Router Static Routing concepts
FortiGate Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-89802-20090903 337
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Another method is to manually change the priority of both of the routes. If the next-hop
administrative distances of two routes on the FortiGate unit are equal, it may not be clear
which route the packet will take. Configuring the priority for each of those routes will make
it clear which next-hop will be used in the case of a tie. You can set the priority for a route
only from the CLI. Lower priorities are preferred. For more information, see the FortiGate
CLI Reference.
All entries in the routing table are associated with an administrative distance. If the routing
table contains several entries that point to the same destination (the entries may have
different gateways or interface associations), the FortiGate unit compares the
administrative distances of those entries, selects the entries having the lowest distances,
and installs them as routes in the FortiGate forwarding table. As a result, the FortiGate
forwarding table contains only those routes having the lowest distances to every possible
destination. For information about how to change the administrative distance associated
with a static route, see “Adding a static route to the routing table” on page 343.
Route priority
After the FortiGate unit selects static routes for the forwarding table based on their
administrative distances, the priority field of those routes determines routing preference.
You configure the priority field through the CLI. The route with the lowest value in the
priority field is considered the best route, and it is also the primary route. The command to
set the priority field is: set priority <integer> under the config route static
command. For more information, see the FortiGate CLI Reference.
In summary, because you can use the CLI to specify which sequence numbers or priority
field settings to use when defining static routes, you can prioritize routes to the same
destination according to their priority field settings. For a static route to be the preferred
route, you must create the route using the config router static CLI command and
specify a low priority for the route. If two routes have the same administrative distance and
the same priority, then they are equal cost multipath (ECMP) routes. Since this means
there is more than one route to the same destination, it can be confusing which route or
routes to install and use. However, you can configure ECMP Route Failover and Load
Balancing to control how sessions are load balanced among ECMP routes. See “ECMP
route failover and load balancing” on page 344.
Blackhole Route
A blackhole route is a route that drops all traffic sent to it. It is very much like /dev/null in
Linux programming.
Blackhole routes are used to dispose of packets instead of responding to suspicious
inquiries. This provides added security since the originator will not discover any
information from the target network.
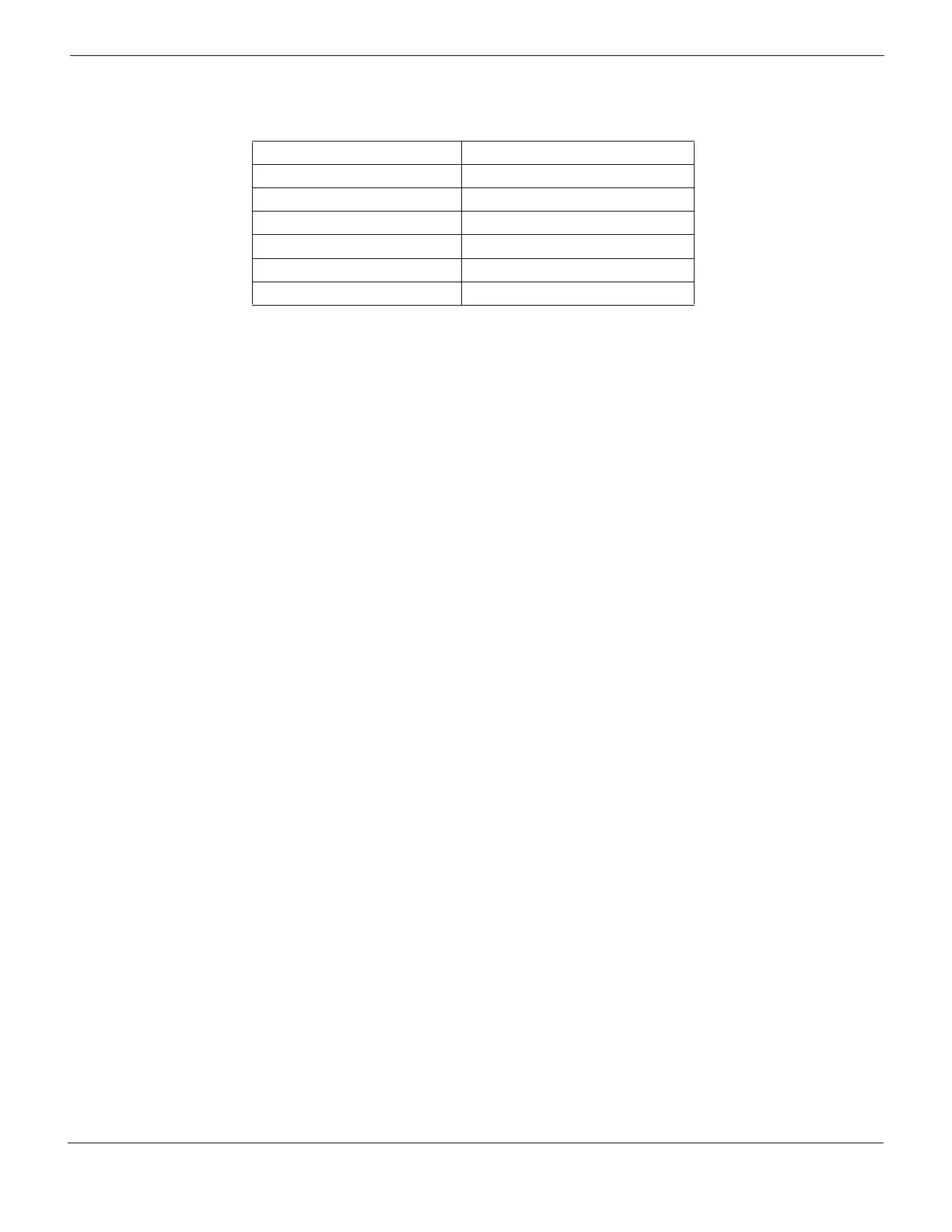
Table 43: Default administrative distances for routing protocols
Routing protocol Default administrative distance
Direct physical connection 1
Static 10
EBGP 20
OSPF 110
RIP 120
IBGP 200

 Loading...
Loading...











