Configuration Guide Managing Routes
Deployment
Configure the address and subnet mask of each interface.
Configure static routes on R 1, R 2, and R 3.
1.2.2 Floating Static Route
Scenario
If no dynamic routing protocol is configured, you can configure floating static routes to implement dynamic switching of routes
to prevent communication interruption caused by the network connection failures.
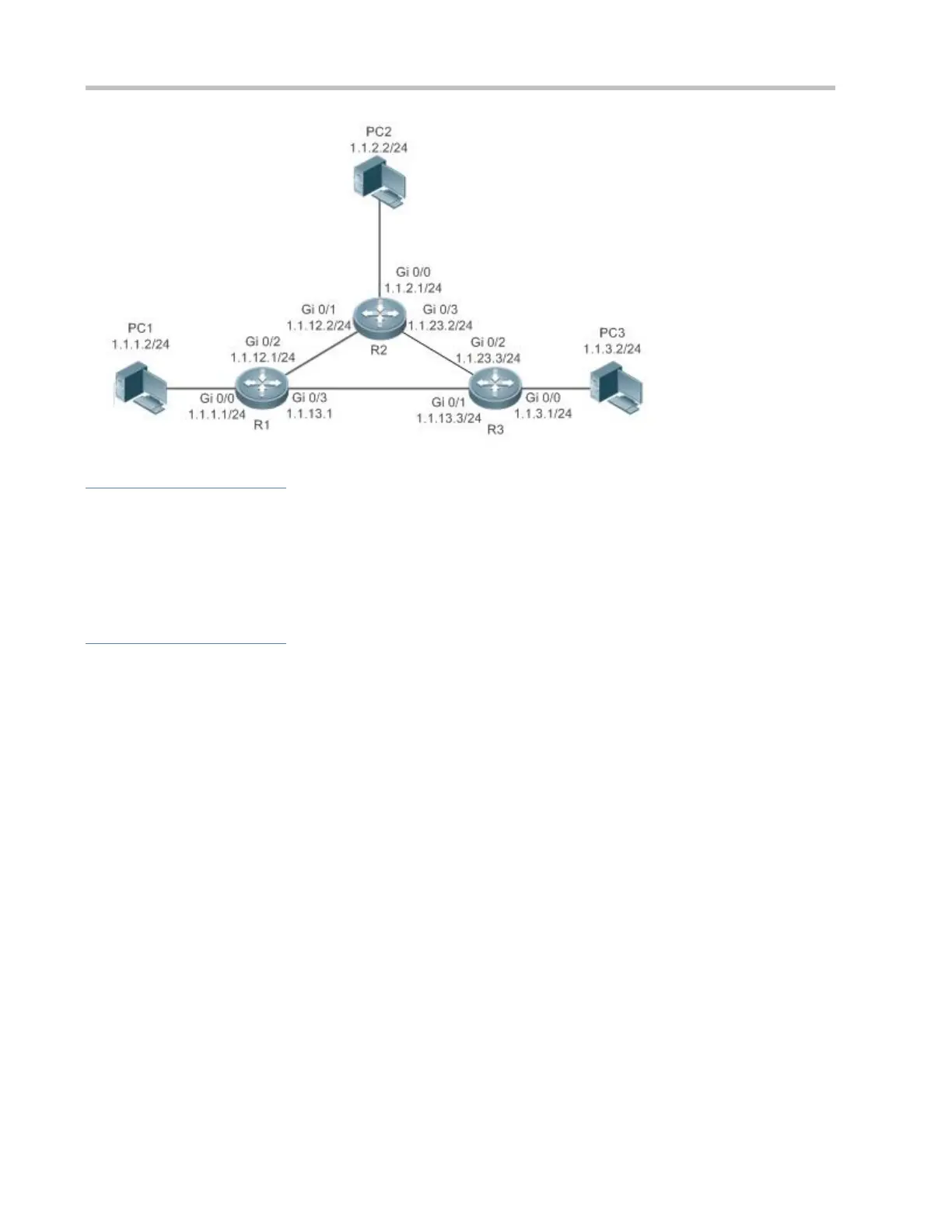
As shown in Figure 1-2, to prevent communication interruption caused by a line failure between R 1 and R 3, you can
configure a floating static route respectively on R 1 and R 3. Normally, packets are forwarded on a path with a small
administrative distance. If a link on this path is down, the route is automatically switched to the path with a large
administrative distance.
On R 1, configure two routes to the network segment of PC 3, including a route through R 3 (default distance = 1) and a
route through R 2 (default distance = 2).
On R 3, configure two routes to the network segment of PC 1, including a route through R 1 (default distance = 1) and a
route through R 2 (default distance = 2).
Figure 1-2

 Loading...
Loading...