RL78/G15 CHAPTER 21 BCD CORRECTION CIRCUIT
R01UH0959EJ0110 Rev.1.10 Page 690 of 765
Mar 7, 2023
21.3 BCD Correction Circuit Operation
The basic operation of the BCD correction circuit is as follows.
1) Addition: Calculating the result of adding a BCD code value and another BCD code value by using a BCD
code value
<1> The BCD code value to which addition is performed is stored in the A register.
<2> By adding the value of the A register and the second operand (value of one more BCD code to be added) as are
in binary, the binary operation result is stored in the A register and the correction value is stored in the BCD
correction result register (BCDADJ).
<3> Decimal correction is performed by adding in binary the value of the A register (addition result in binary) and the
BCDADJ register (correction value), and the correction result is stored in the A register and CY flag.
Caution The value read from the BCDADJ register varies depending on the value of the A register when it is
read and those of the CY and AC flags. Therefore, execute the instruction <3> after the instruction
<2> instead of executing any other instructions. To perform BCD correction in the interrupt enabled
state, saving and restoring the A register is required within the interrupt function. PSW (CY flag and
AC flag) is restored by the RETI instruction.
An example is shown below.
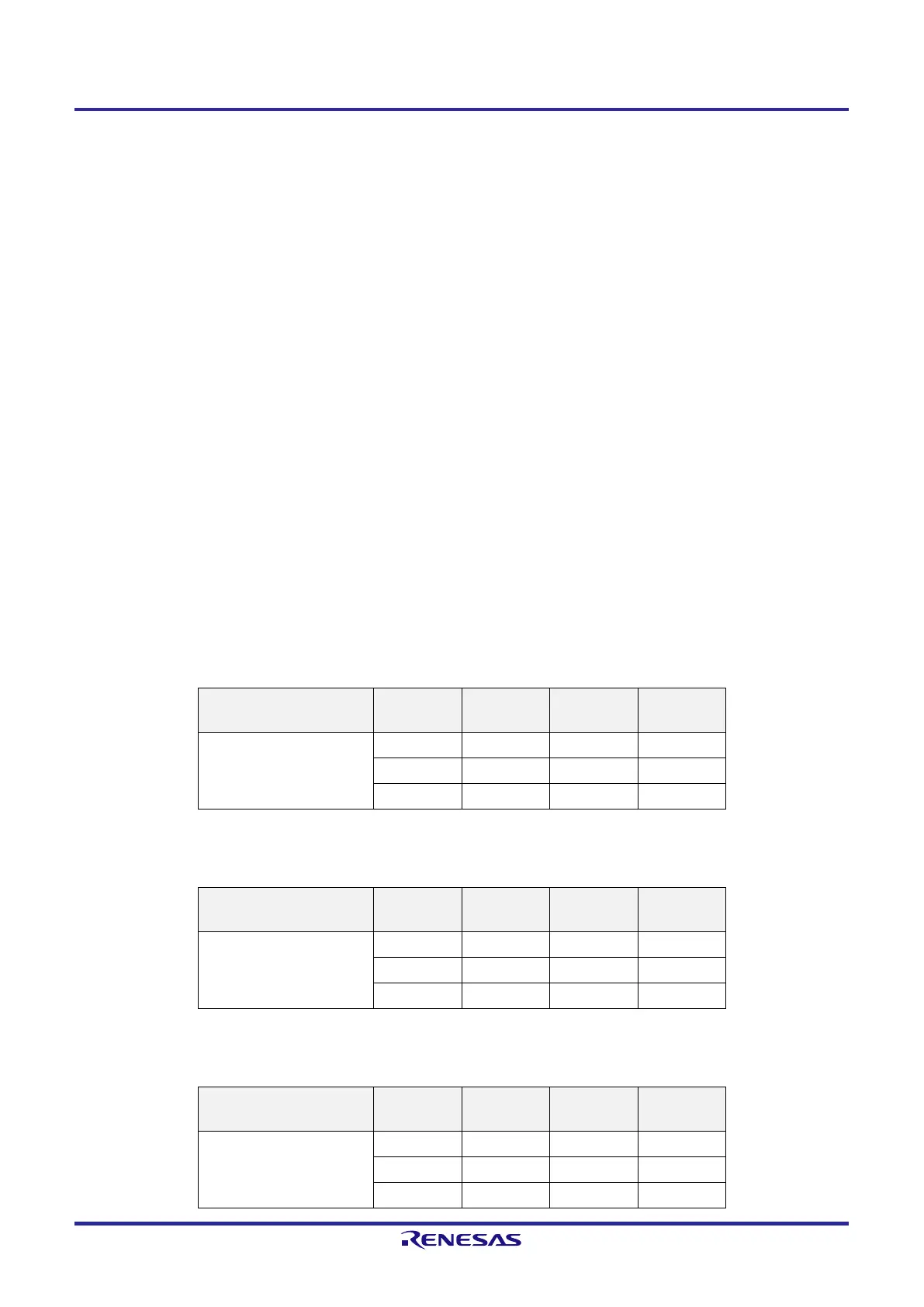
Examples 1: 99 + 89 = 188
Instruction A Register CY Flag AC Flag
BCDADJ
Register
MOV A, #99H ; <1>
99H — — —
ADD A, #89H ; <2>
22H 1 1 66H
ADD A, !BCDADJ ; <3>
88H 1 0 —
Examples 2: 85 + 15 = 100
Instruction A Register CY Flag AC Flag
BCDADJ
Register
MOV A, #85H ; <1>
85H — — —
ADD A, #15H ; <2>
9AH 0 0 66H
ADD A, !BCDADJ ; <3>
00H 1 1 —
Examples 3: 80 + 80 = 160
Instruction A Register CY Flag AC Flag
BCDADJ
Register
MOV A, #80H ; <1>
80H — — —
ADD A, #80H ; <2>
00H 1 0 60H
ADD A, !BCDADJ ; <3>
60H 1 0 —

 Loading...
Loading...