14-3
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch Software Configuration Guide—Release 8.7
OL-8978-04
Chapter 14 Configuring MLS
Understanding How Layer 3 Switching Works
Understanding IP Unicast Rewrite
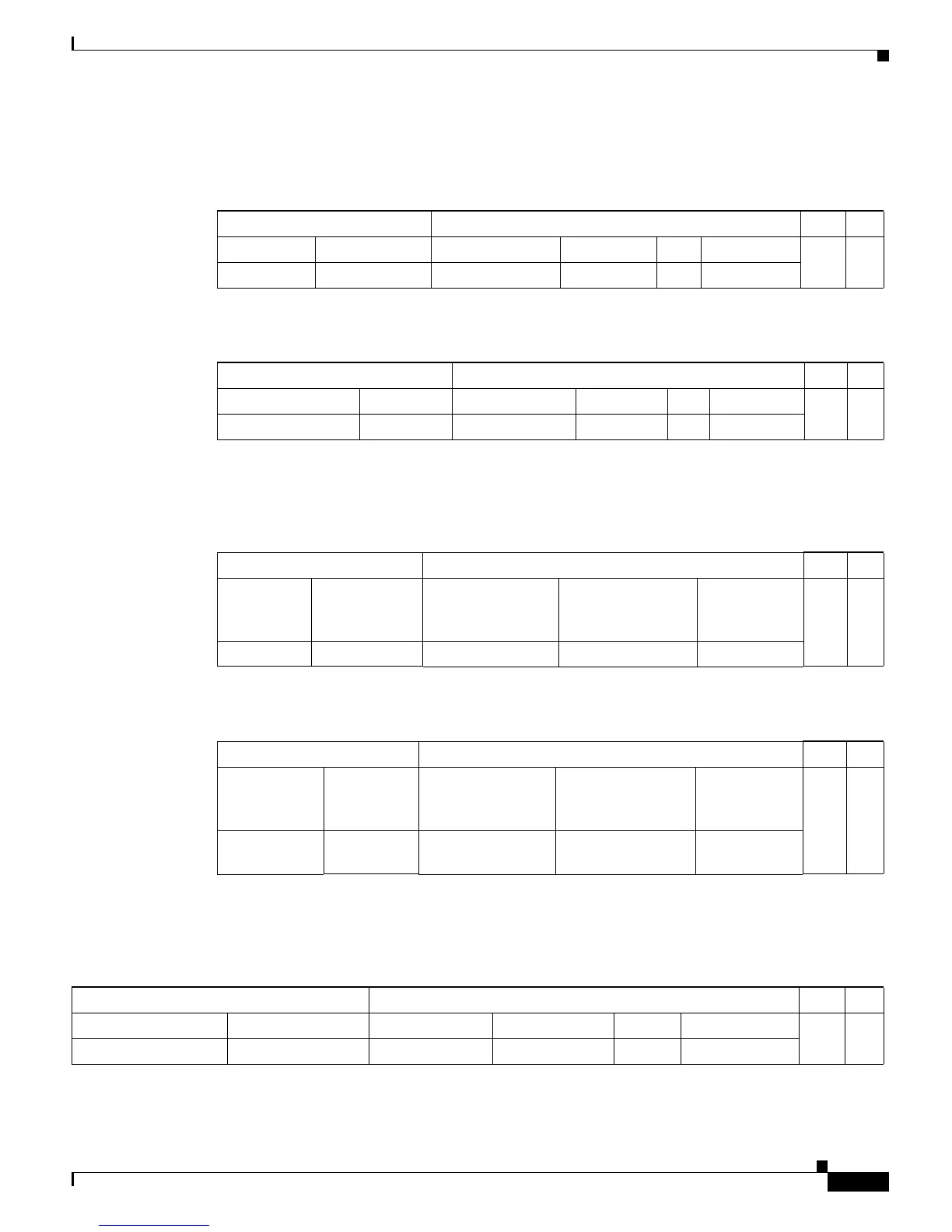
Received IP unicast packets are (conceptually) formatted as follows:
After the switch rewrites an IP unicast packet, it is (conceptually) formatted as follows:
Understanding IPX Unicast Rewrite
Received IPX packets are (conceptually) formatted as follows:
After the switch rewrites an IPX packet, it is (conceptually) formatted as follows:
Understanding IP Multicast Rewrite
Received IP multicast packets are (conceptually) formatted as follows:
Layer 2 Frame Header Layer 3 IP Header Data FCS
Destination Source Destination Source TTL Checksum
MSFC MAC Source A MAC Destination B IP Source A IP n calculation1
Layer 2 Frame Header Layer 3 IP Header Data FCS
Destination Source Destination Source TTL Checksum
Destination B MAC MSFC MAC Destination B IP Source A IP n-1 calculation2
Layer 2 Frame Header Layer 3 IPX Header Data FCS
Destination Source Checksum/
IPX Length/
Transport Control
Destination Net/
Node/
Socket
Source Net/
Node/
Socket
MSFC MAC Source A MAC n Destination B IPX Source A IPX
Layer 2 Frame Header Layer 3 IPX Header Data FCS
Destination Source Checksum/
IPX Length/
Transport Control
Destination Net/
Node/
Socket
Source Net/
Node/
Socket
Destination B
MAC
MSFC MAC n+1 Destination B IPX Source A IPX
Layer 2 Frame Header Layer 3 IP Header Data FCS
Destination Source Destination Source TTL Checksum
Group G1 MAC
1
1. In this example, Destination B is a member of Group G1.
Source A MAC Group G1 IP Source A IP n calculation1
 Loading...
Loading...











