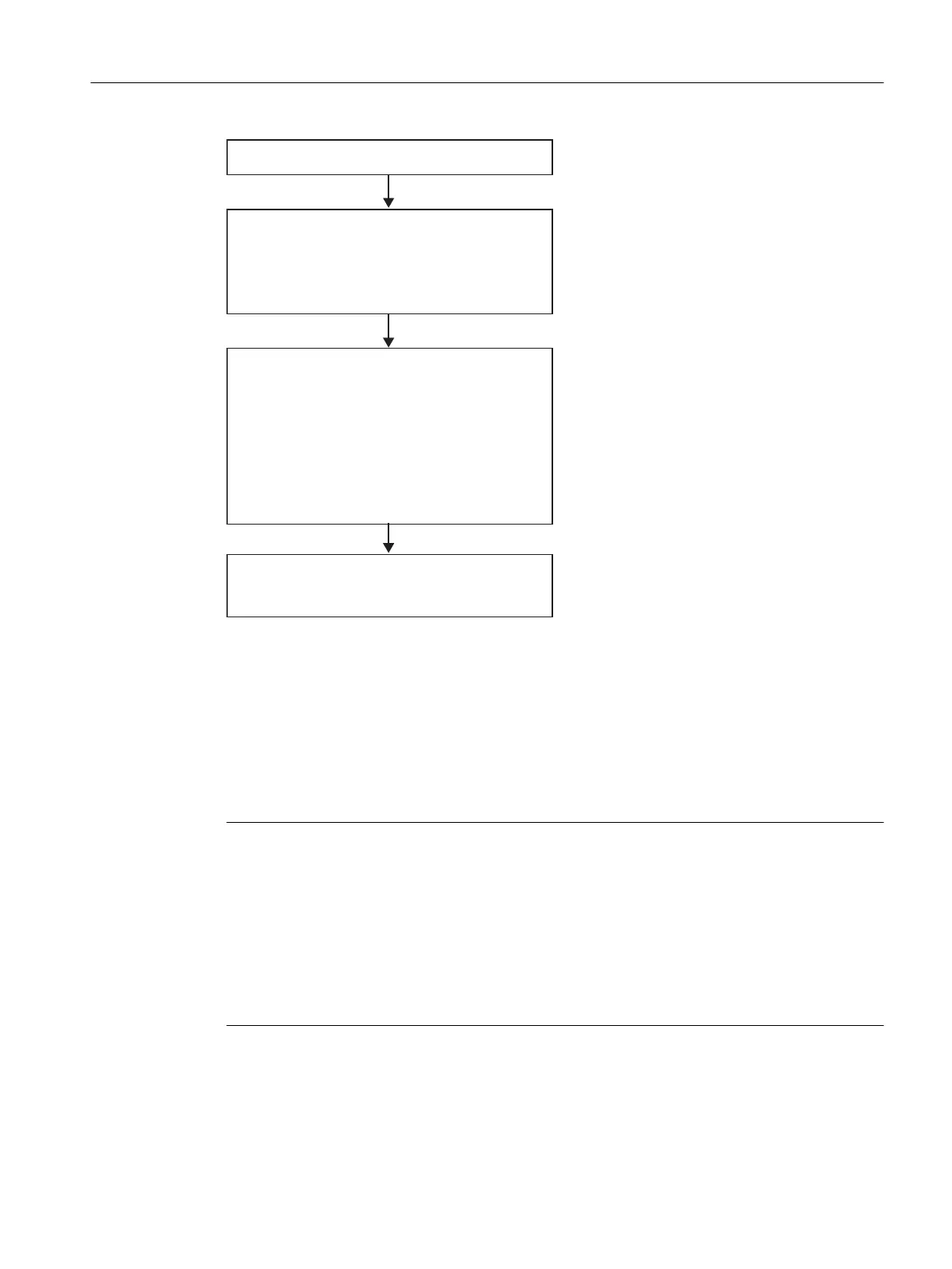
&UHDWHDQHZSURGXFWLRQRUGHU
6SHFLI\WKHSURSHUWLHVRIWKHRUGHU
ವ2UGHUQDPH
ವ7RWDOTXDQWLW\IRUWKHRUGHU
ವ(DUOLHVWVWDUWDQGODWHVWFRPSOHWLRQ
6SHFLI\SURSHUWLHVIRUHDFKEDWFK
ವ&KDQJHSUHVHWTXDQWLW\
ವ6WDUWPRGHDQGWLPHLIWLPHGULYHQ
ವReference to formula (with assigned
master recipe)
ವ,IQHFFKDQJHIRUPXODXQLWDOORFDWLRQ
ವ,IQHFFKDQJHSURFHVVLQJVHTXHQFHE\
FKDLQLQJZLWKRWKHUEDWFKHV
&KHFN
ವ7RWDOTXDQWLW\RYHUDOOEDWFKHV
ವ5XQWLPHRIHDFKLQGLYLGXDOEDWFK
Basic procedure
You create the batches for the production orders in BatchCC. By defining and selecting a
master batch, numerous batches with similar properties can be created quickly. In the
properties of each batch, you specify the reference to a released formula with assigned master
recipe or to a released master recipe without a formula category assignment. You can specify
the batch quantity and Start mode for every batch. By chaining the batches, you can define
the order in which they are processed.
Note
Excluding blocking effects with batches
Depending on the current status of the batches, the batch structure, the number of released
batches and their start mode, it is possible that batches block each other when they are running.
This effect can occur in particular when there is a failover of redundant BATCH servers or
when exiting and restarting a BATCH server.
To make sure that batches do not block each other while they are running, configure start
allocations or work with chains in the "End" mode. This is particularly important when using
synchronization functions.
Additional information
"Allocation" tab (Page 756)
BATCH Control Center
9.6 Batch Planning
SIMATIC BATCH V8.2
Operating Manual, 02/2016, A5E35958174-AA 349

 Loading...
Loading...











