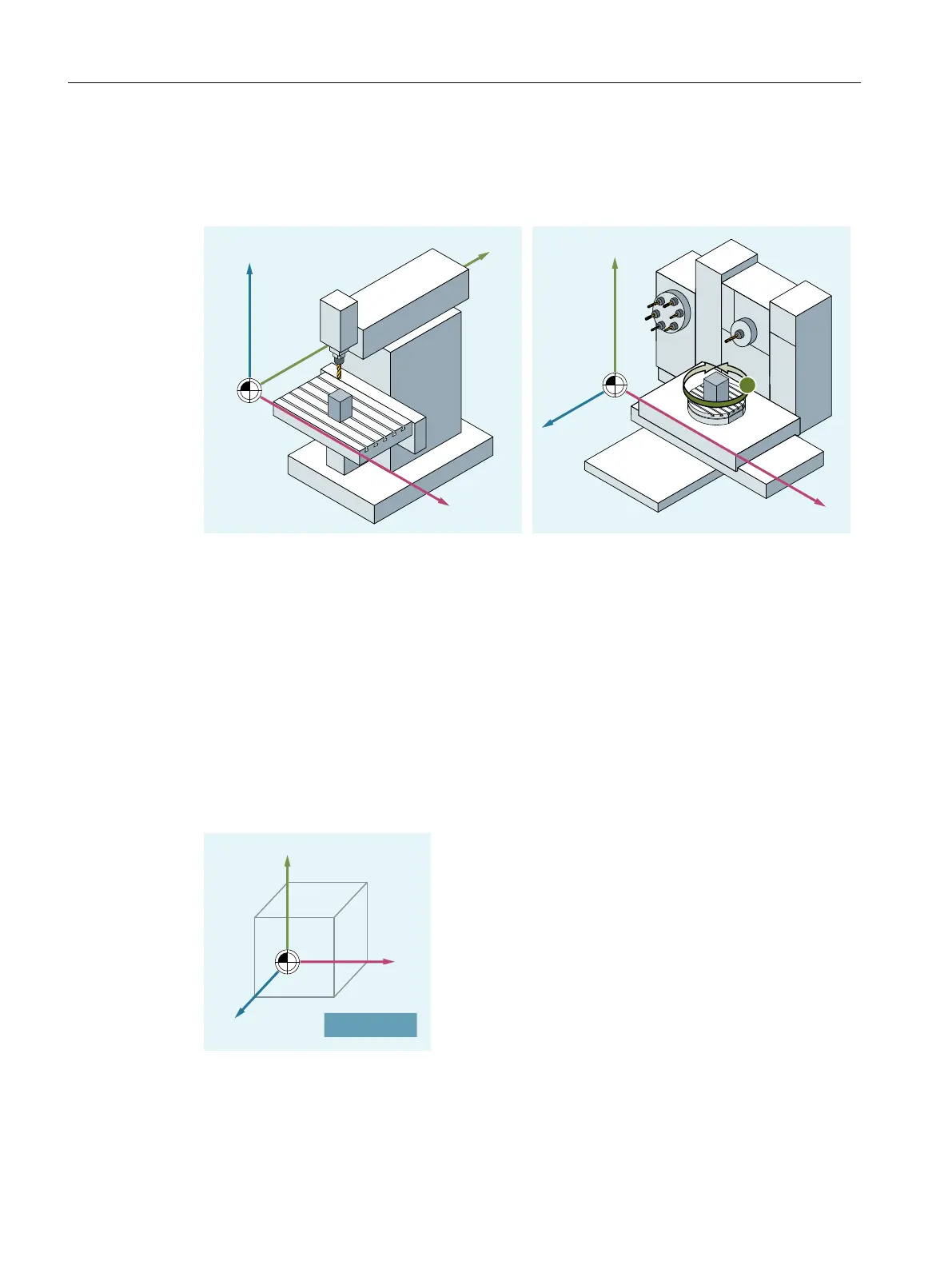
Position of the coordinate system in different machine types
The position of the coordinate system resulting from the "three-finger rule" can have a different
orientation for different machine types, which are shown in the following two examples:
Vertical 3-axis milling machine
Horizontal 4-axis milling machine
2.1.4.2 Basic coordinate system (BCS)
The basic coordinate system (BCS) consists of three mutually perpendicular axes (geometry
axes) as well as other special axes, which are not interrelated geometrically.
Machine tools without kinematics transformation
BCS and MCS always coincide when the BCS can be mapped onto the MCS without
kinematics transformation (e.g. 5-axis transformation, TRANSMIT/TRACYL/TRAANG).
On such machines, machine axes and geometry axes can have the same names.
Fundamentals
2.1 Fundamental Geometrical Principles
NC programming
38 Programming Manual, 12/2019, 6FC5398-2EP40-0BA0

 Loading...
Loading...



















