xStack® DGS-3120 Series Layer 3 Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch Web UI Reference Guide
227
Click the <<Back button to return to the previous window.
Enter a page number and click the Go button to navigate to a specific page when multiple pages exist.
DVMRP
The Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP) is a hop-based method of building multicast delivery
trees from multicast sources to all nodes of a network. Because the delivery trees are ‘pruned’ and ‘shortest path’,
DVMRP is relatively efficient. Because multicast group membership information is forwarded by a distance-vector
algorithm, propagation is slow. DVMRP is optimized for high delay (high latency) relatively low bandwidth networks,
and can be considered as a ‘best-effort’ multicasting protocol.
DVMRP resembles the Routing Information Protocol (RIP), but is extended for multicast delivery. DVMRP builds a
routing table to calculate ‘shortest paths’ back to the source of a multicast message, but defines a ‘route cost’
(similar to the hop count in RIP) as a relative number that represents the real cost of using this route in the
construction of a multicast delivery tree to be ‘pruned’ - once the delivery tree has been established.
When a sender initiates a multicast, DVMRP initially assumes that all users on the network will want to receive the
multicast message. When an adjacent router receives the message, it checks its routing table to determine the
interface that gives the shortest path (lowest cost) back to the source. If the multicast was received over the
shortest path, then the adjacent router enters the information into its tables and forwards the message. If the
message is not received on the shortest path back to the source, the message is dropped.
Route cost is a relative number that is used by DVMRP to calculate which branches of a multicast delivery tree
should be ‘pruned’. The ‘cost’ is relative to other costs assigned to other DVMRP routes throughout the network.
The higher the route cost, the lower the probability that the current route will be chosen to be an active branch of
the multicast delivery tree (not ‘pruned’) - if there is an alternative route.
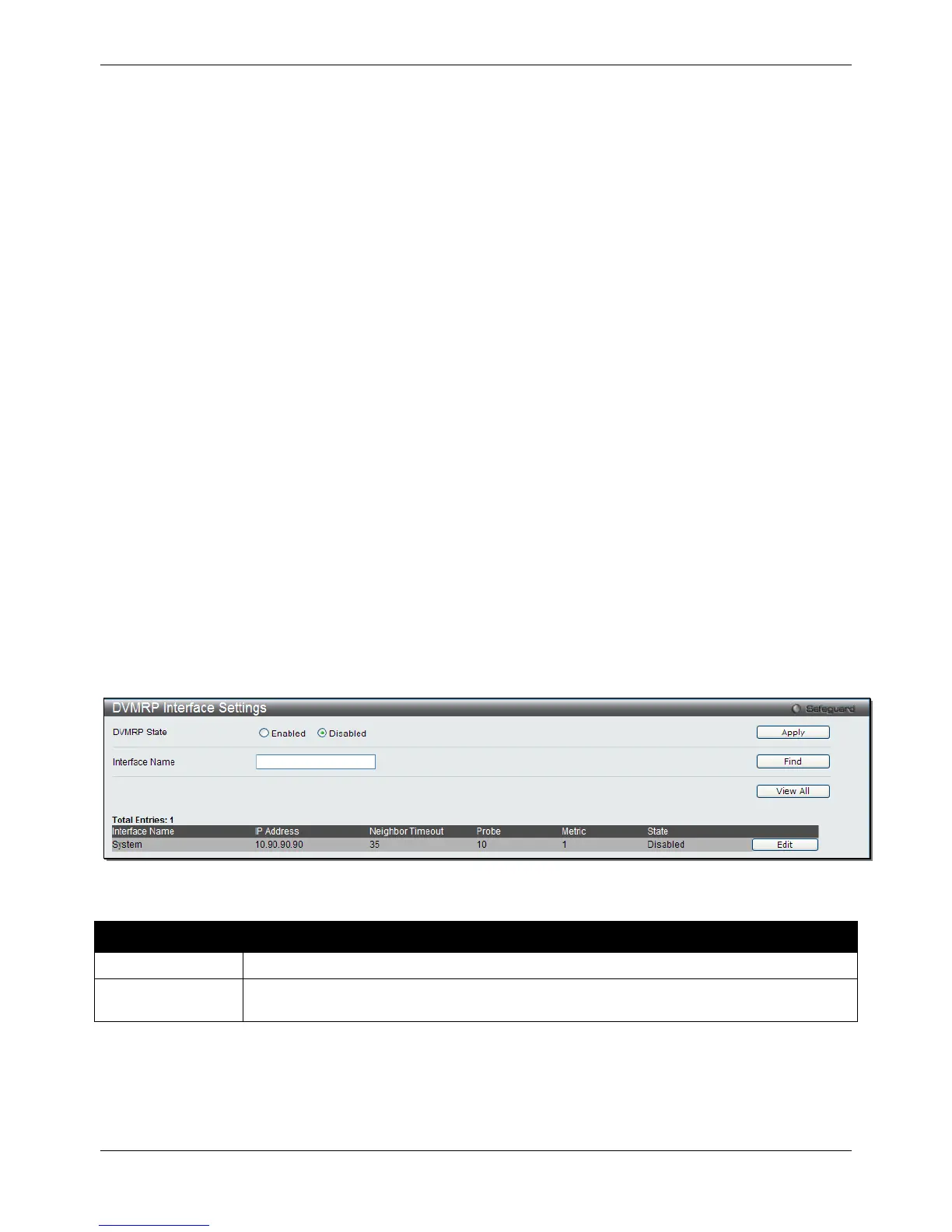
DVMRP Interface Settings
This window is used to configure the DVMRP global state and allow the DVMRP to be configured for each IP
interface defined on the Switch. Each IP interface configured on the Switch is displayed in the below DVMRP
Interface Settings window.
To view the following window, click L3 Features > IP Multicast Routing Protocol > DVMRP > DVMRP Interface
Settings, as shown below:
Figure 5-102 DVMRP Interface Settings window
The fields that can be configured are described below:
Parameter Description
 Loading...
Loading...











