Configuration Guide Configuring IPv4/IPv6 REF
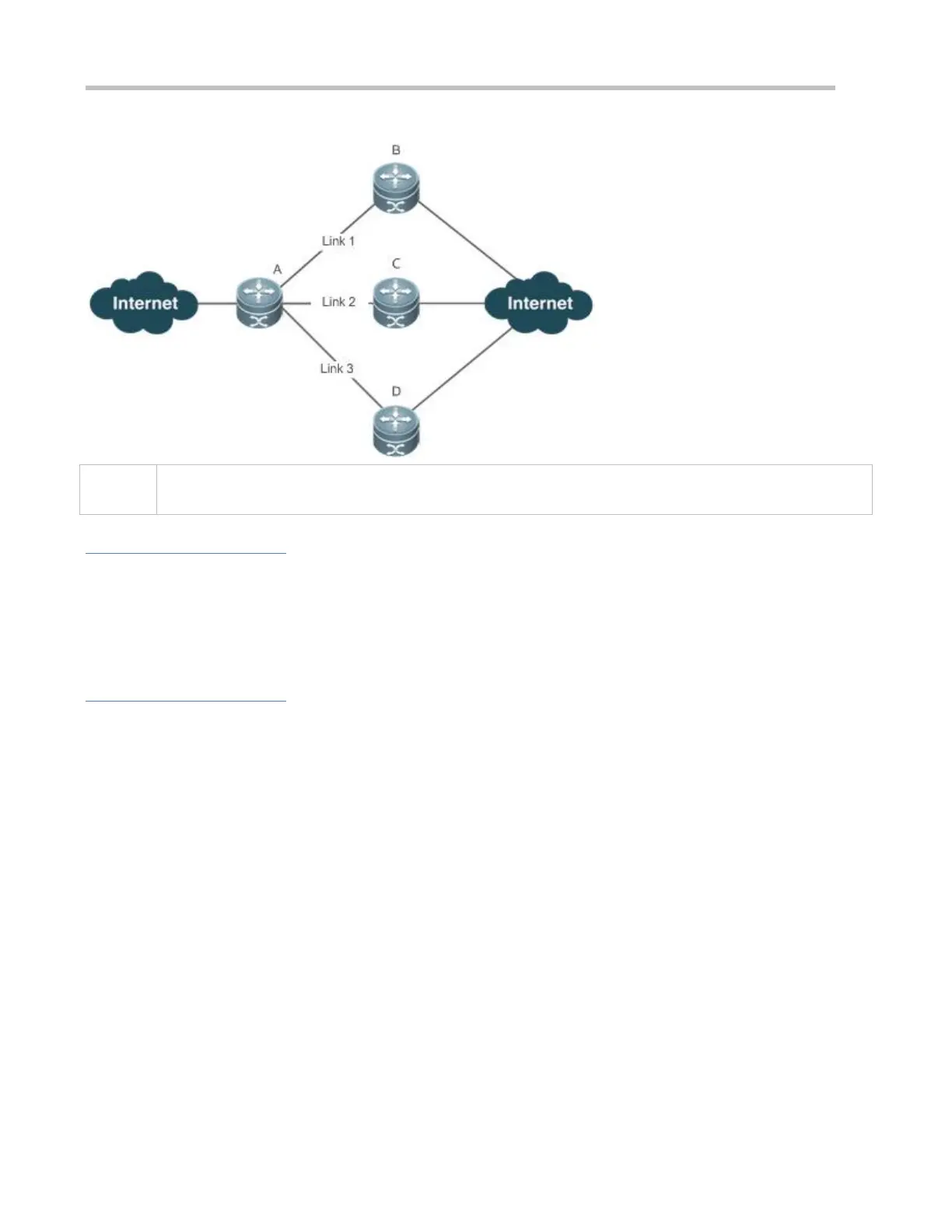
Figure 9-1
A is a router that runs REF.
B, C and D are forwarding devices.
Deployment
Run REF on router A.
9.3 Features
Basic Concepts
IPv4/IPv6 REF involves the following basic concepts:
Routing table
An IPv4/IPv6 routing table stores routes to the specific destinations and contains the topology information. During packet
forwarding, IPv4/IPv6 REF selects packet transmission paths based on the routing table.
Adjacent node
An adjacent node contains output interface information about routed packets, for example, the next hop, the next component
to be processed, and the link layer encapsulation. When a packet is matched with an adjacent node, the packet is directly
encapsulated and then forwarded. For the sake of query and update, an adjacent node table is often organized into a hash
table. To support routing load balancing, the next hop information is organized into a load balance entry. An adjacent node
may not contain next hop information. It may contain indexes of next components (such as other line cards and multi-service
cards) to be processed.
Active resolution
REF supports next hop resolution. If the MAC address of the next hop is unknown, REF will actively resolve the next hop.
IPv4 REF requests the ARP module for next hop resolution while IPv6 REF applies the ND module to resolution.

 Loading...
Loading...