Chapter 3 3-27
Troubleshooting
EISA
The Extended Industry Standard Architecture (EISA) supports the following features:
• 32-bit memory addressing for CPU, DMA devices, and bus masters.
• 16 or 32-bit data transfers for CPU, DMA devices, and bus masters.
• Synchronized data transfers for bus masters and CPUs which allows burst
transactions up to 33 Mbytes per second.
• Supports intelligent bus master peripheral controllers.
• Enhanced DMA transactions for EISA slave controllers.
• Centralized rotational bus arbitration.
NOTE
Even though the EISA standard allows for predecessor architecture
compatibility, the HP 9000 D Class Enterprise Server only supports
interfacing to an HP defined set of EISA controllers.
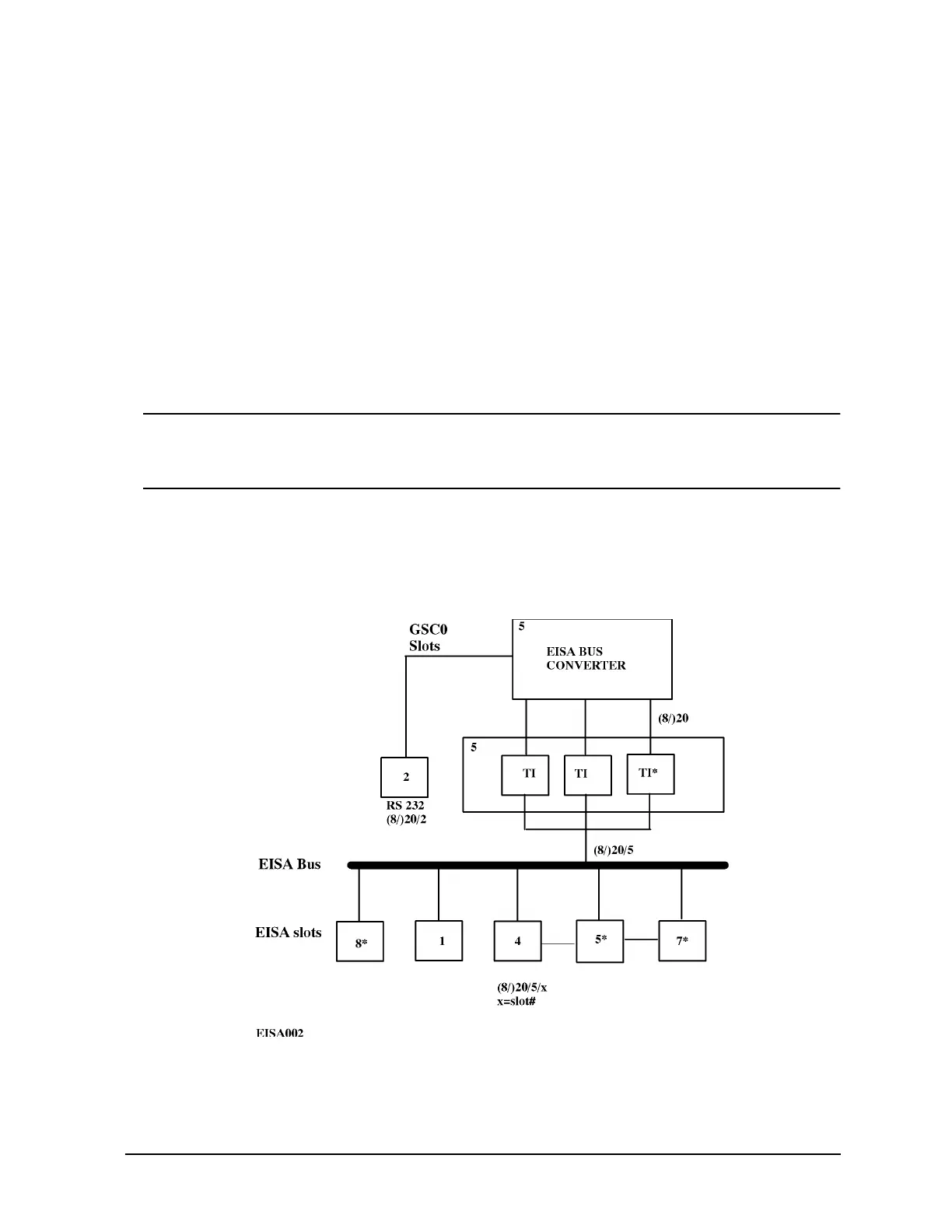
Figure 3-6 shows the implementation of EISA on the System/Core I/O card. The EISA
circuitry is comprised of three layers, the EISA bus converter, a set of 2 or 3 TI
components, and up to seven EISA connector slots on the D3xx System/Core I/O card.
Figure 3-6 EISA Block Diagram
The TI component and EISA connector slots marked with an asterisk (*) are not present
on the D2xx System/Core I/O card.
 Loading...
Loading...











