K1: Mode group, channel, program operation, reset response
9.3 Mode types and mode type change
Basic Functions
490 Function Manual, 09/2011, 6FC5397-0BP40-2BA0
9.3.1 Monitoring functions and interlocks of the individual modes
Channel status determines monitoring functions
Monitoring functions in operating modes
Different monitoring functions are active in individual operating modes. These monitoring functions are not
related to any particular technology or machine.
In a particular mode only some of the monitoring functions are active depending on the operating status. The
channel status determines which monitoring functions are active in which mode and and in which operating state.
Interlocking functions in operating modes
Different interlocks can be active in the different operating modes. These interlocking functions are not related to
any particular technology or machine.
Almost all the interlocks can be activated in every mode, depending on the operating status.
9.3.2 Mode change
Introduction
A mode change is requested and activated via the mode group interface (DB11, ...). A mode group will either be
in AUTOMATIC, JOG, or MDA mode, i.e. it is not possible for several channels of a mode group to take on
different modes at the same time.
What mode transitions are possible and how these are executed can be configured in the PLC program on a
machine-specific basis.
Possible mode changes
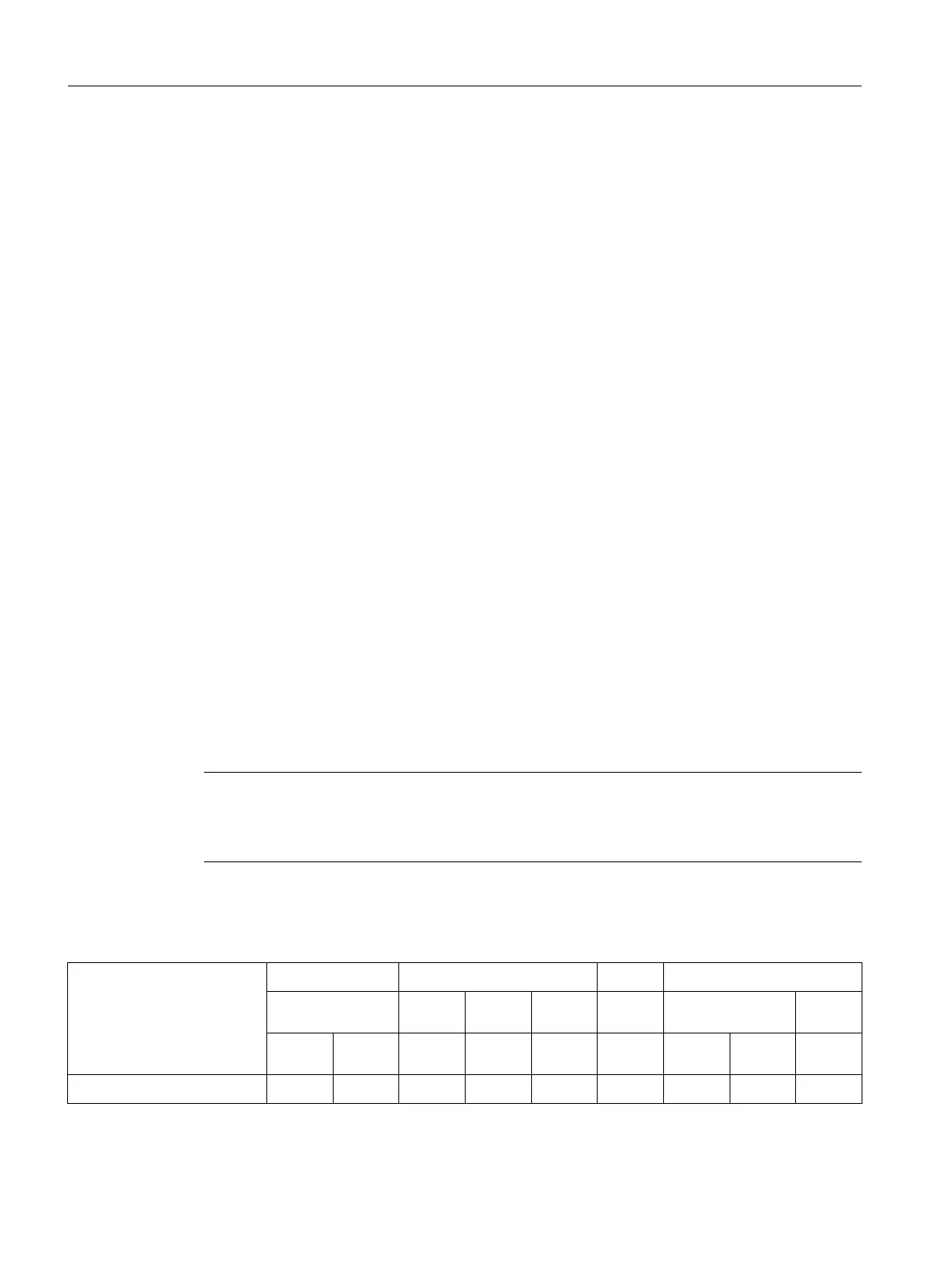
The following table shows possible mode changes for one channel.
Note
The mode is not changed internally until the signal "Channel status active" is no longer
pending. For error-free mode change however, all channels must assume a permissible
operating mode.
AUTOMATIC JOG MDA
AUTO MDA JOG without
handwheel
AUTO
Reset Interrup
t
Reset Interrup
t
Interrup
t
Reset Interrup
t
active Interrup
t
AUTOMATIC XX X

 Loading...
Loading...


















