Models 2500 and 2502 User’s Manual Sweep Operation 9-13
Staircase sweep programming example
As an example of linear staircase sweep operation, assume the Model 2500 is to be used to
generate the reverse-biased V-I characteristics of a photodiode. For the purposes of this
test, assume the following basic sweep parameters:
Source and measure channel: channel 2
Source mode: sweep
Start voltage: 1V
Stop voltage: 10V
Step voltage: 1V
Source delay: 100ms
Table 9-3 lists the command sequence for the photodiode programming example. See
Section 2, “Connections,” for details on how to connect the photodiode to the channel 2
INPUT and OUTPUT connectors.
NOTE See Appendix H for a complete program listing.
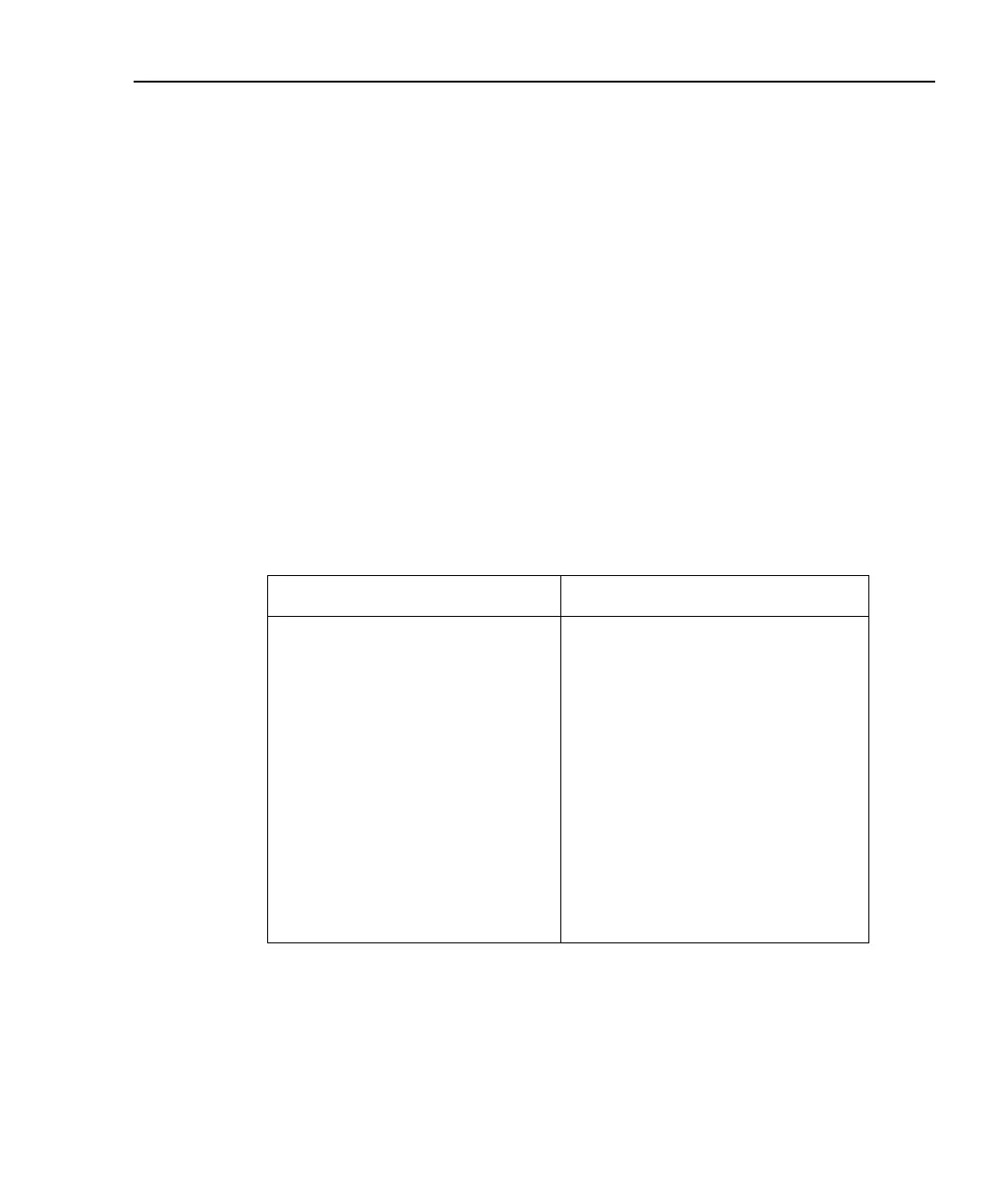
Table 9-3
Staircase sweep programming example (photodiode test)
Command Description
*RST
:FORM:ELEM CURR2
:SENS2:CURR:RANG:AUTO ON
:SOUR2:VOLT:START 1
:SOUR2:VOLT:STOP 10
:SOUR2:VOLT:STEP 1
:SOUR2:VOLT:MODE SWE
:SOUR2:SWE:RANG AUTO
:SOUR2:SWE:SPAC LIN
:TRIG:COUN 10
:SOUR2:DEL 0.1
:OUTP2 ON
:READ?
:OUTP2 OFF
Restore GPIB default conditions.
Select channel 2 measurement data.
Enable channel 2 measure auto range.
1V channel 2 start voltage.
10V channel 2 stop voltage.
1V channel 2 step voltage.
Select channel 2 sweep mode.
1
Channel 2 auto source ranging.
Select channel 2 linear staircase sweep.
Trigger count = # sweep points.
2
100ms source delay.
Turn on channel 2 source output.
Trigger sweep, request data.
Turn off channel 2 source output.
1
This command should normally be sent after START, STOP, and STEP to avoid delays caused by
rebuilding sweep when each command is sent.
2
For single sweep, trigger count should equal number of points in sweep: Points = (Stop-Start)/Step
+ 1. You can use SOUR:SWE:POIN? query to read the number of points.
Test Equipment Depot - 800.517.8431 - 99 Washington Street Melrose, MA 02176
TestEquipmentDepot.com

 Loading...
Loading...