328 Rockwell Automation Publication 1783-UM007G-EN-P - February 2017
Chapter 7 Configure Switch Features
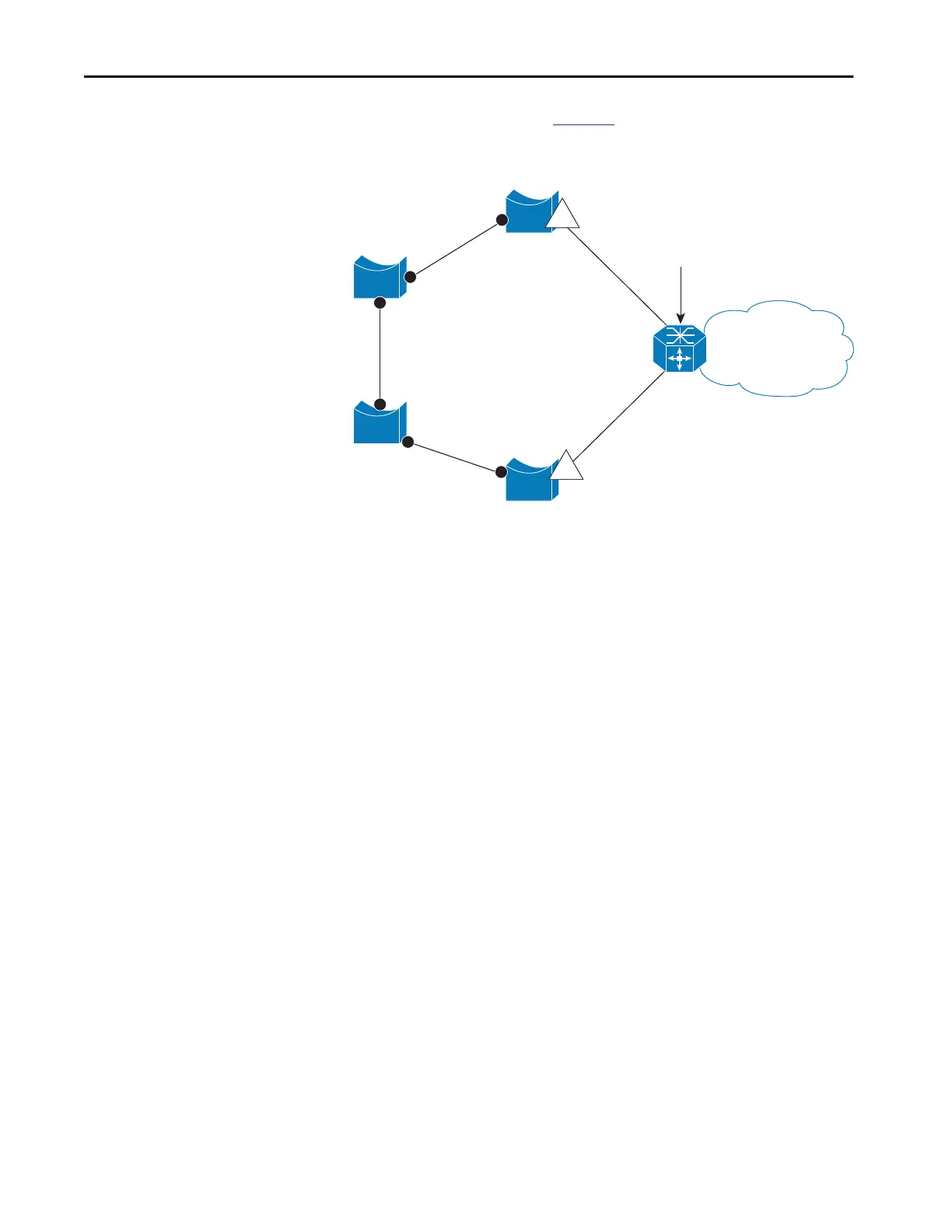
In the example that is shown in Figure 45, E1 or E2 can be configured as the
primary no-neighbor port.
Figure 45 - Ring Topology Example
REP has these limitations:
• You must configure each segment port; an incorrect configuration can
cause forwarding loops in the networks.
• REP can manage only one failed port within the segment; multiple port
failures within the REP segment cause loss of network connectivity.
Configure REP in networks only with redundancy. Configuring REP in a
network without redundancy causes loss of connectivity.
Link Integrity
REP does not use an end-to-end polling mechanism between edge ports to
verify link integrity. It implements local link failure detection. The REP Link
Status Layer (LSL) detects its REP-aware neighbor and establishes
connectivity within the segment. All VLANs are blocked on an interface until
it detects the neighbor. After the neighbor is identified, REP determines the
neighbor port to become the alternate port and which ports forward traffic.
Each port in a segment has a unique port ID. The port ID format is similar to
the format used by the spanning tree algorithm: a port number (unique on the
bridge), associated to a MAC address (unique in the network). When a
segment port is coming up, its LSL starts sending packets that include the
segment ID and the port ID. The port is declared as operational after it
performs a three-way handshake with a neighbor in the same segment.
273792
R
R
E
E
273792
REP Not Supported
REP Ports Configured at Transit Ports
E1
E2

 Loading...
Loading...











