D2 Drive User Guide v1.8 6. Drive Tuning
HIWIN Mikrosystem Corp. 165
6.6. Advanced gains
Important tasks of servo drive include whether the time from the motor starting moving to
arriving the position, i.e. “Move & Settle” (see Section 3.7), is very small, and whether the
position error is very small and the velocity is very smooth during motion. These performance
improvements can be achieved by tuning gains and parameters. The simplest way of D2 drive
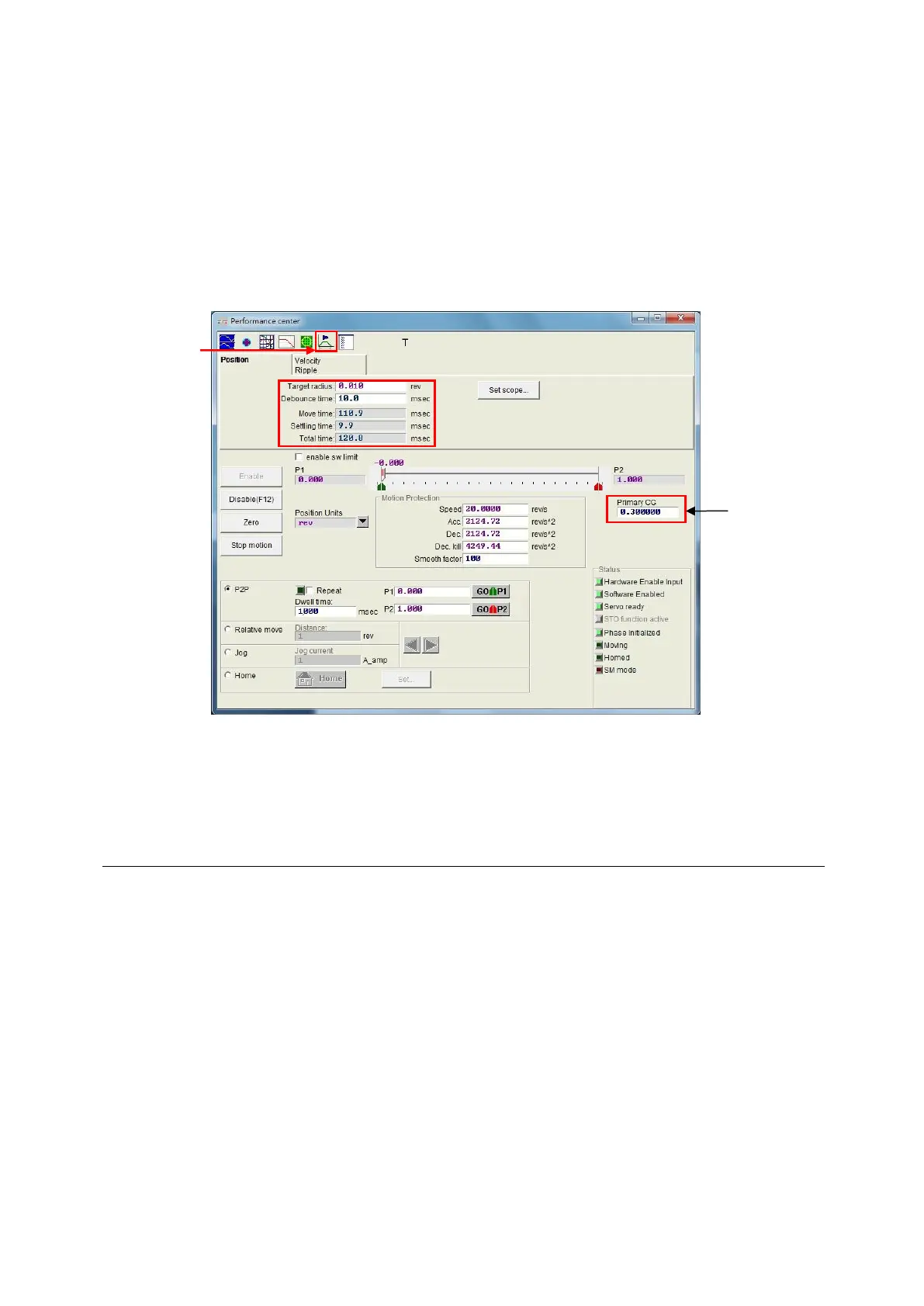
to adjust the performance of motor motion is to tune the common gain (“Primary CG”). The
greater the common gain is, the stronger the servo rigidity is. However, if the servo rigidity is
too strong, the system vibration or electrical noise may be generated. These phenomena are
various with the mechanical status.
Fig. 6-23 Performance center
When using only common gain cannot fulfill the required performance, this system also
provides “Advanced gains”, included functions of “Filter”, “Acc feedforward”, “Schedule Gains
+ vpg”, “Analog input”, “current loop”, and so on.
6.6.1. Filter
The filter is located in the servo control loop on the inside of drive. Its main purposes are to
eliminate the control problem caused by the high-frequency vibration of system, and to deal
with the resonant frequency of overall mechanical system. The performance of system control
can be enhanced via the filter. D2 drive provides two filters that can be used simultaneously
and set in the form of low pass filter or notch filter. To design a filter, the frequency analyzer is
usually used to analyze the system characteristic. By clicking the “Bode…” button given in Fig.
6-24, the simulation interface of “Bode plot” is appeared for the filter design. Settings of two
common used filters are described in the following.
gains
 Loading...
Loading...