263
Configuring ARP
This chapter describes how to configure the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP).
Overview
ARP resolves IP addresses into MAC addresses on Ethernet networks.
ARP message format
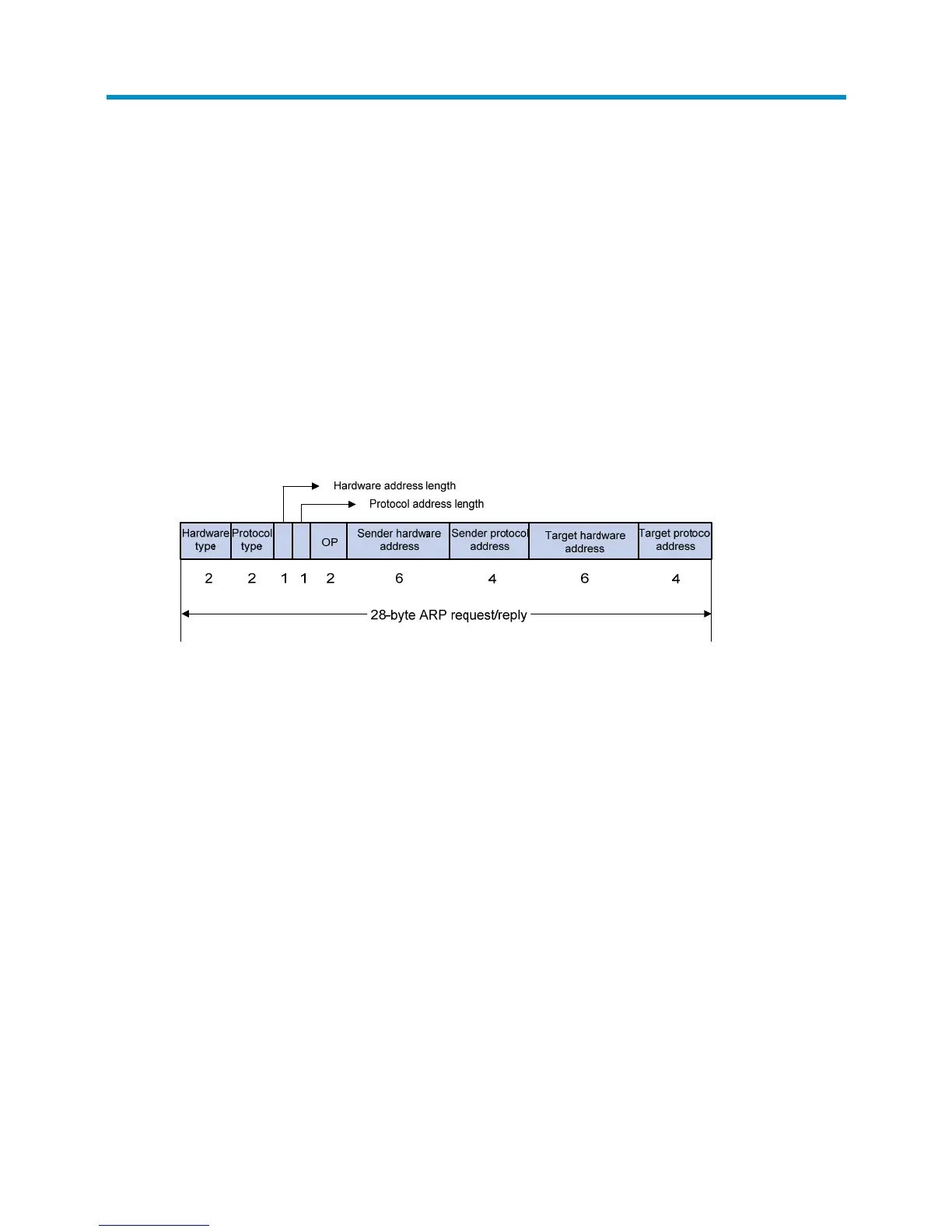
ARP messages are classified into ARP requests and ARP replies. Figure 229 shows the format of the ARP
request/reply messages. Numbers in the figure refer to field lengths.
Figure 229 ARP message format
The following describe the fields in Figure 229:
• Hardware type—The hardware address type. The value 1 represents Ethernet.
• Protocol type—The type of the protocol address to be mapped. The hexadecimal value 0x0800
represents IP.
• Hardware address length and protocol address length—Length, in bytes, of a hardware address
and a protocol address, in bytes. For an Ethernet address, the value of the hardware address length
field is 6. For an IPv4 address, the value of the protocol address length field is 4.
• OP—Operation code. The type of the ARP message. The value 1 represents an ARP request and 2
represents an ARP reply.
• Sender hardware address—Hardware address of the device sending the message.
• Sender protocol address—Protocol address of the device sending the message.
• Target hardware address—Hardware address of the device the message is being sent to.
• Target protocol address—Protocol address of the device the message is being sent to.
ARP operating mechanism
As shown in Figure 230, Host A and Host B are on the same subnet. Host A sends a packet to Host B as
follows:

 Loading...
Loading...











