5–Managing Switches
Configuring the Network
5-30 59266-01 B
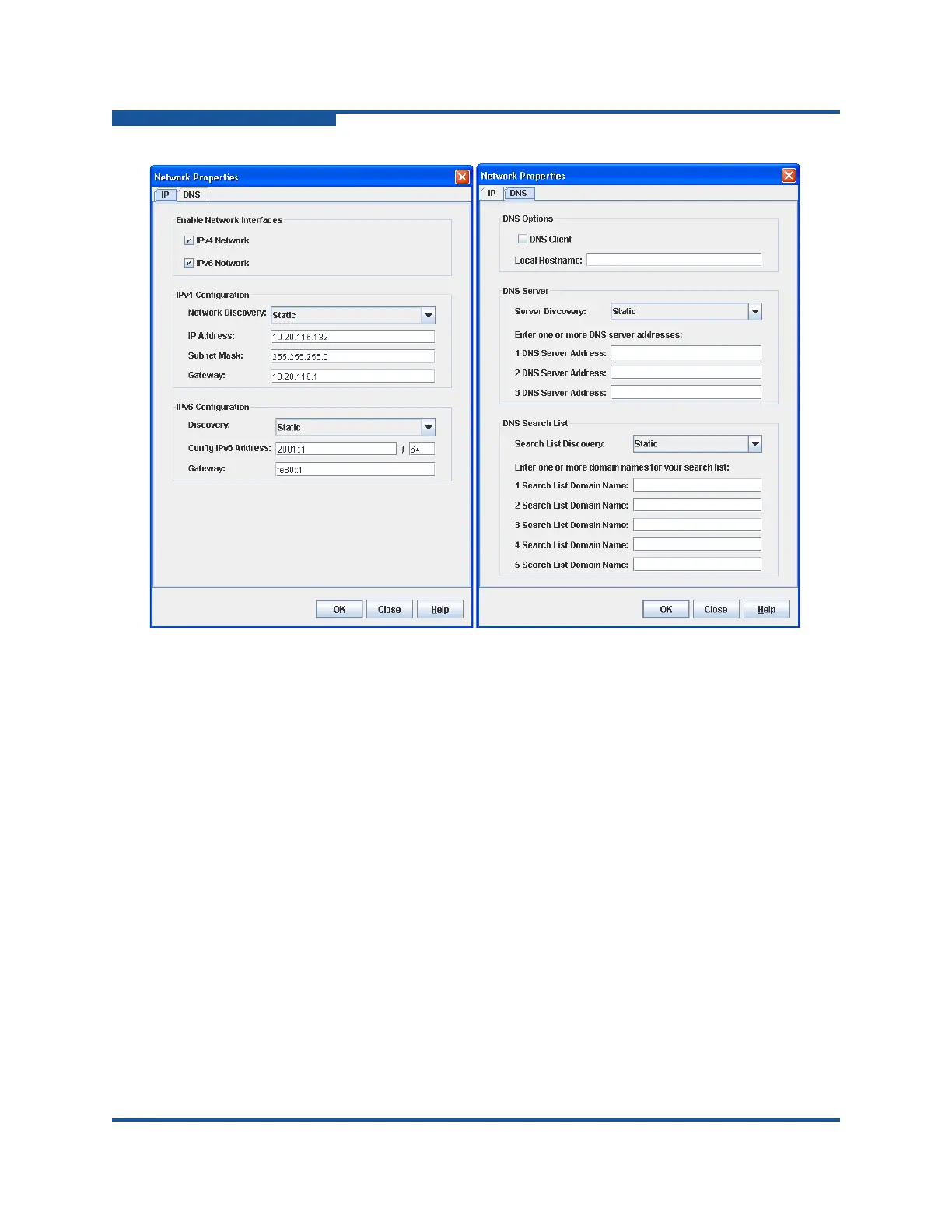
Figure 5-15. Network Properties Dialog Boxes
Network IP Configuration
The IP configuration identifies the switch on the Ethernet network, determines
which network discovery method to use, and enables/disables the IPv4 and IPv6
network addressing. An IPv4 address is 32 bits and consists of four blocks of
decimal numbers, with each block separated by a period. Each block can have up
to three numbers. A single zero character displayed in a block indicates that the
block consists of all zeroes. An example of an IPv4 address is 10.20.30.5. All four
blocks contain numbers. Table 5-4 describes the IPv4 and IPv6 configuration
parameters.
An IPv6 address provides a much wider range of IP addresses than an IPv4
address. An IPv6 address is 128 bits, and consists of eight blocks of hexadecimal
numbers, with each block separated by a colon. The maximum number of
numerals in each block is four. One or more blocks with all zeroes are represented
by two colon characters. The total number of blocks always adds up to eight. To
determine how many contiguous blocks contain only zeroes, subtract the number
of populated blocks from eight. For example, the IPv6 address
2eee::49:24:7a:54:3434 is equivalent to 2eee:0000:0000:49:24:7a:54:3434. The
number of blocks containing zeroes in this example is two (8-6=2).
 Loading...
Loading...