In certain scenarios, the Optimization Factor is set to 13: One of the purposes of the
Jitter Buffer mechanism is to compensate for clock drift. If the two sides of the VoIP call are
not synchronized to the same clock source, one RTP source generates packets at a lower
rate, causing under-runs at the remote Jitter Buffer. In normal operation (optimization factor
0 to 12), the Jitter Buffer mechanism detects and compensates for the clock drift by
occasionally dropping a voice packet or by adding a BFI packet.
Fax and modem devices are sensitive to small packet losses or to added BFI packets.
Therefore, to achieve better performance during modem and fax calls, the Optimization
Factor should be set to 13. In this special mode the clock drift correction is performed less
frequently - only when the Jitter Buffer is completely empty or completely full. When such
condition occurs, the correction is performed by dropping several voice packets
simultaneously or by adding several BFI packets simultaneously, so that the Jitter Buffer
returns to its normal condition.
The procedure below describes how to configure the jitter buffer using the Web interface.
To configure jitter buffer using the Web interface:
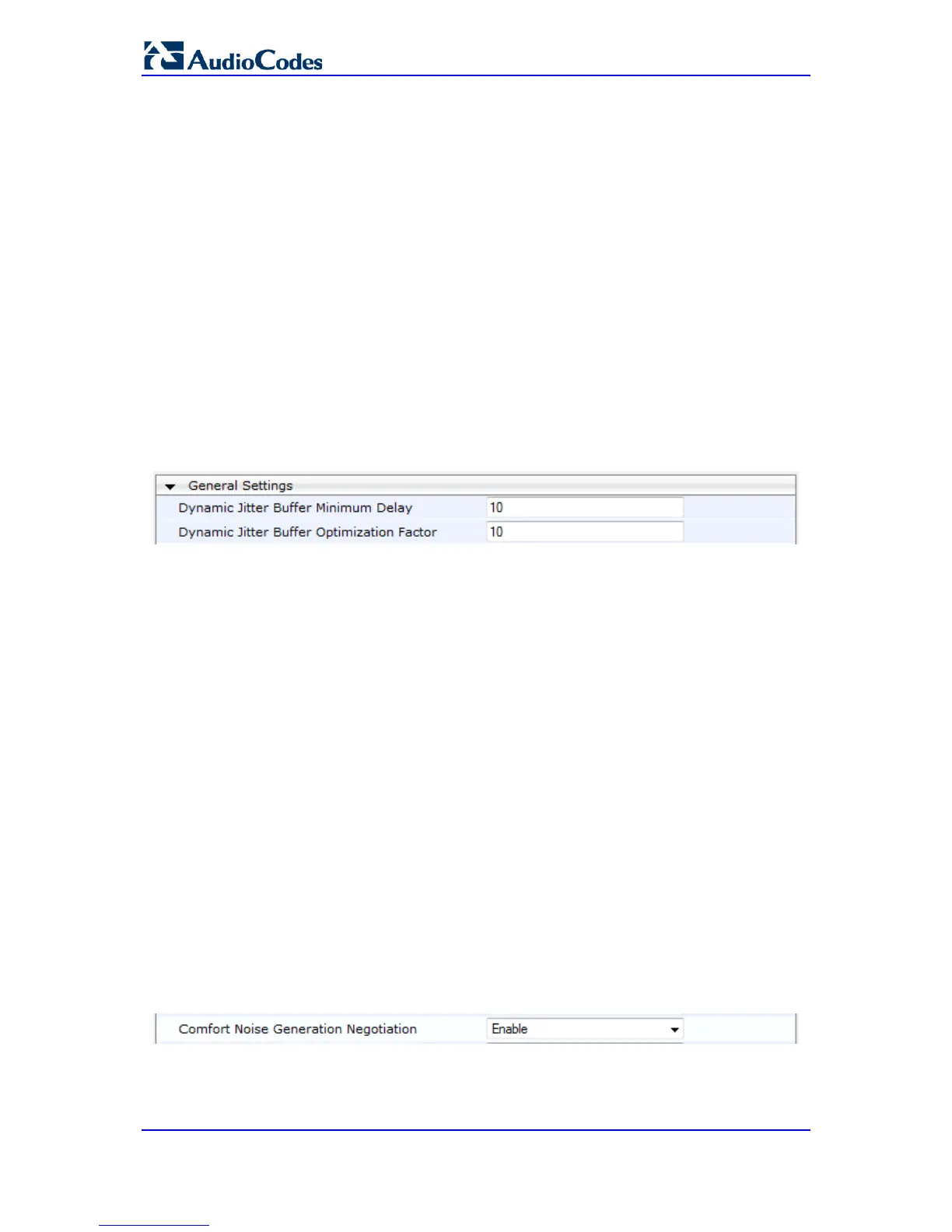
1. Open the RTP/RTCP Settings page (Configuration tab > VoIP menu > Media
submenu > RTP/RTCP Settings). The relevant parameters are listed under the
'General Settings' group, as shown below:
Figure 16-3: Jitter Buffer Parameters in the RTP/RTCP Settings Page
2. Set the 'Dynamic Jitter Buffer Minimum Delay' parameter (DJBufMinDelay) to the
minimum delay (in msec) for the Dynamic Jitter Buffer.
3. Set the 'Dynamic Jitter Buffer Optimization Factor' parameter (DJBufOptFactor) to the
Dynamic Jitter Buffer frame error/delay optimization factor.
4. Click Submit to apply your settings.
16.3.2 Comfort Noise Generation
The device can generate artificial background noise, called comfort noise, in the voice
channel during periods of silence (i.e. when no call party is speaking). This is useful in that
it reassures the call parties that the call is still connected. The device detects silence using
its Voice Activity Detection (VAD) mechanism. When the Calling Tone (CNG) is enabled
and silence is detected, the device transmits Silence Identifier Descriptors (SIDs)
parameters to reproduce the local background noise at the remote (receiving) side.
The Comfort Noise Generation (CNG) support also depends on the silence suppression
(SCE) setting for the coder used in the voice channel. For more information, see the
description of the CNG-related parameters.
The procedure below describes how to configure CNG using the Web interface.
To configure CNG using the Web interface:
1. Open the RTP/RTCP Settings page (Configuration tab > VoIP menu > Media
submenu > RTP/RTCP Settings). The relevant parameters are listed under the
'General Settings' group, as shown below:
Figure 16-4: Comfort Noise Parameter in RTP/RTCP Settings Page
2. Set the 'Comfort Noise Generation Negotiation' parameter (ComfortNoiseNegotiation)
to Enable.
3. Click Submit to apply your changes.

 Loading...
Loading...