197
Supported Escape Codes
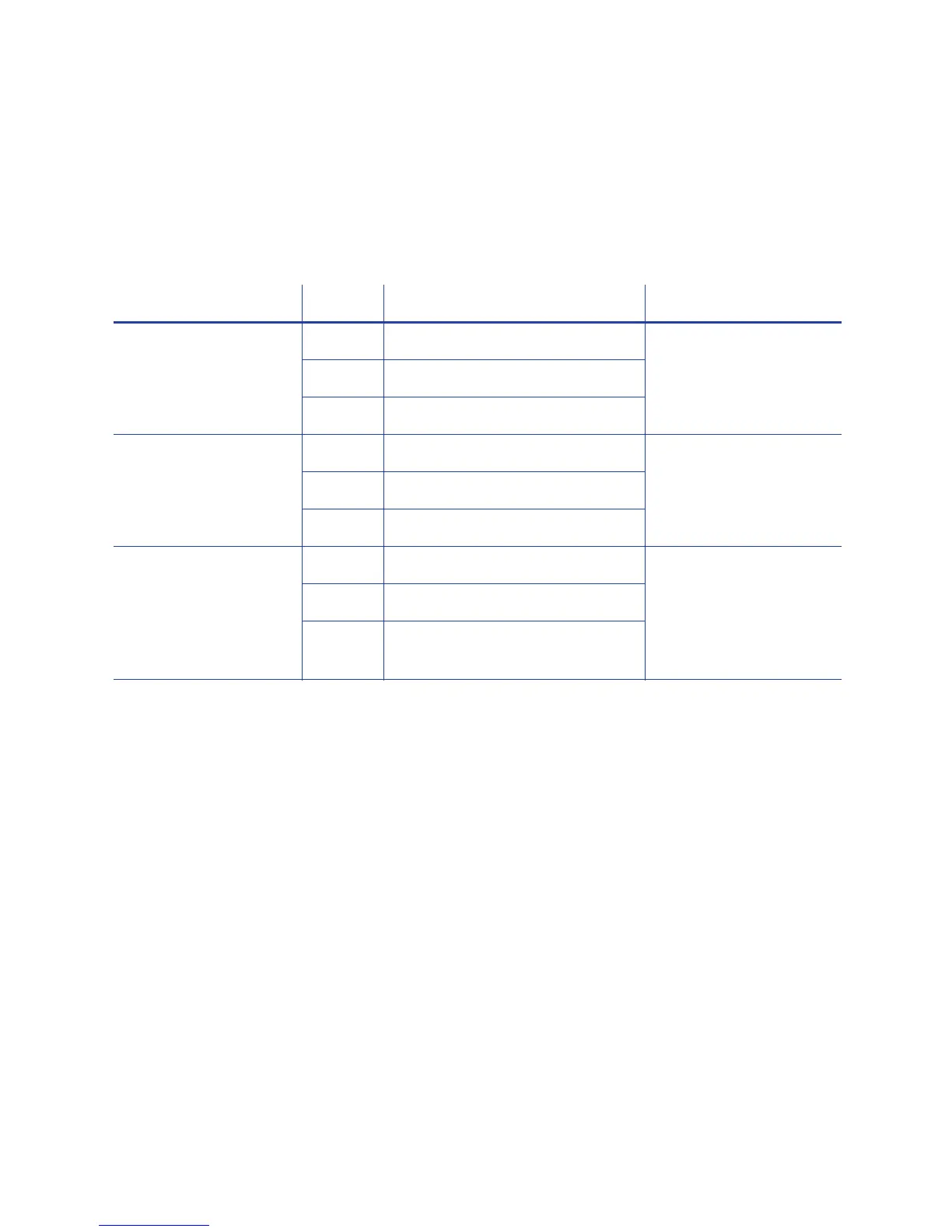
The Escape Code defines the track for the data. The data format for each track is
set in the printer, and you must enter the type of data the format requires. The
table below shows the default ISO format data, and how the data looks when
formatted. The syntax column shows the general statement for how the data must
be provided. For each track there is an example of how the data looks.
Syntax Track Example Manufacturer
~<track#><data> 1 (IATA) ~1ENCODING WITH ESCAPES Eltron/Zebra
2 (ABA) ~21234567890
3 (TTS) ~31234567890
~<track#>=<data> 1 (IATA) ~1=ENCODING WITH ESCAPES Atlantek
2 (ABA) ~2=1234567890
3 (TTS) ~3=1234567890
~<track#>
<Start Sentinel>
<d
ata> <End Sentinel>
1 (IATA) ~1%ENCODI
NG WITH ESCAPES? Datacard HiFX, RP90x,
and SRxxx; JVC; and
Fargo
The on
ly Start Sentinel
p
ermitted for
tracks 2
and 3 is ; (semicolon)
2 (ABA) ~2;1234567890?
3 (TTS) ~3;1234567890
HINTS & TIPS
• The driver recognizes all supported escape codes.
• Use a small font size to shorten lines of text to encode.
• Keep text to print on a different line from text to encode.
• When the driver adds lines of te
xt for the same track,
the sequence is
determined by the application. Test your application with the driver to make
sure the data is in the correct order.
• Magnetic stripe data sent by the driver is always encoded on
side 2 of the
card.
• Magnetic stripe data wi
ll be converted to uppercase (capital) letters if needed.
• If not-allowed characters are sent within the magnetic stripe da
ta, the printer
displays a message.
 Loading...
Loading...



