App. A Advantageous Use of Inverters (Notes on Electrical Noise)
A-4
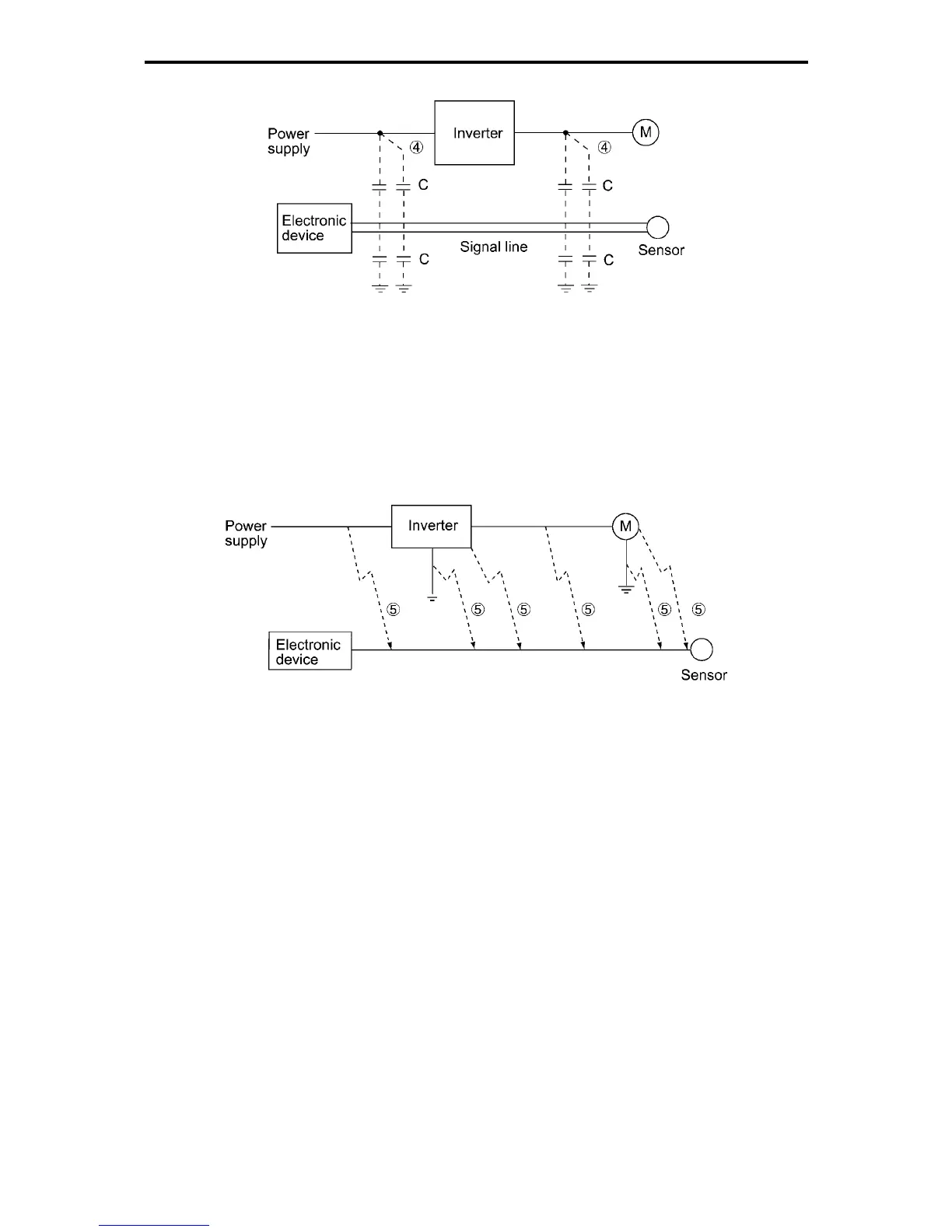
Figure A-5 Electrostatic Induced Noise
(3) Radiation Noise
Noise generated in an inverter may be radiated through the air from the main circuit and grounding wires
(that act as antennas) at the input and output sides of the inverter so as to affect peripheral devices as well
as broadcast and wireless communication. This noise is called "radiation noise" g as shown below. Not
only wires but motor frames or control system panels containing inverters may also act as antennas.
Figure A-6 Radiation Noise
A.3 Noise prevention
The more noise prevention is strengthened, the more effective. However, with the use of appropriate
measures, noise problems may be resolved easily. It is necessary to implement economical noise
prevention according to the noise level and the equipment conditions.
[1] Noise prevention prior to installation
Before installing an inverter in your control panel or installing an inverter panel, you need to consider noise
prevention. Once noise problems occur, it will cost additional materials and time for solving them.
Noise prevention prior to installation includes:
1. Separating the wiring of main circuits and control circuits
2. Putting main circuit wiring into a metal conduit pipe
3. Using shielded wires or twisted shielded wires for control circuits.
4. Implementing appropriate grounding work and grounding wiring.
These noise prevention measures can avoid most noise problems.

 Loading...
Loading...











