49-7
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Software Configuration Guide—Release 8.7
OL-8978-04
Chapter 49 Configuring SPAN, RSPAN and the Mini Protocol Analyzer
Configuring SPAN on the Switch
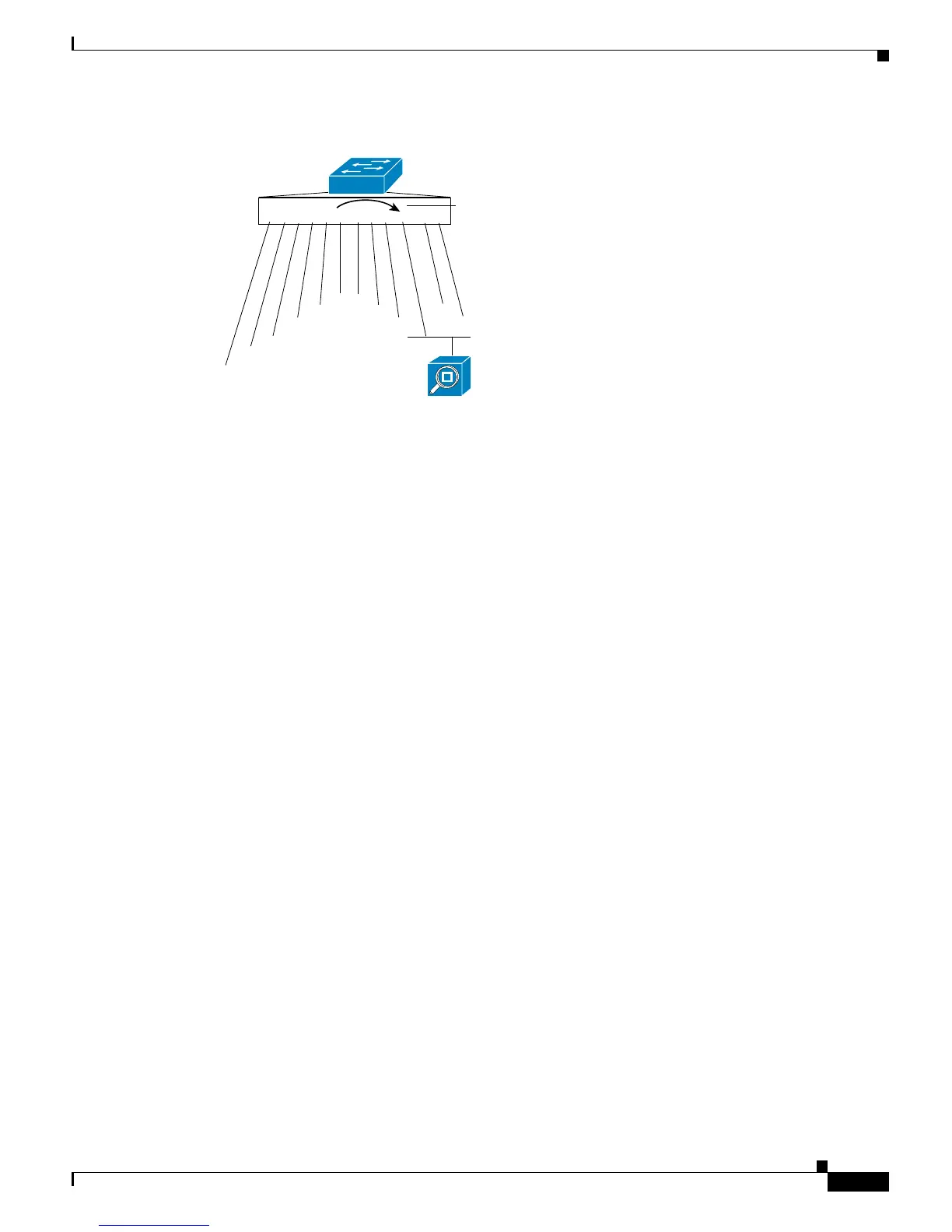
Figure 49-1 SPAN Configuration
For SPAN configuration, the source ports and the destination ports must be on the same switch.
SPAN does not affect the switching of network traffic on the source ports; a copy of the packets that are
received or transmitted by the source ports is sent to the destination ports.
SPAN Configuration Guidelines
This section describes the guidelines for configuring SPAN:
• Use a network analyzer to monitor ports.
• For the SPAN source ports, SPAN is not supported with the ATM ports; it works with the Ethernet
10/100/1000-Mbps ports and 10-Gbps ports.
• When enabled, SPAN uses any previously entered configuration. If you have not entered any
configuration commands, SPAN uses the default parameters.
• If you specify multiple SPAN source ports, the ports can belong to the different VLANs.
• See the “SPAN, RSPAN and Mini Protocol Analyzer Session Limits” section on page 49-5.
• The RSPAN sessions can coexist with the SPAN sessions within the SPAN/RSPAN limits that are
described in the “SPAN, RSPAN and Mini Protocol Analyzer Session Limits” section on page 49-5.
• The optional inpkts keyword is disabled by default. Use the inpkts keyword with the optional
enable keyword to allow the SPAN destination ports to receive the normal incoming traffic. Enter
the optional disable keyword to prevent the SPAN destination ports from receiving the normal
incoming traffic.
• When you enable the optional inpkts keyword, a warning message notifies you that the destination
port does not support the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and may cause loops if you enable this
option.
• Learning is enabled by default. Use the inpkts keyword with the optional learning keyword to
enable or disable learning for a specific port.
• You can specify a Multilayer Switch Module (MSM) port as the SPAN source port. However, you
cannot specify an MSM port as the SPAN destination port.
• When you configure multiple SPAN sessions, the destination module number/port number must be
known to index the particular SPAN session.
 Loading...
Loading...











