Programming and Operating Manual (Turning)
01/2017
131
Subroutine technique
11.16.1
General information
Usage
Basically, there is no difference between a main program and a subroutine.
Frequently recurring machining sequences are stored in subroutines, e.g. certain contour shapes. These subroutines are
called at the appropriate locations in the main program and then executed.
One form of a subroutine is the
. Machining cycles contain universally valid machining scenarios. By
assigning values via included transfer parameters, you can adapt the subroutine to your specific application.
The structure of a subroutine is identical to that of a main program (see Section "Program structure (Page 77)"). Like main
programs, subroutines contain
in the last block of the program sequence. This means a return to the
program level where the subroutine was called from.
The end instruction
can also be used instead of the M2 program end in the subroutine.
The RET instruction is used when G64 continuous-path mode is not to be interrupted by a return. With M2, G64 is
interrupted and exact stop is initiated.
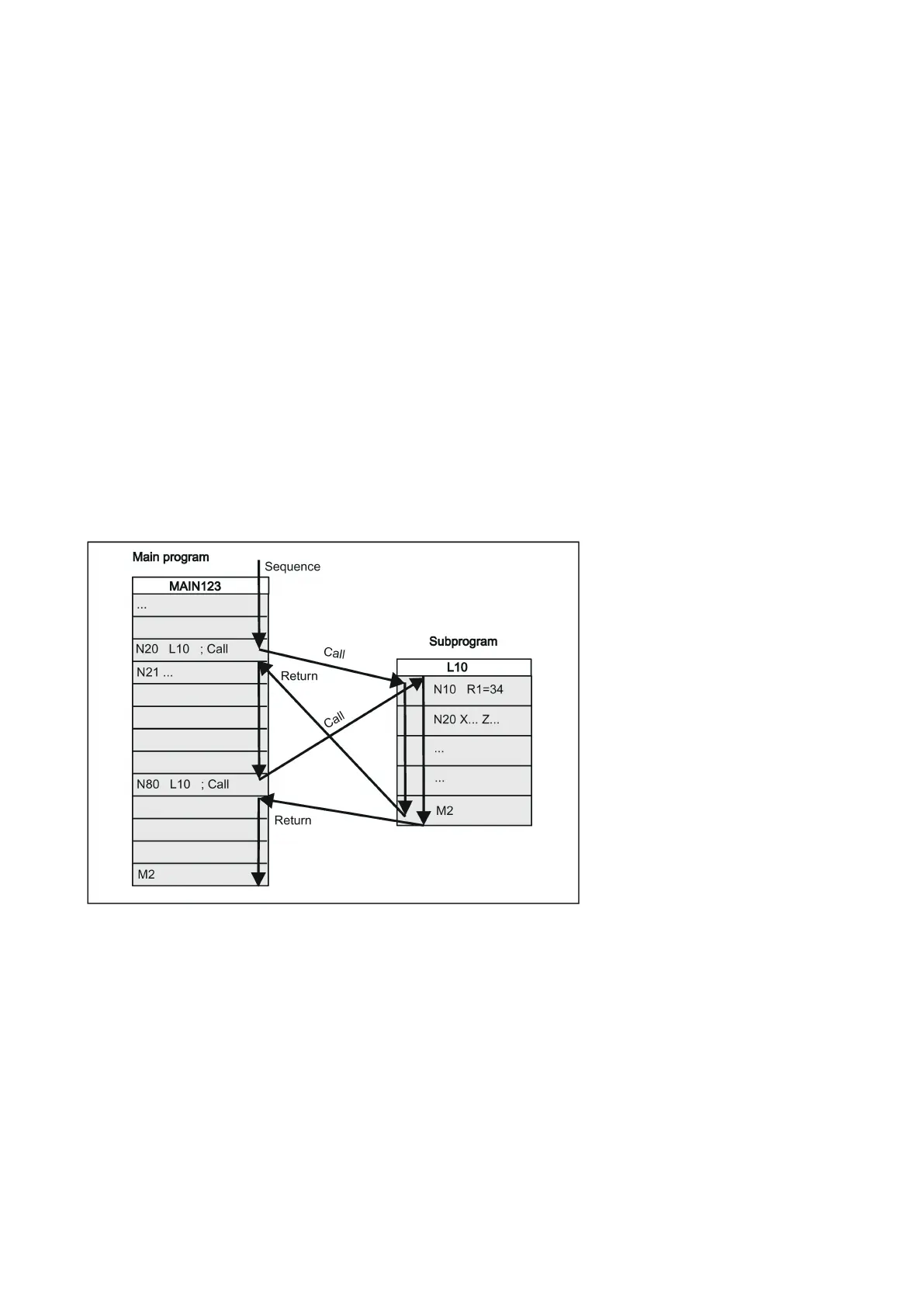
See the following example of a sequence when a subroutine is called in a two-channel manner:
The subprogram is given a unique name allowing it to be selected from several subroutines. When you create the program,
the program name may be freely selected provided the following conventions are observed:
The same rules apply as for the names of main programs.
Example:
It is also possible to use the address word
in subroutines. The value can have 7 decimal places (integers only).
Please observe: With address L, leading zeros are meaningful for differentiation.
Example:
is not
or
.
These are 3 different subroutines.
Note: The subroutine name
is reserved for tool change.
 Loading...
Loading...











