1
10.04 Introduction
1.4 Fundamentals
1
Siemens AG, 2004. All rights reserved
SINUMERIK 840D/840Di/810D Operation/Programming ShopMill (BAS) – 10.04 Edition 1-49
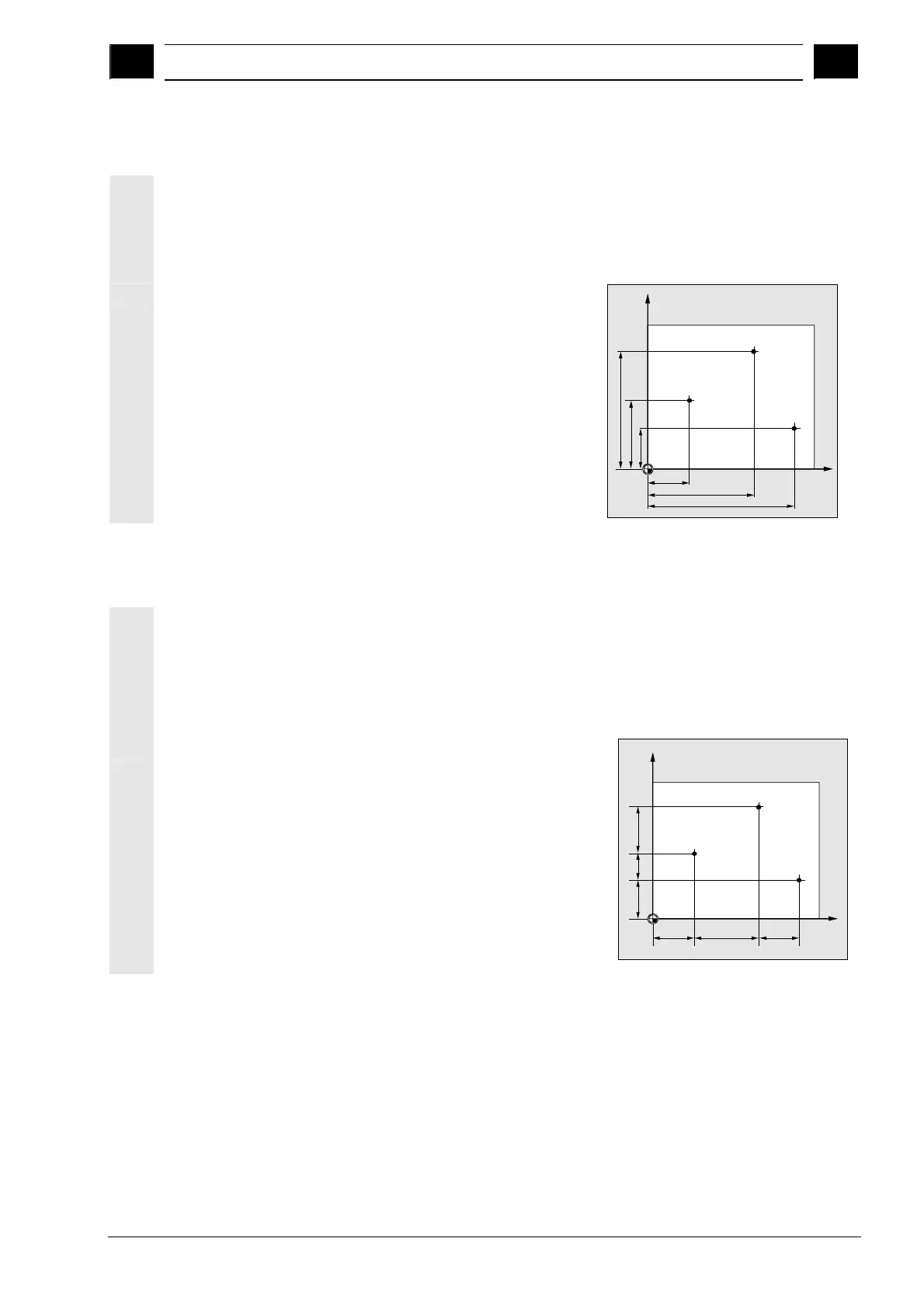
1.4.3 Absolute dimensions
With absolute dimensions, all the positional data refer to the currently
valid zero point. Applied to tool movement this means:
The absolute dimensions describe the position to which the tool is to
travel.
Example:
The positional parameters for
points P1 to P3 in absolute
dimensions relative to the zero
point are the following:
P1: X20 Y35
P2: X50 Y60
P3: X70 Y20
X
Y
70
50
20
P2
P3
P1
60
35
20
1.4.4 Incremental dimensions
In the case of production drawings in which dimensions refer to some
other point on the workpiece rather than the zero point, it is possible
to enter an incremental dimension.
With incremental dimension input, each item of positional data refers
to a point programmed beforehand.
Example:
The positional data for points P1
to P3 in incremental dimensions
are:
P1: X20 Y35 ;(relative to the
zero point)
P2: X30 Y20 ;(relative to P1)
P3: X20 Y -35 ;(relative to P2)
X
Y
P1
20 2030
P2
P3
20
15
20
 Loading...
Loading...























