Monitoring functions
SIMOCODE pro
GWA 4NEB 631 6050- 22 DS 03
5-13
5.5 Active power monitoring
Description
SIMOCODE pro can indirectly monitor the state of a device or system via
the active power. For example, by monitoring the active power of a pump
motor, conclusions can be drawn from the active power level about the flow
rate or fluid fill levels. The active power curve of a motor is a precise
reflection of its actual load across the entire range. Excess load results in
increased wear of the motor and, thus, may lead to premature motor failure.
Insufficient active power can, for example, be a sign of non-load motor
operation.
SIMOCODE pro supports two-phase monitoring of the active power for
freely-selectable upper and lower current limits. The response of
SIMOCODE pro when a pre-warning or trip level has been reached can be
freely parameterized and delayed.
Voltage is measured by current/voltage measuring modules.
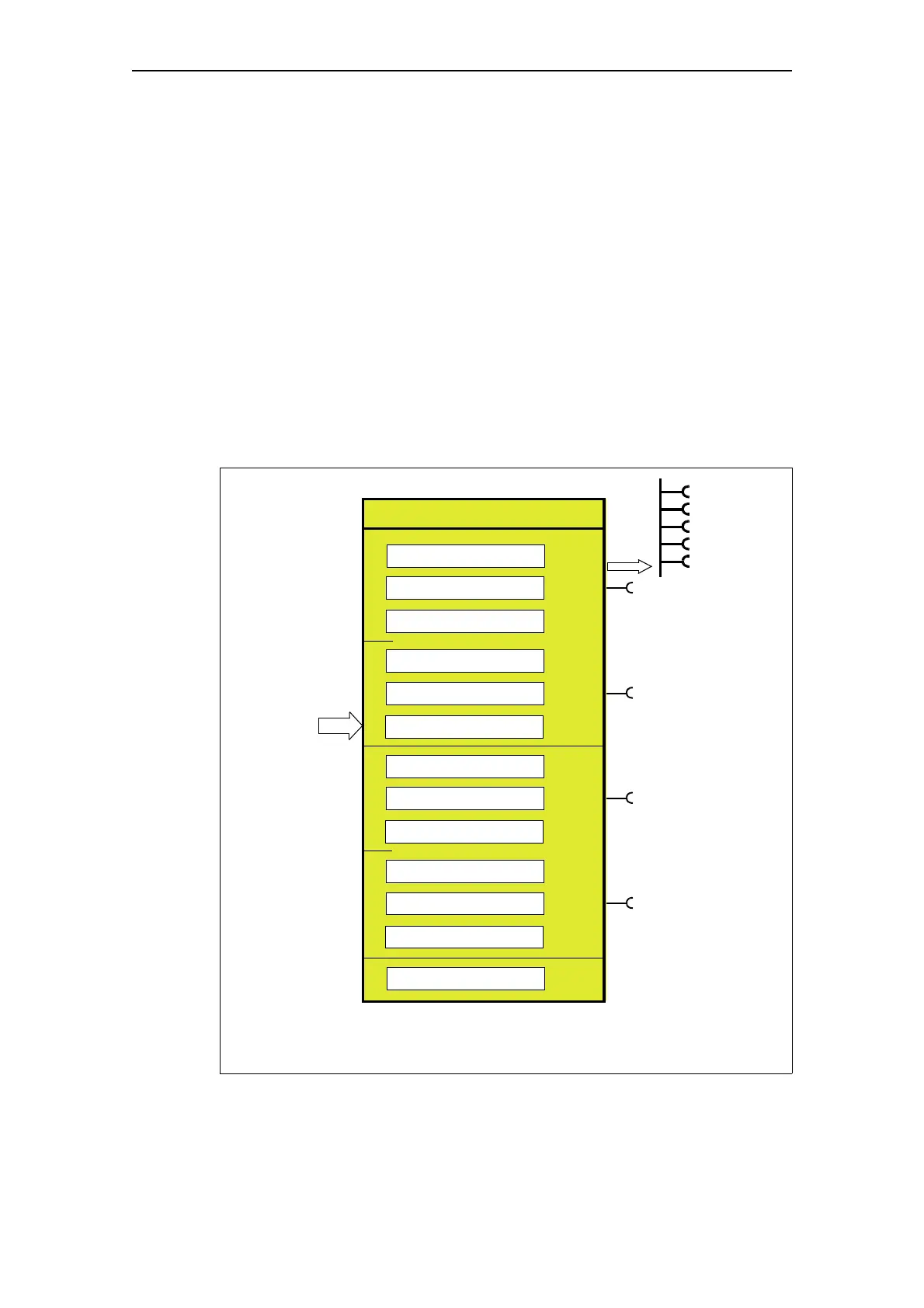
Fig. 5-6: "Power Monitoring" function block
Event
Event
Event
- Trip level P>
Event
- Warning level P>
- Trip level P<
- Warning level P<
Trip level: P>
1)
Response when P>
Delay when P>
Warning level: P>
Response when P>
Delay when P>
Trip level: P<
2)
Response when P<
Delay when P<
Warning level: P<
Response when P<
Delay when P<
See
Table 5-11
See
Table 5-12
See
Table 5-11
See
Table 5-12
Power monitoring
Tripping
QE1
QE2
QE3
QE4
QE5
Active power from
Current/voltage
measuring module
Hysteresis
3
)
1) Upper limit
2) Lower limit
3) Hysteresis for voltage, cos phi, power
(see "Voltage Monitoring" function block)

 Loading...
Loading...

















