10-8 Art: 714372-00L Rev. Date: 30-Jul-12
Time to Test
Test samples collected in capillary tubes immediately to avoid clotting
(especially in neonates whose blood may clot more quickly).
Warming Area
Blood flow can be stimulated by warming the puncture site. Follow the
facility’s policy and procedure for warming (arterializing) an infant’s heel or
other skin puncture area.
ACT, cTnI, CK-MB,
and BNP Cartridges
Skin puncture samples are not
recommended for ACT, cTnI, CK-MB,
and BNP measurements.
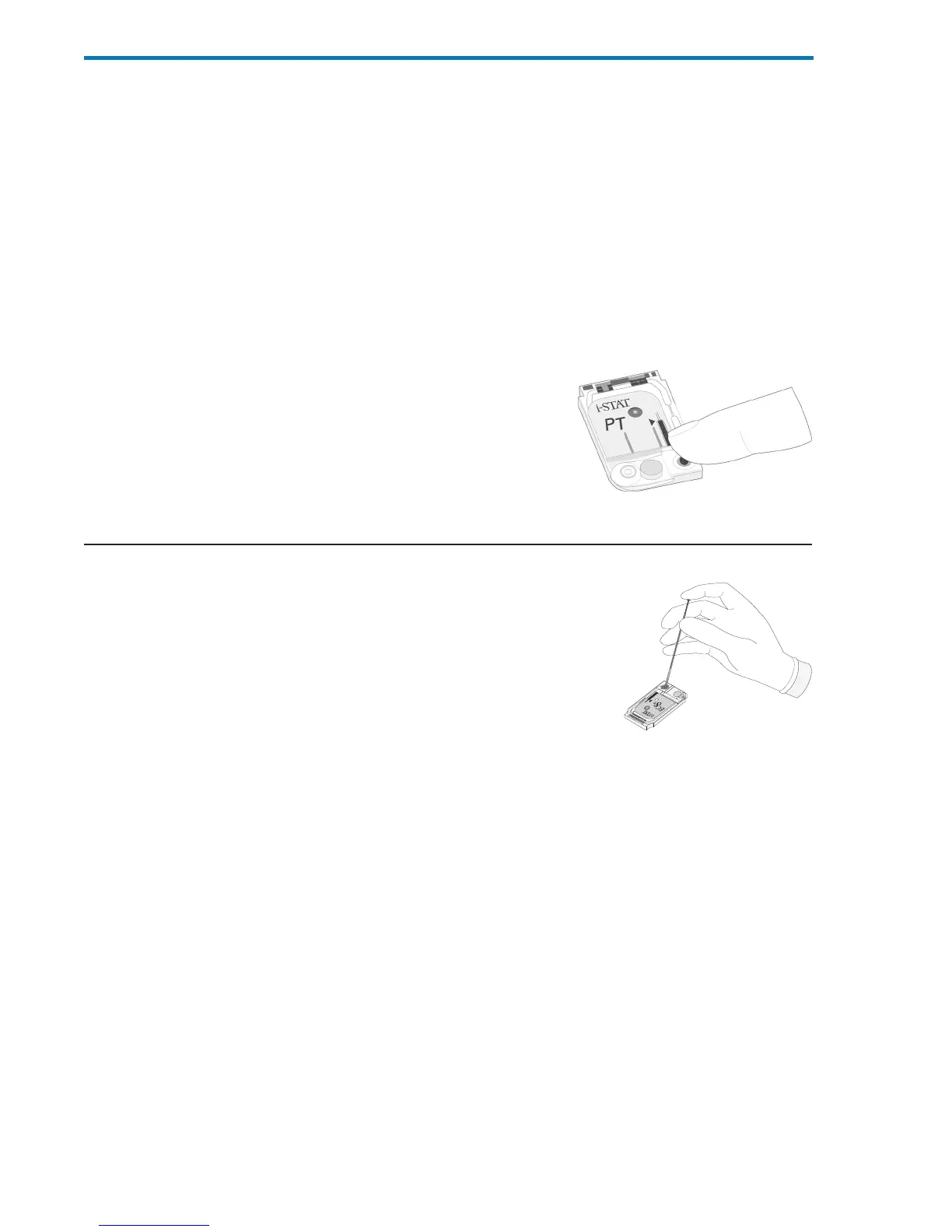
PT/INR Cartridges
i-STAT PT/INR cartridges should be
filled directly from the puncture site by
allowing blood to flow from the site into
the cartridge - no transfer device should
be used.
SAMPLE TRANSFER DEVICES
Dispensers A dispenser can be used to avoid the use of
needles when transferring a blood sample from a
blood collection tube.
Do not use dispensers that would introduce air
into the sample when ionized calcium, pH, or
PCO
2
are being measured.
For coagulation testing the dispenser must be
plastic and must not contain anticoagulant.
Anticoagulant
Most heparinized capillary tubes are not suitable for electrolyte
measurements, especially ionized calcium, due to the high concentration of
heparin (50 U/mL or more). Use balanced heparin tubes or plain tubes.
Capillary Tube
While a sample can be transferred directly from a skin puncture to a cartridge, a
capillary tube is preferred.
Capillary tubes can be used to transfer sample from a tube to a cartridge. For
coagulation testing, the capillary tube must be plastic and must not contain
anticoagulant.
Syringe
A 1cc syringe (such as a tuberculin) and needle (no smaller than 20 gauge) can
be used to withdraw a sample from an blood collection tube.
Take care not to draw air with the sample when ionized calcium, pH, PCO
2
, or
TCO
2
are being measured.
For coagulation testing, the syringe must be plastic and must not contain
anticoagulant.

 Loading...
Loading...