ssl.root SSL VPN
FortiGate Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
634 01-410-89802-20090903
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
ssl.root
The FortiGate unit has a virtual SSL VPN interface called ssl.<vdomname>. The root
VDOM, called ssl.root, appears in the firewall policy interface lists and static route
interface lists. You can use the ssl-root interface to allow access to additional networks
and facilitate a connected user’s ability to browse the Internet through the FortiGate unit.
SSL VPN tunnel-mode access requires the following firewall policies:
• External > Internal, with the action set to SSL, with an SSL user group
• ssl.root > Internal, with the action set to Accept
• Internal > ssl.root, with the action set to Accept.
Access also requires a new static route: Destination network - <ssl tunnel mode assigned
range> interface ssl.root.
If you are configuring Internet access through an SSL VPN tunnel, you must add the
following configuration: ssl.root > External, with the action set to Accept, NAT enabled.
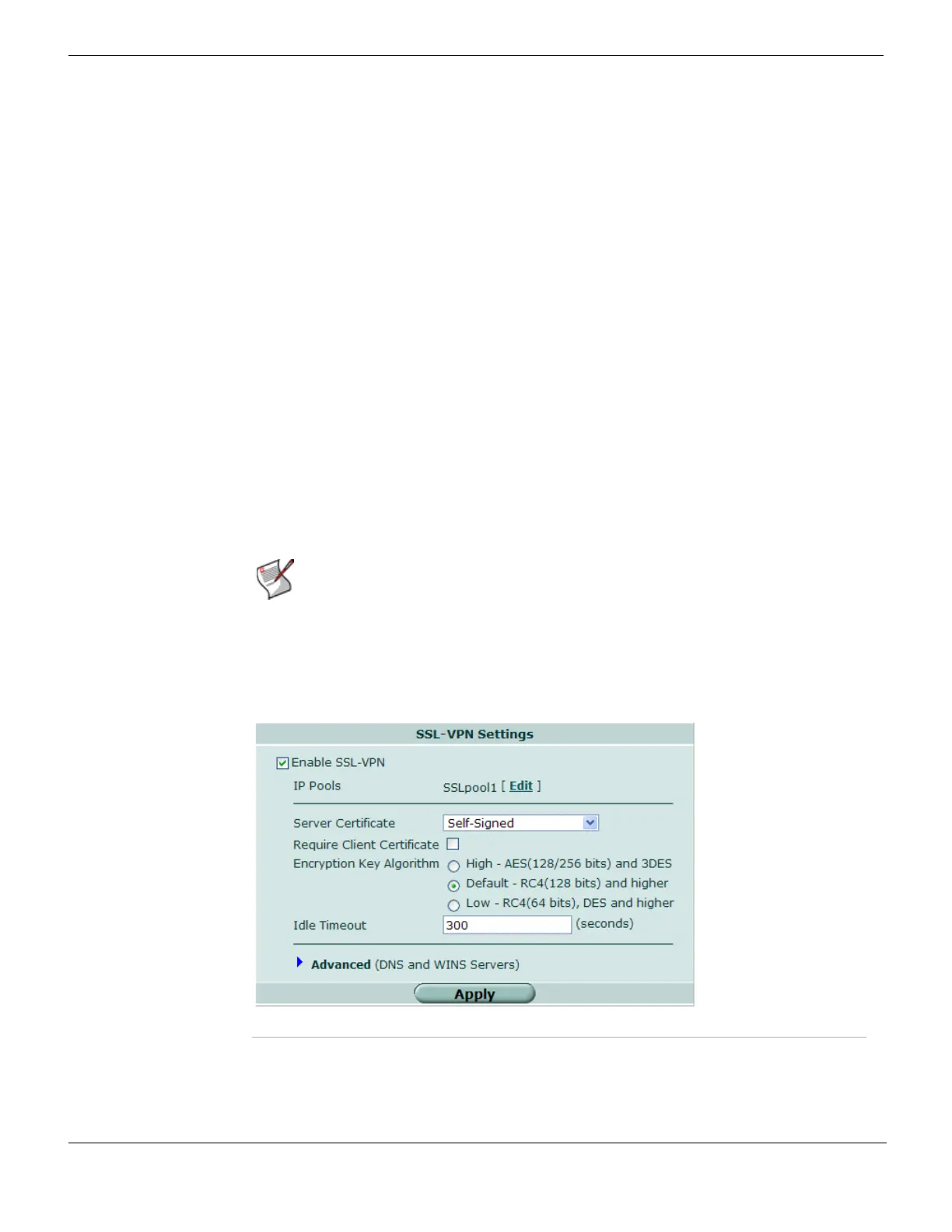
Configuring SSL VPN
You can configure basic SSL VPN settings including timeout values and SSL encryption
preferences. If required, you can also enable the use of digital certificates for
authenticating remote clients.
To enable SSL VPN connections and configure SSL VPN settings, go to VPN > SSL >
Config and select Enable SSL-VPN. When you have completed configuring the settings,
select Apply.
Figure 389: SSL-VPN Settings
Note: If required, you can enable SSL version 2 encryption (for compatibility with older
browsers) through a FortiGate CLI command. For more information, see the
ssl
settings
command in the FortiGate CLI Reference.
Enable SSL VPN Select to enable SSL VPN connections.
IP Pools Select Edit to select the firewall addresses that represent IP address
ranges reserved for tunnel-mode SSL VPN clients. If the appropriate
addresses do not exist, go to Firewall > Address to create them.
 Loading...
Loading...











