500
• Burst size—The capacity of the token bucket, or the maximum traffic size permitted in each burst. It
is usually set to the committed burst size (CBS). The set burst size must be greater than the maximum
packet size.
One evaluation is performed on each arriving packet. In each evaluation, if the number of tokens in the
bucket is enough, the traffic conforms to the specification and the tokens for forwarding the packet are
taken away; if the number of tokens in the bucket is not enough, it means that too many tokens have been
used and the traffic is excessive.
The working mechanism of rate limit
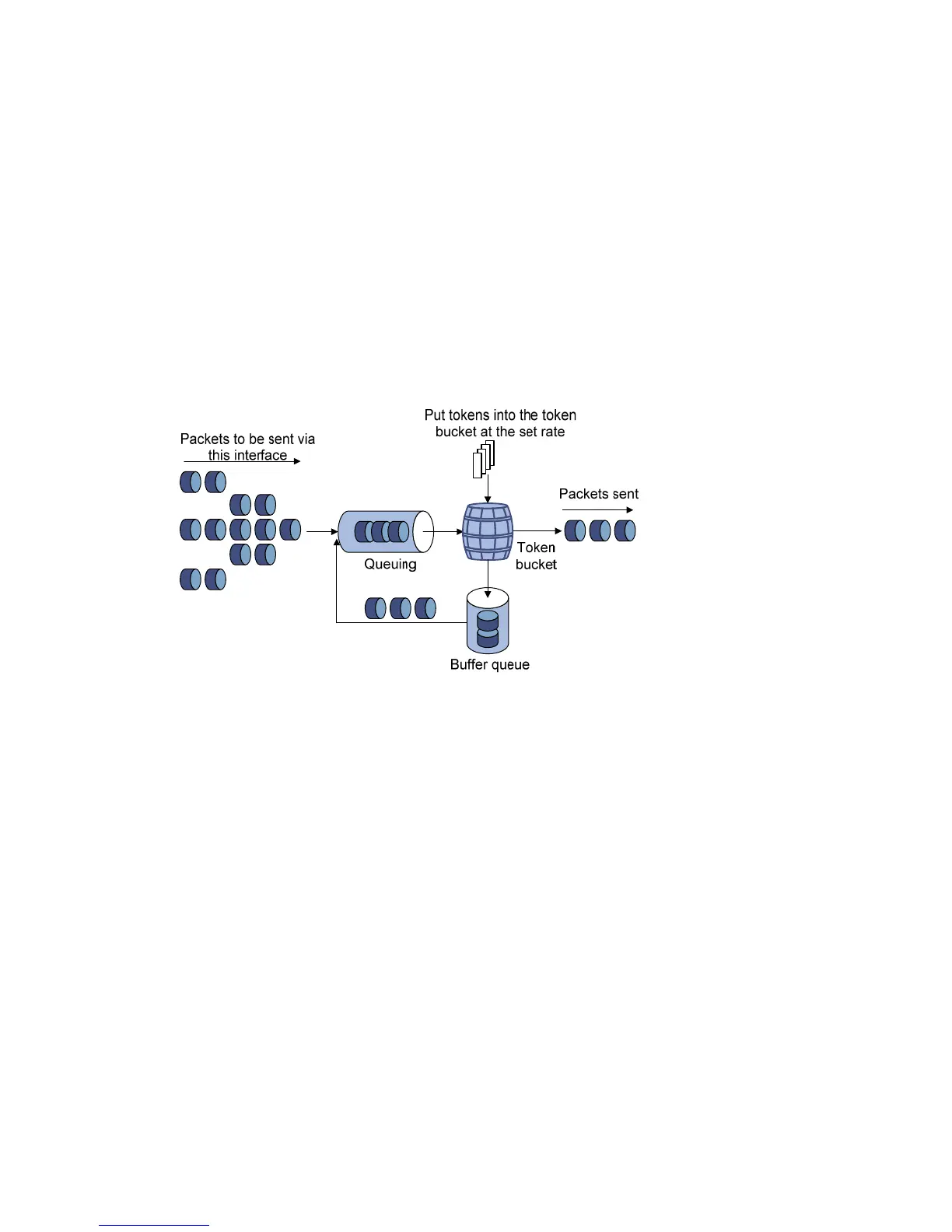
This section uses the outgoing packets for example. When rate limit is configured on an interface, a token
bucket handles all packets to be sent through the interface for rate limiting. If the token bucket has enough
tokens, packets can be forwarded; otherwise, packets are put into QoS queues for congestion
management. In this way, the traffic passing the physical interface is controlled.
Figure 480 Rate limit implementation
With a token bucket used for traffic control, when the token bucket has tokens, the bursty packets can be
transmitted; if no tokens are available, packets cannot be transmitted until new tokens are generated in
the token bucket. In this way, the traffic rate is restricted to the rate for generating tokens, the traffic rate
is limited, and bursty traffic is allowed.
Priority mapping
Concepts
When a packet enters a network, it is marked with a certain priority to indicate its scheduling weight or
forwarding priority. Then, the intermediate nodes in the network process the packet according to the
priority.
When a packet enters a device, the device assigns to the packet a set of predefined parameters
(including the 802.1p priority, DSCP values, IP precedence, and local precedence).
• For more information about 802.1p priority, DSCP values, and IP precedence, see "Packet
pr
ecedences."
• Local precedence is a locally significant precedence that the device assigns to a packet. A local
precedence value corresponds to an output queue. Packets with the highest local precedence are
processed preferentially.
 Loading...
Loading...











