1. Enabling DHCP and configuring
advanced parameters for the
DHCP relay agent
(Required)
Enable DHCP globally and configure advanced DHCP parameters.
By default, global DHCP is disabled.
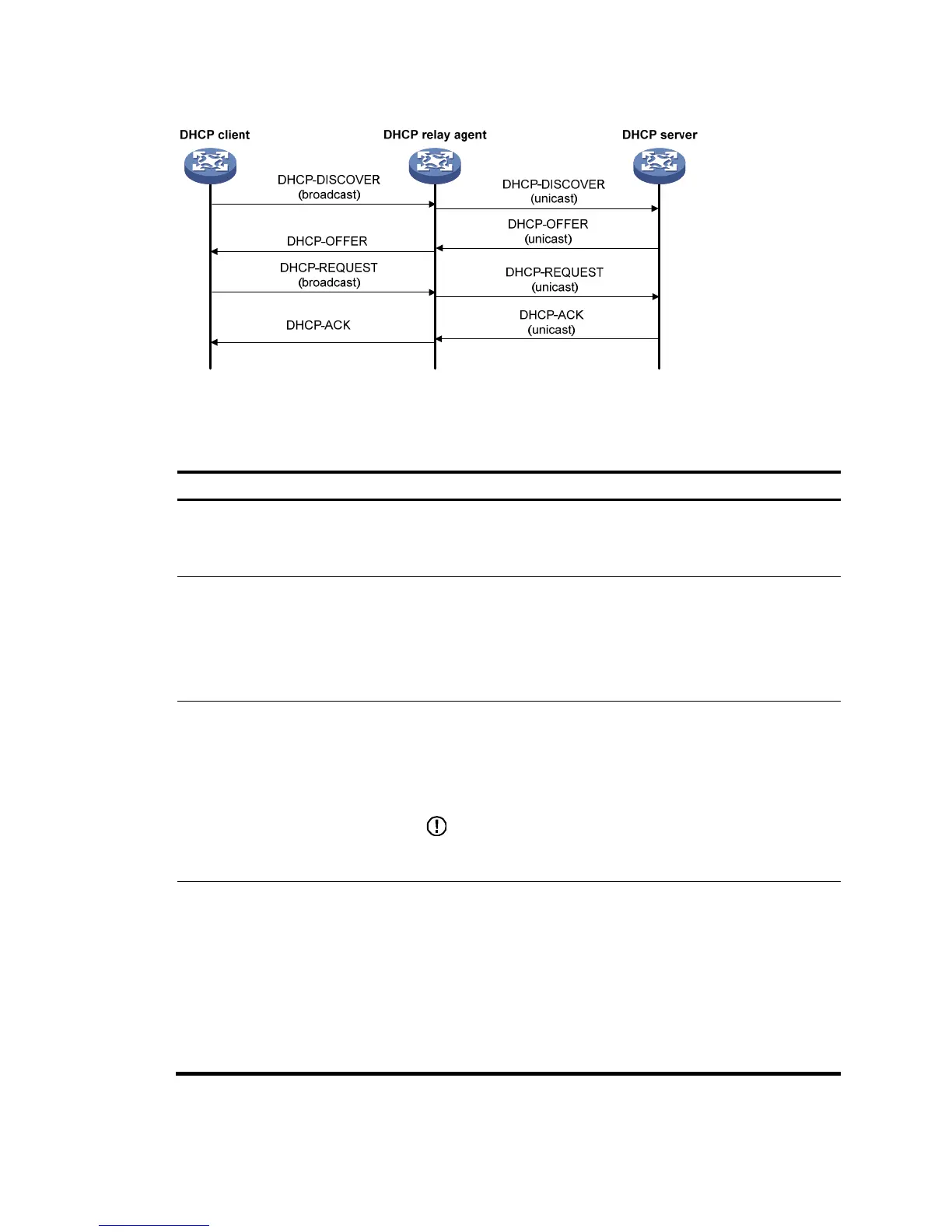
2. Creating a DHCP server group
(Required)
To improve reliability, you can specify several DHCP servers as a
group on the DHCP relay agent and correlate a relay agent interface
with the server group. When the interface receives requesting
messages from clients, the relay agent will forward them to all the
DHCP servers of the group.
3. Enabling the DHCP relay agent
on an interface
(Required)
Enable the DHCP relay agent on an interface, and correlate the
interface with a DHCP server group.
With DHCP enabled, interfaces operate in the DHCP server mode by
default.
IMPORTANT:
The DHCP relay agent works on interfaces with IP addresses manually
configured only.
4. Configuring and displaying
clients' IP-to-MAC bindings
(Optional)
Create a static IP-to-MAC binding, and view static and dynamic
bindings.
The DHCP relay agent can dynamically record clients’ IP-to-MAC
bindings after clients get IP addresses. It also supports static bindings,
that is, you can manually configure IP-to-MAC bindings on the DHCP
relay agent, so that users can access external network using fixed IP
addresses.
By default, no static binding is created.

 Loading...
Loading...











