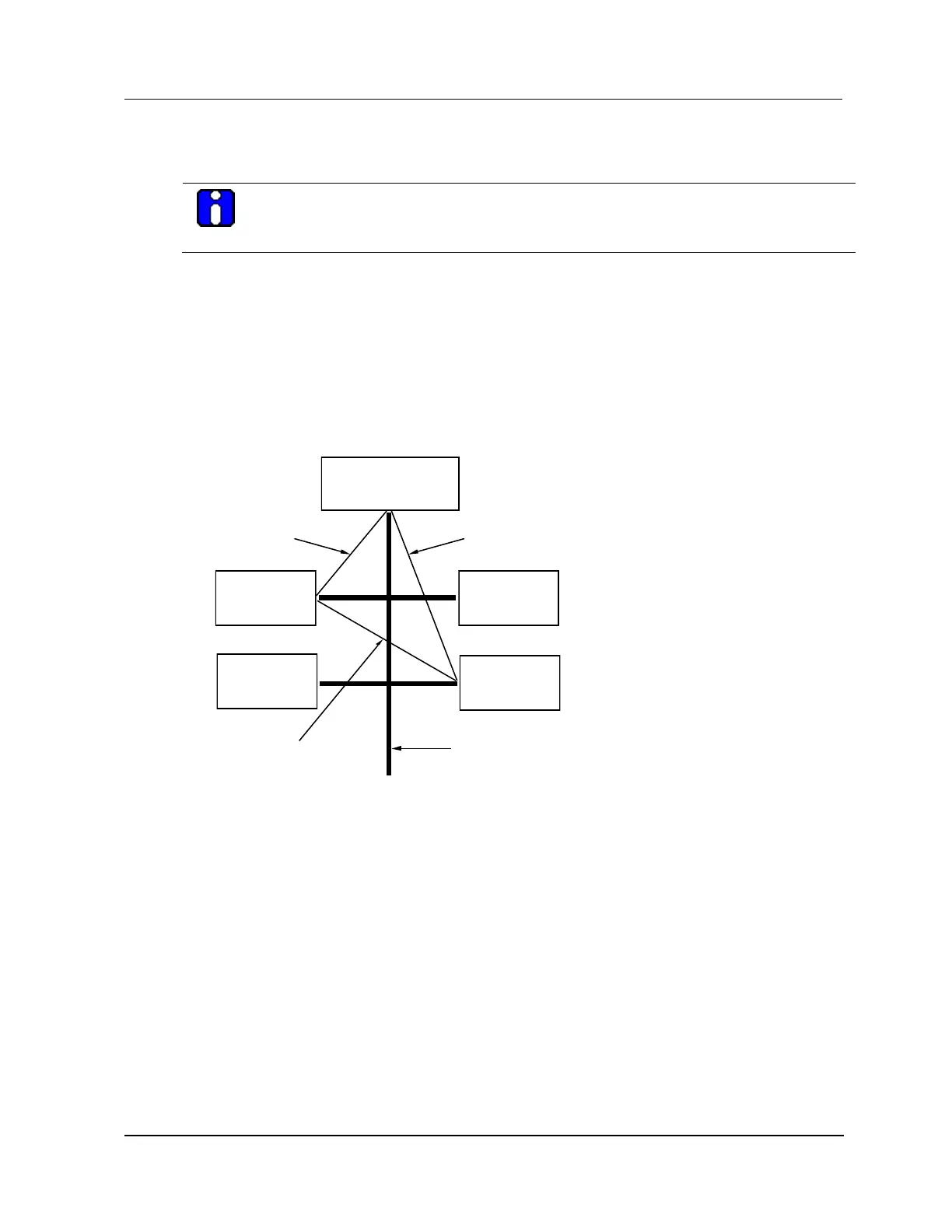
In the triangulation test, as illustrated in the following figure, only nodes that are configured in the test
are capable of token passing participate. For example, HPMs that have not been loaded, cannot pass
tokens and therefore do not participate. For those nodes that do participate, the test Master issues a
message to another node in the test and requests the message to be forwarded to a third node. The third
node in the test then sends a message back to the test Master, which verifies that the path has
successfully completed. While passing the message, the following communication paths are checked:
Master (NIM) to Slave 1, Slave 1 to Slave 2, and Slave 2 to back to the Master.
Figure 192 Triangulation Test
Timeout policy
Because a message may be lost or an error may occur, the Master has a reasonable timeout policy for
receiving the response back from Slave 2. The timeout policy assumes that each Slave in the test is
serving only one Master. This means that responses arriving late are considered errors. By examining
several paths together, it is usually possible to determine which nodes are experiencing communication
problems.

 Loading...
Loading...











