220 Rockwell Automation Publication 2198-UM005C-EN-P - February 2022
Appendix C Motor Control Feature Support
When used for SLAT control, an application dependent VelocityCommand
value is applied to the drive via an MAJ instruction or MDS instruction. An
application dependent TorqueTrim value is also applied via cyclic write. Under
normal operation, VelocityCommand is set to a level that results in the velocity
regulator's control effort becoming saturated when the motor's speed is
mechanically limited. The TorqueReference value equals the TorqueTrim
value, resulting in a positive VelocityError value.
Should the mechanical speed limitation be removed (example: web break), the
motor accelerates and VelocityError becomes negative. At this time, a forced
transition to velocity regulation occurs, and the motor's speed is regulated to
the VelocityCommand attribute.
The axis remains in velocity regulation until VelocityError exceeds
SLATSetPoint for a time specified by SLATTimeDelay. At this point, the axis
returns to operating as a torque regulator.
Figure 114 - SLAT Min Speed/Torque
See the Integrated Motion on the EtherNet/IP™ Network Reference Manual,
publication MOTION-RM003, for more information on SLAT attributes.
SLAT Max Speed/Torque
SLAT Max Speed/Torque is a special mode of operation primarily used in web
handling applications. The drive typically operates as a torque regulator,
provided that the TorqueTrim attribute is greater than the torque output due
to the velocity regulator's control effort. The drive can automatically enter
velocity regulation based on conditions within the velocity regulator and the
magnitude of the velocity regulator's output relative to the torque reference.
When used for SLAT control, an application dependent VelocityCommand
value is applied to the drive via an MAJ instruction or MDS instruction. An
application dependent TorqueTrim value is also applied via cyclic write. Under
normal operation, VelocityCommand is set to a level that results in the velocity
regulator's control effort becoming saturated when the motor's speed is
mechanically limited. The TorqueReference value equals the TorqueTrim
value, resulting in a negative VelocityError value.
Should the mechanical speed limitation be removed (example: web break), the
motor accelerates and VelocityError becomes positive. At this time, a forced
transition to velocity regulation occurs, and the motor's speed is regulated to
the VelocityCommand attribute.
The axis remains in velocity regulation until VelocityError is less than
SLATSetPoint for a time specified by SLATTimeDelay. At this point, the axis
returns to operating as a torque regulator.
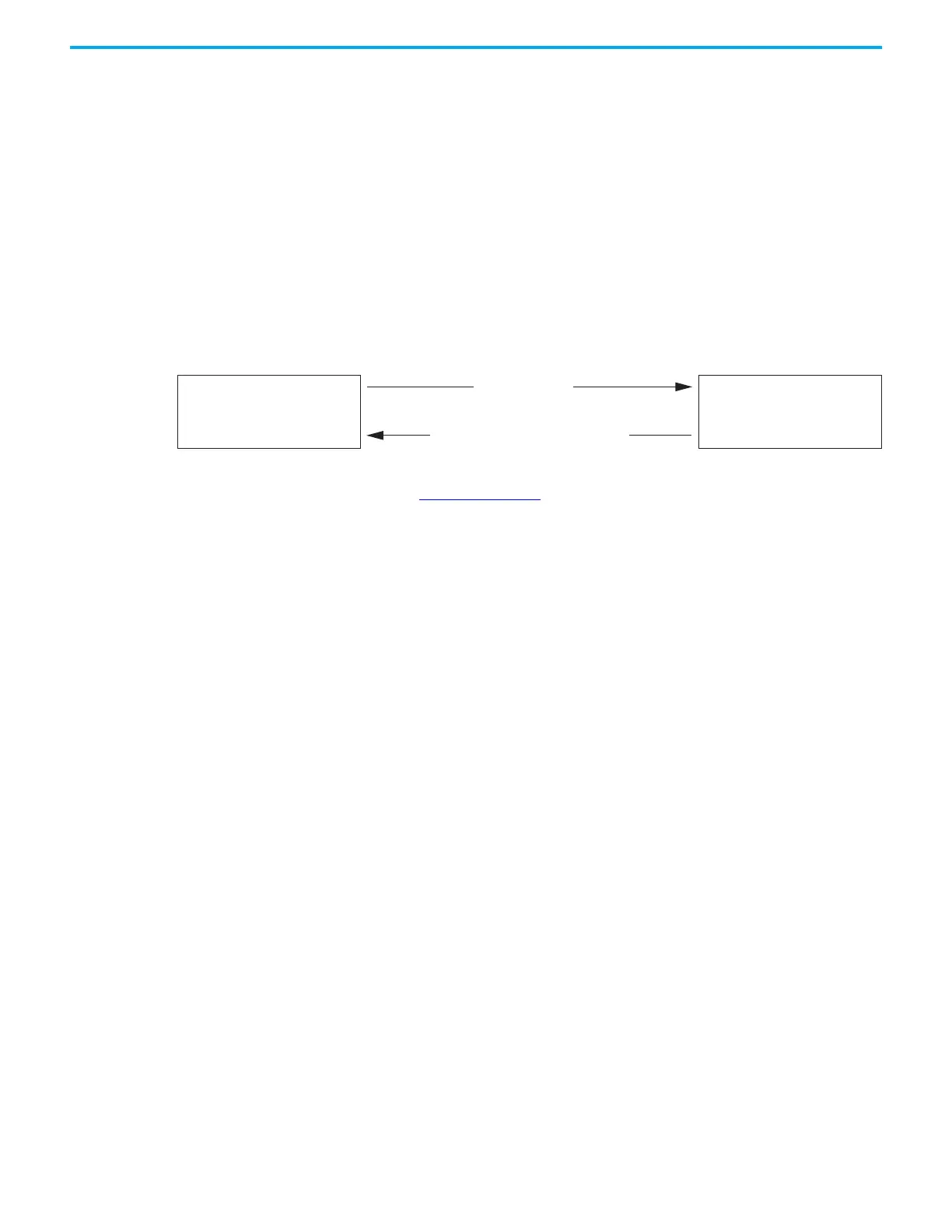
Select Minimum of Velocity Loop Output
or Torque Command
(speed control is OFF)
Select Velocity Loop Output
(speed control is ON)
Velocity Error < 0
Velocity Error > SLAT Setpoint for SLAT Time

 Loading...
Loading...











