SIP User's Manual 450 Document #: LTRT-65412
MP-11x & MP-124
10.2 NAT (Network Address Translation) Support
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a mechanism that maps a set of internal IP
addresses used within a private network to global IP addresses, providing transparent
routing to end hosts. The primary advantages of NAT include (1) Reduction in the number
of global IP addresses required in a private network (global IP addresses are only used to
connect to the Internet); (2) Better network security by hiding its internal architecture.
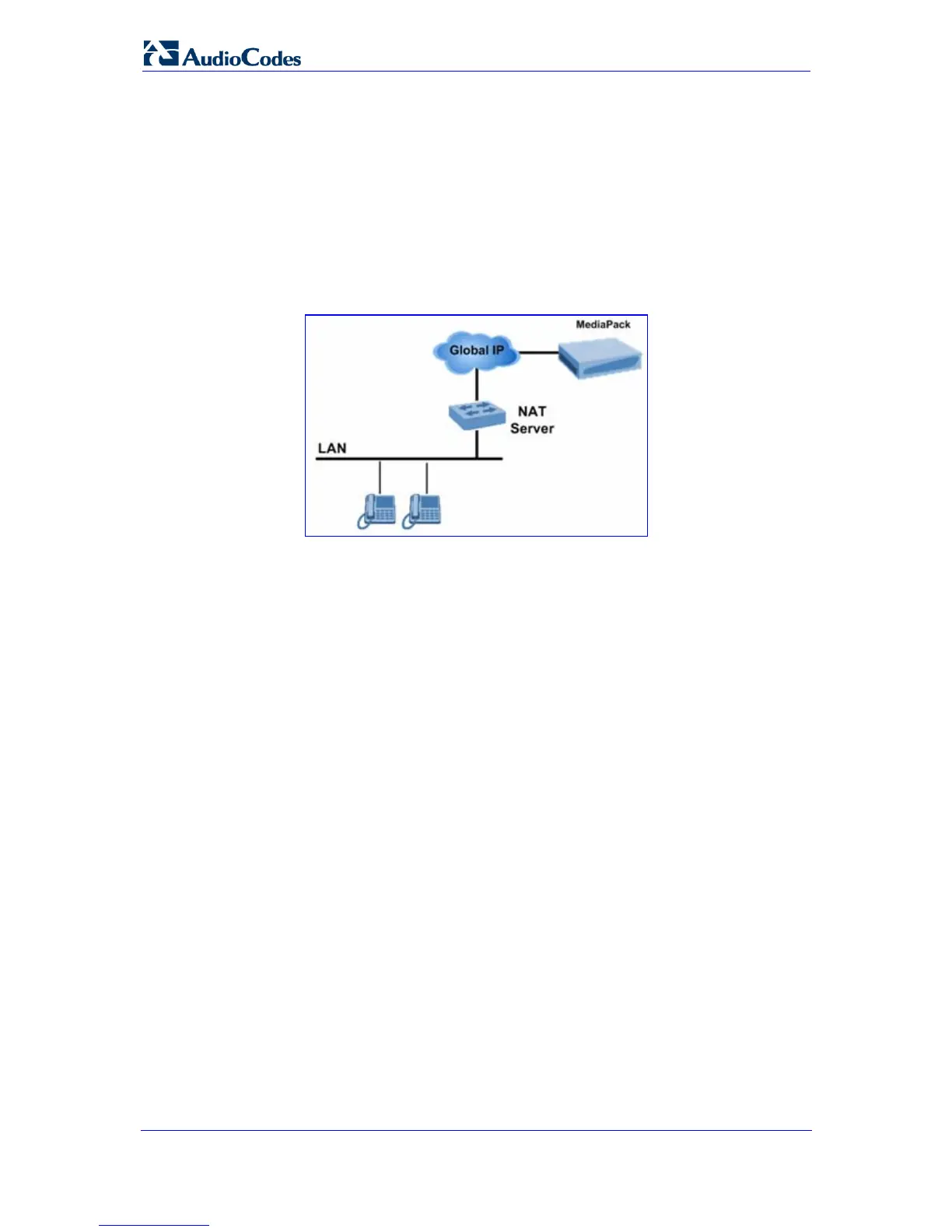
The following figure illustrates the device's supported NAT architecture.
Figure 10-1: Nat Functioning
The design of SIP creates a problem for VoIP traffic to pass through NAT. SIP uses IP
addresses and port numbers in its message body and the NAT server can’t modify SIP
messages and therefore, can’t change local to global addresses. Two different streams
traverse through NAT: signaling and media. A device (located behind a NAT) that initiates a
signaling path has problems in receiving incoming signaling responses (they are blocked by
the NAT server). Furthermore, the initiating device must notify the receiving device where to
send the media.
To resolve these issues, the following mechanisms are available:
STUN (refer to ''STUN'' on page 450)
First Incomin
g Packet Mechanism (refer to ''First Incoming Packet Mechanism'' on
page 451)
RTP No
-Op packets according to the avt-rtp-noop draft (refer to ''No-Op Packets'' on
page 452)
For info
rmation on SNMP NAT traversal, refer to the Product Reference Manual.
10.2.1 STUN
Simple Traversal of UDP through NATs (STUN), based on RFC 3489 is a client / server
protocol that solves most of the NAT traversal problems. The STUN server operates in the
public Internet and the STUN clients are embedded in end-devices (located behind NAT).
STUN is used both for the signaling and the media streams. STUN works with many
existing NAT types and does not require any special behavior.
STUN enables the device to discover the presence (and types) of NATs and firewalls
located between it and the public Internet. It provides the device with the capability to
determine the public IP address and port allocated to it by the NAT. This information is later
embedded in outgoing SIP / SDP messages and enables remote SIP user agents to reach
the device. It also discovers the binding lifetime of the NAT (the refresh rate necessary to
keep NAT ‘Pinholes’ open).

 Loading...
Loading...











