Configuring how a FortiGate unit stores logs Log&Report
FortiGate Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
714 01-410-89802-20090903
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
5 Select Apply.
Local logging to memory
The FortiGate system memory has a limited capacity for log messages. The FortiGate
system memory displays only the most recent log entries. It does not store traffic and
content logs in system memory due to their size and the frequency of log entries. When
the system memory is full, the FortiGate unit overwrites the oldest messages. All log
entries are cleared when the FortiGate unit restarts.
For local logs, the SQL log storage format is the default for all log types except content
archiving and traffic logs. This is the only format from which you can generate reports.
Content archiving is not available in SQL format. You can enable SQL format logging for
traffic logs, but this can cause some loss of logs because SQL format writing is slower
than the compressed format.
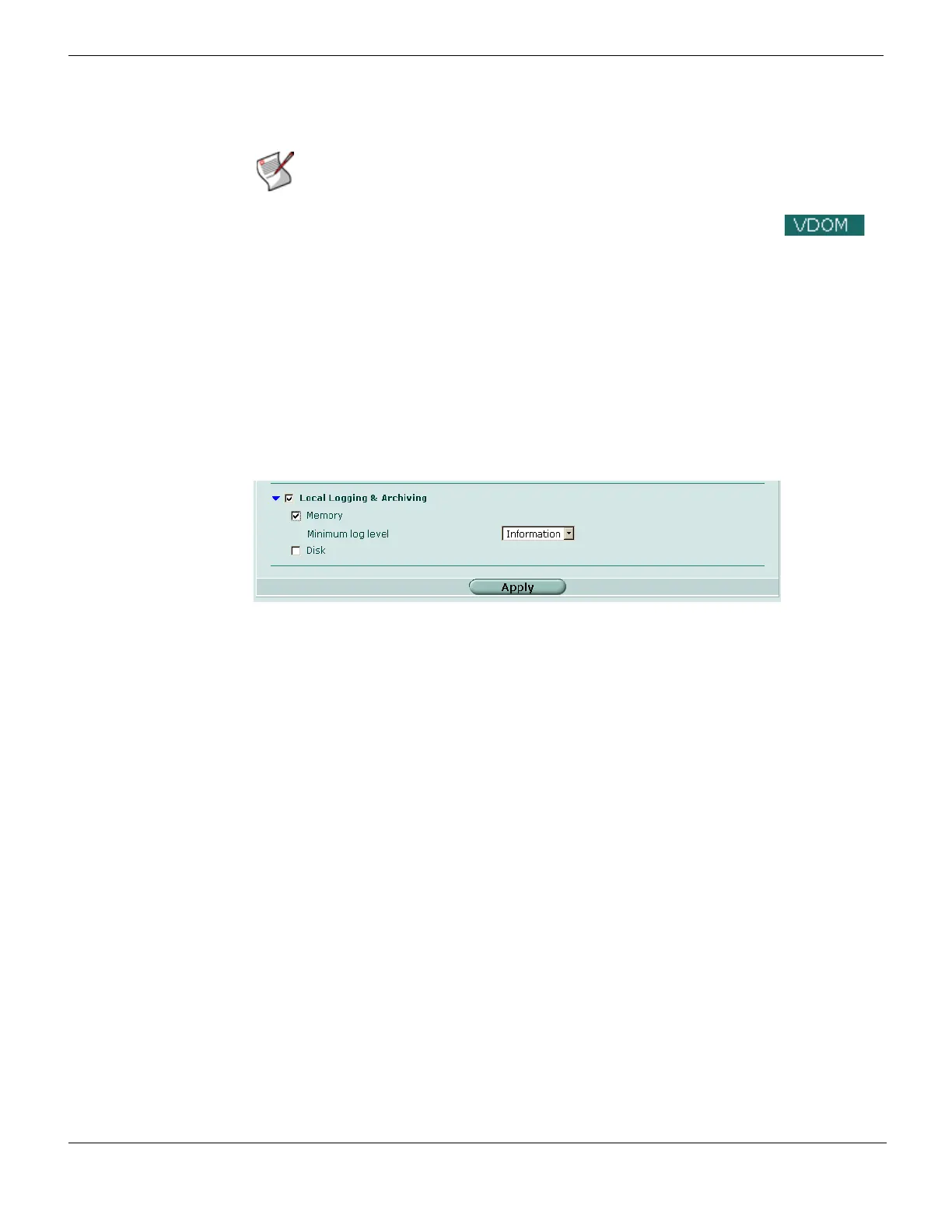
Figure 442: Configuring local logging to memory
To configure the FortiGate unit to save logs in memory
1 Go to Log&Report > Log Config > Log Setting.
2 Select Local Logging & Archiving and select the check box beside Memory.
3 Select Minimum log level for memory logs
The FortiGate unit logs all messages at and above the logging severity level you
select. For more information about the logging levels, see “Log severity levels” on
page 733.
Local logging to disk
If your FortiGate unit contains a hard disk, an AMC hard disk, or an ASM-SAS module you
can configure logging to disk. You can specify the minimum log level and how the
FortiGate unit handles local logging if the hard disk becomes full.
For local logs, the SQL log storage format is the default for all log types except content
archiving and traffic logs. This is the only format from which you can generate reports.
Content archiving is not available in SQL format. You can enable SQL format logging for
traffic logs, but this can cause some loss of logs because SQL format writing is slower
than the compressed format.
Note: If more than one Syslog server is configured, the Syslog servers and their settings
appear on the Log Settings page. You can configure multiple Syslog servers in the CLI. For
more information, see the FortiGate CLI Reference.
 Loading...
Loading...











