42-4
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Software Configuration Guide—Release 8.7
OL-8978-04
Chapter 42 Configuring Web-Based Proxy Authentication
Understanding How Web-Based Proxy Authentication Works
The initial login page is sent using HTTP and HTTPS and is used for submitting user credentials to the
Catalyst 6500 series switch. Until HTTPS functionality is fully operational, HTTP is used for credential
transfer.
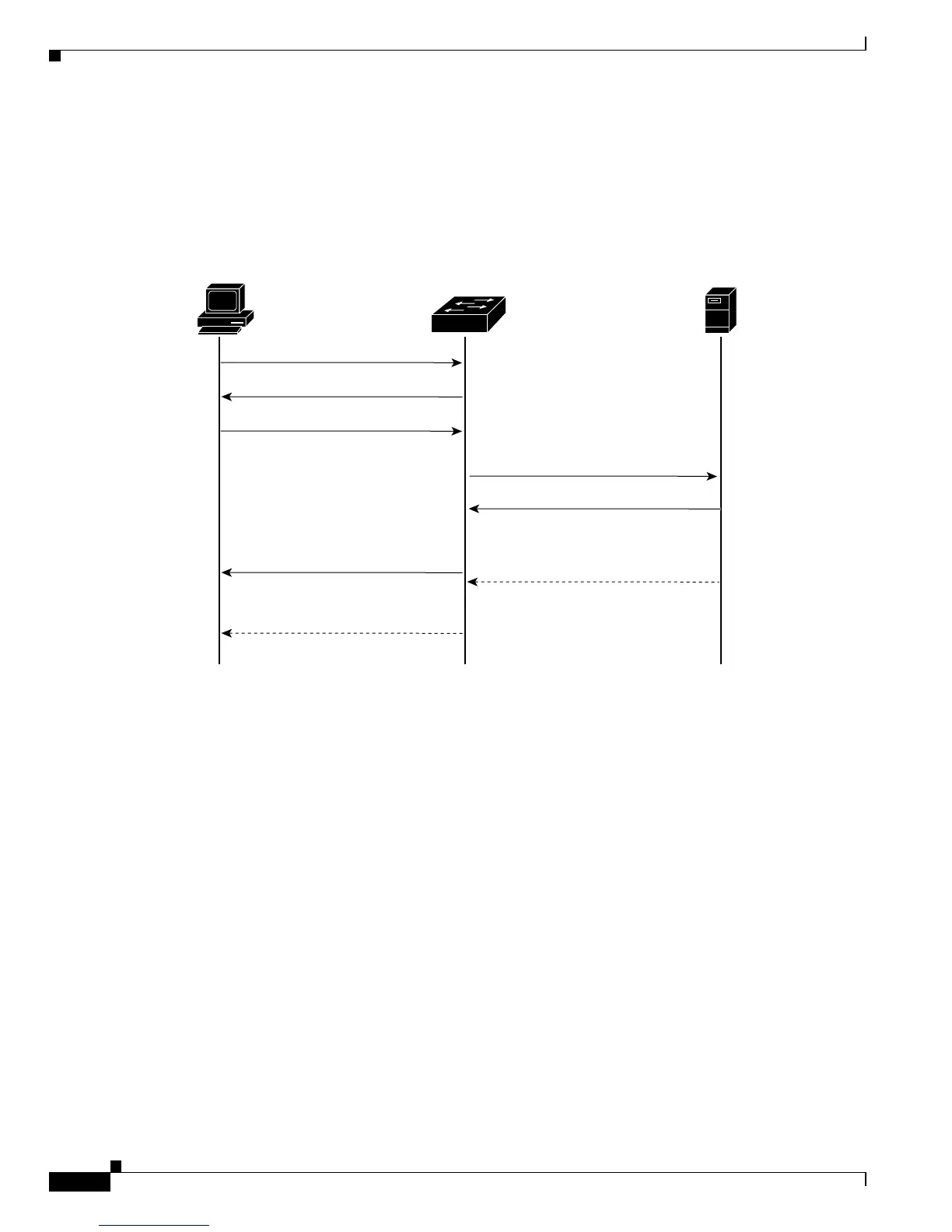
The authentication initiation and message exchange sequence of events is shown in Figure 42-2.
Figure 42-2 Authentication Initiation and Message Exchange
Host Detection and HTTP Traffic Interception
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) inspection is used to address hosts with static IP addresses assigned.
When ARP inspection receives any ARP request on a web-authenticated port, web-based proxy
authentication is triggered for a host IP address. If web-based proxy authentication is enabled on a port
that is operational, the web-based proxy authentication is initiated on all IP addresses in the Dynamic
Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping table. If a DHCP snooping entry does not exist,
web-based proxy authentication is not triggered until a DHCP snooping entry is created or an ARP
request is received.
Once the host is detected, the HTTP traffic from the host is intercepted and redirected to the supervisor
engine. This process is called URL redirection. To configure URL redirection, you must configure an
ACL to redirect all TCP port 80 ingress traffic to the supervisor engine by entering the permit
url-redirect command. The permit url-redirect command redirects all TCP port 80 traffic to the
supervisor engine.
Any ACL that is mapped to a port/port-VLAN with this access control entry (ACE) redirects all the
HTTP/HTTPS protocol packets that match the ACE criteria to the supervisor engine.
 Loading...
Loading...











