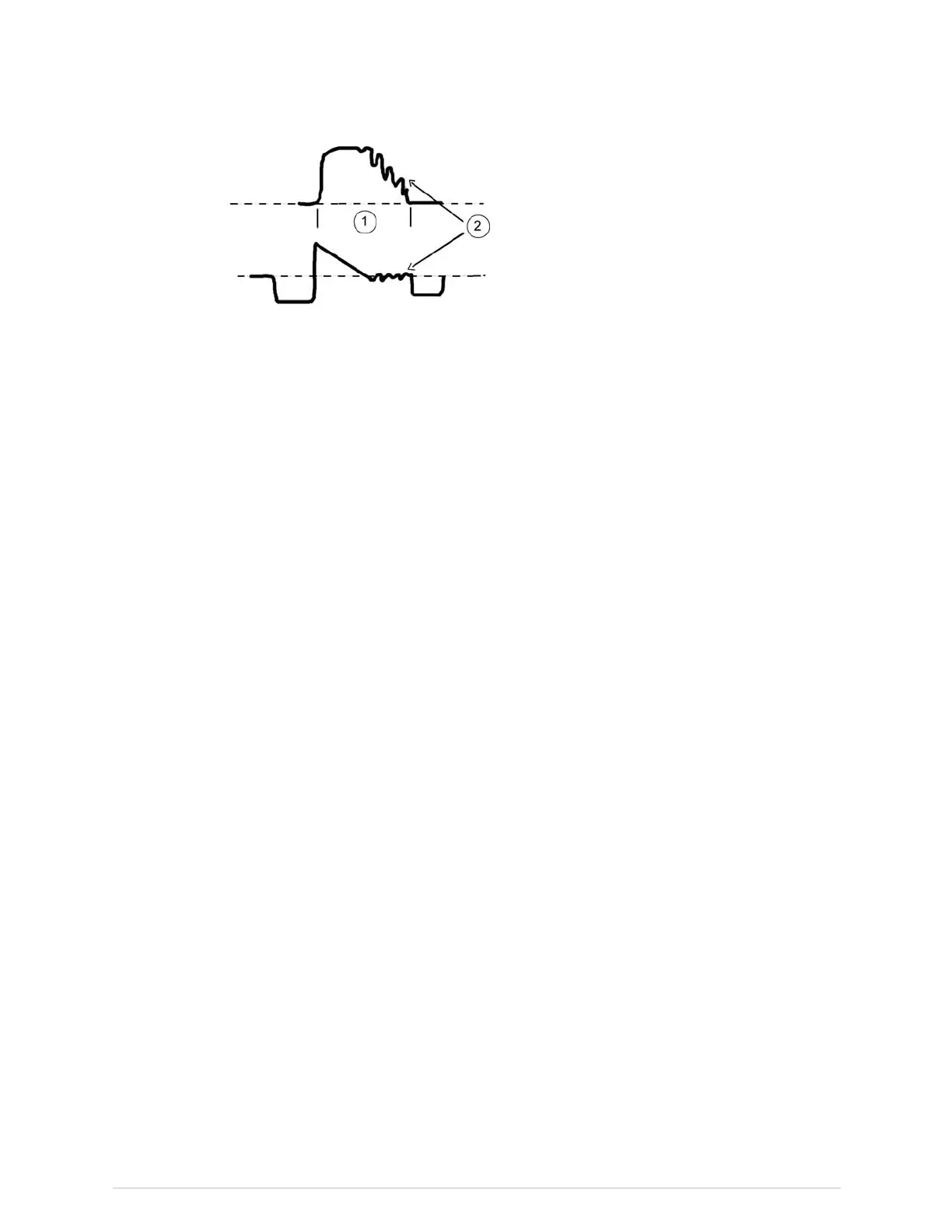
CO₂
1.Expiration
2.Cardiogenicoscillations
Cardiogenicoscillationsappearwhen:
●AcontinuousfreshgasowisfedintothepatientY-piece.
●SidestreamgassamplingisdoneattheY-piece.
●Thepatientisventilatedwithalongexpirationtimeorlowrespirationtimes,and
whenthereisalongzeroowatend-expirationforsomeotherreason.
CO₂measurementpracticalities
Ventilationmanagement
Normoventilation(adequatealveolarventilationofapatient)canbemaintained
bymonitoringtheend-tidalcarbondioxideandoxygenconcentrations,and
adequacyofventilationcanbemaintainedbymonitoringairwaypressures,volumes
andspirometryloops.Alveolarminuteventilationisusuallyadjustedtoachieve
normocapnia,whereEtCO
2
isintherangeof4.5%to5.5%(34mmHgto41mmHg).
Thisiscallednormoventilationasitisthenormalsituationinhealthypeople.
AlowEtCO
2
concentration(EtCO
2
<4%/30mmHg)indicateshyperventilation.
NOTE
AlowEtCO
2
valueinitselfisdependentontheventilation
volumevs.circulationstatus(lungperfusion).Thismeans
thatincaseoflowbloodpressure(e.g.shock),shunting,a
pulmonaryembolism,oraleak,lowEtCO
2
valuesmaybe
observedwhileusinga“normal”TV/MV.
IncreasedEtCO
2
concentration(EtCO
2
>6.0%/45mmHg)indicateshypoventilationor
ineffectivealveolarventilation,whichwillleadtohypercapniaandrespiratoryacidosis.
IncreasedinspiratoryCO
2
(FiCO
2
)concentrationsmayalsobecausedby:
●ExhaustedCO
2
absorber.
●Malfunctionofthebreathingsystemvalves.
●RebreathingwhenarebreathingsystemwithoutaCO
2
absorberisusedwith
inadequatefreshgasows.
NOTE
Duringsomesurgicalprocedures,e.g.laparoscopy,CO
2
may
beusedtoinatetheabdomenwhichmayresultinriseof
PaCO
2
duetotheabsorptionofCO
2
intothebloodviathe
vascularwoundbed.Thismayleadtoanincreaseinthe
EtCO
2
.
2094480-001CARESCAPEONE193
CARESCAPE ONE User Manual DRAFT 26 October 2017
 Loading...
Loading...