33-7
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Software Configuration Guide—Release 8.7
OL-8978-04
Chapter 33 Configuring DHCP Snooping and IP Source Guard
Configuring DHCP Snooping on a VLAN
Configuration Examples for DHCP Snooping
These configuration examples show how to enable DHCP snooping.
Example 1: Enabling DHCP Snooping
This example shows how to enable DHCP snooping for VLAN 10 with a DHCP server on port 1/2:
Console> (enable) set security acl ip dhcpsnoop permit dhcp-snooping
Successfully configured DHCP Snooping for ACL dhcpsnoop. Use 'commit' command to
save changes.
Console> (enable) set security acl ip dhcpsnoop permit ip any any
dhcpsnoop editbuffer modified. Use 'commit' command to apply changes.
Console> (enable) commit security acl dhcpsnoop
ACL commit in progress.
ACL 'dhcpsnoop' successfully committed.
Console> (enable) set security acl map dhcpsnoop 10
Mapping in progress.
ACL dhcpsnoop successfully mapped to VLAN 10.
Console> (enable) set port dhcp-snooping 1/2 trust enable
Port(s) 1/2 state set to trusted for DHCP Snooping.
Console> show dhcp-snooping config
DHCP Snooping MAC address matching is enabled.
DHCP Snooping host-tracking information option is disabled.
Remote ID used in information option is 00-d0-00-4c-1b-ff.
Console> show port dhcp-snooping 1/1-2
Port Trust
---- ------
1/1 untrusted
1/2 trusted
Console> (enable)
Note If you want to configure DHCP-snooping host tracking after enabling DHCP snooping, enter the set
dhcp-snooping information-option host-tracking command.
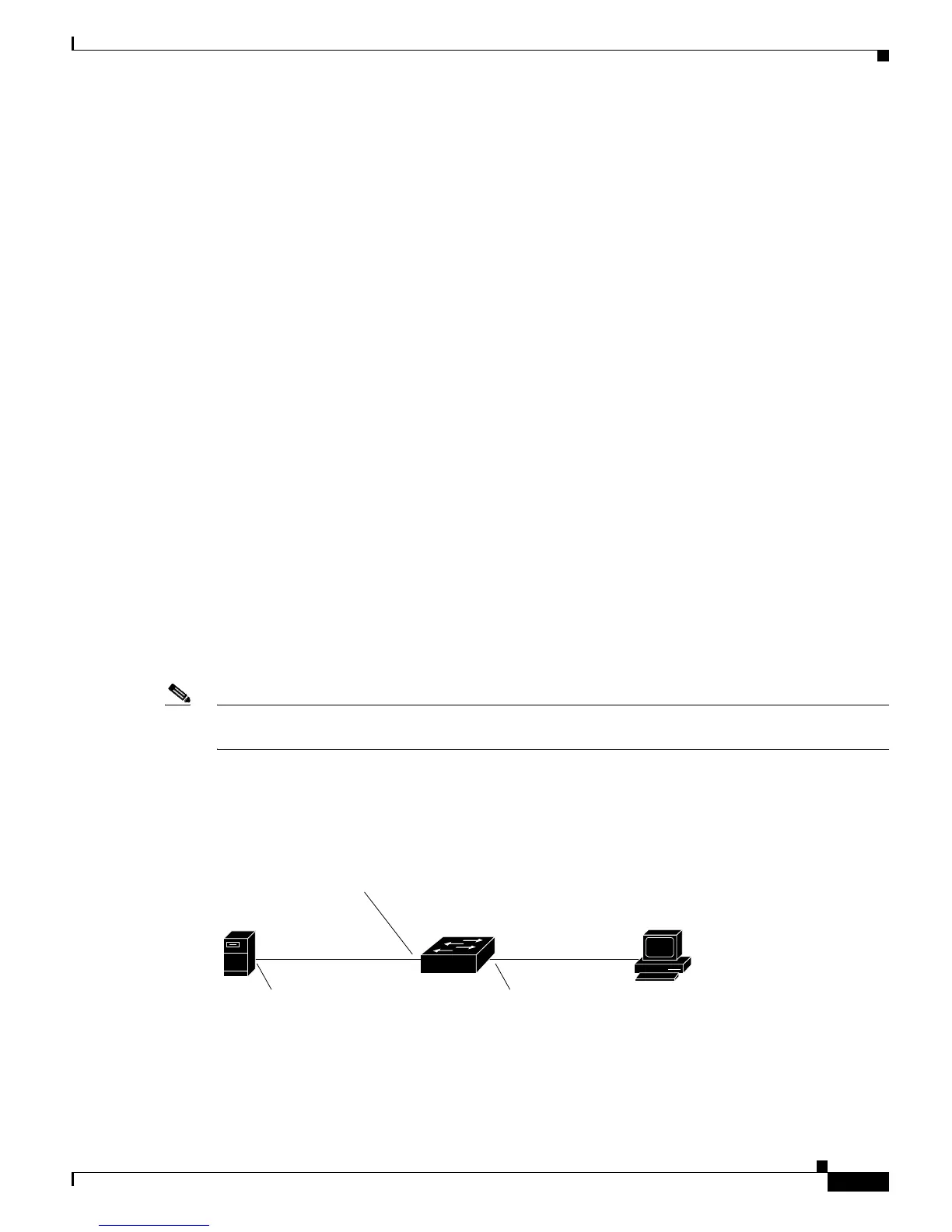
Figure 33-1 shows the typical topology that is used when you configure DHCP snooping in a
client/server network.
Figure 33-1 DHCP Snooping Configured for a Client and Server

 Loading...
Loading...











