8.1 Symbols Used in Block Diagrams and their Meanings
8-1
Chapter 8 BLOCK DIAGRAMS FOR CONTROL LOGIC
FRENIC-MEGA series of inverters is equipped with a number of function codes to match a variety of motor
operations required in your system. Refer to Chapter 5 "FUNCTION CODES" for details of the function codes.
The function codes have functional relationship each other. Several special function codes also work with
execution priority each other depending on their functions or data settings.
This chapter explains the main block diagrams for control logic in the inverter. You are requested to fully
understand the inverter's control logic together with the function codes in order to set the function code data
correctly.
The block diagrams contained in this chapter show only function codes having mutual relationship. For the
function codes that work independently and for detailed explanation of each function code, refer to Chapter 5
"FUNCTION CODES."
8.1 Symbols Used in Block Diagrams and their Meanings
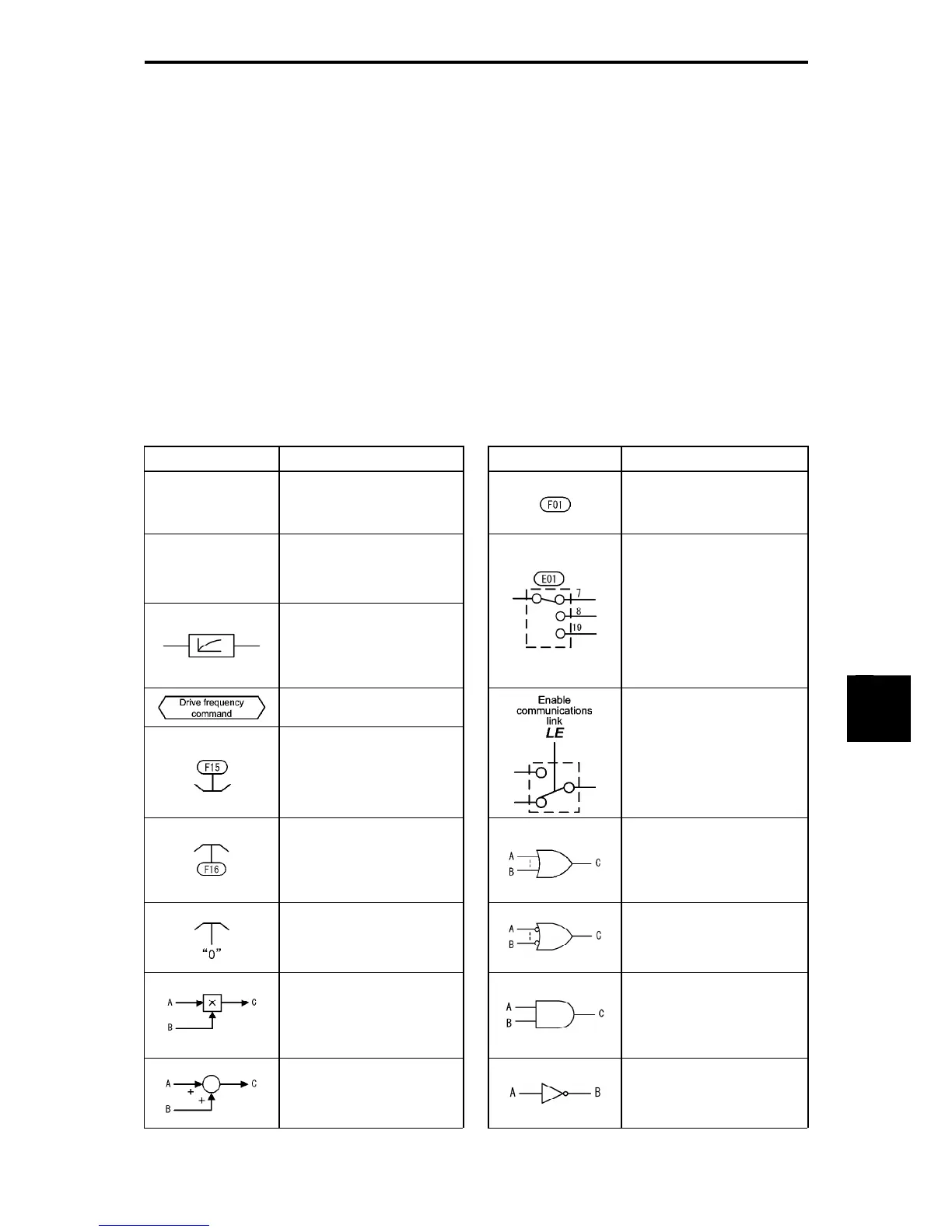
Table 8.1-1 lists symbols commonly used in block diagrams and their meanings with some examples.
Table 8.1-1 Symbols and Meanings
Symbol Meaning Symbol Meaning
[FWD], [Y1]
etc.
General-purpose I/O
terminals of the inverter
control circuit terminal block.
Function code.
FWD, REV
etc.
Control signals (input) or
status signals (output),
assigned to control circuit
terminals.
Low-pass filter: Features
appropriate characteristics
by changing the time
constant through the
function code data.
Switch controlled by a
function code. Numbers
assigned to the terminals
express the function code
data.
Internal control signal for
inverter logic.
High limiter: Limits the
upper value by a constant or
data set to a function code.
Switch controlled by a
terminal command. In the
example shown on the left,
the enable communications
link command LE assigned
to one of the digital input
terminals from [X1] to [X9]
controls the switch.
Low limiter: Limits the lower
value by a constant or data
set to a function code.
OR logic:
In normal logic, if any input
is ON, then C = ON. Only if
all inputs are OFF, then C =
OFF.
Zero limiter: Prevents data
from dropping to a negative
value.
NOR (NOT-OR) logic:
In normal logic, if any input
is OFF, then C = ON. If all
inputs are ON, C = OFF.
Gain multiplier for reference
frequencies given by current
and/or voltage input or for
analog output signals. C = A
× B
AND logic:
In normal logic, only if A =
ON and B = ON, then C =
ON. Otherwise, C = OFF.
Adder for 2 signals or
values. C = A + B
If B is negative then C = A –
B (acting as a subtracter).
NOT logic:
In normal logic, if A = ON,
then B = OFF, and vice
versa.

 Loading...
Loading...











