L2TP (see 'Configuring L2TP Server' on page 563)
43.1 Configuring IPSec
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is a series of guidelines for the protection of Internet
Protocol (IP) communications. It specifies procedures for securing private information
transmitted over public networks. The IPSec protocols include:
IKE (Internet Key Exchange) negotiates connection parameters, including keys for the
other two services.
Services supported by the IPSec protocols (AH, ESP) include confidentiality (encryption),
authenticity (proof of sender), integrity (detection of data tampering), and replay protection
(defense against unauthorized resending of data). IPSec also specifies methodologies for
key management. Internet Key Exchange (IKE), the IPSec key management protocol,
defines a series of steps to establish keys for encrypting and decrypting information; it
defines a common language on which communications between two parties is based.
Developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), IPSec and IKE together
standardize the way data protection is performed, thus making it possible for security
systems developed by different vendors to interoperate.
To configure IPSec:
1. Click the IPSec item (Configuration tab > Data menu > VPN submenu > IPSec); the
following page appears:
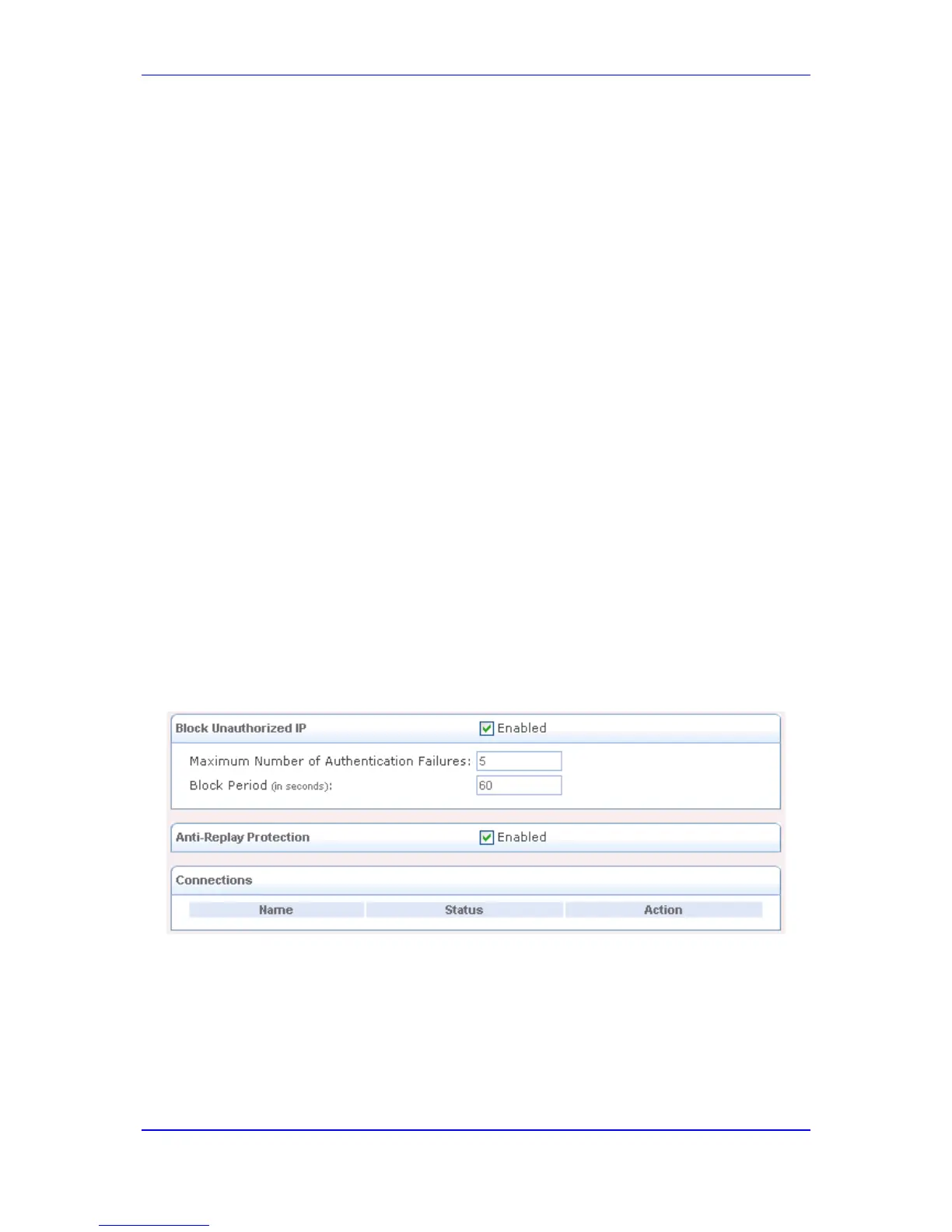
Figure 43-1: Configuring VPN IPSec
The Connections' group displays a list of IPSec connections (to create an IPSec
connection, see 'Configuring Network Connections' on page 583).
2. To block unauthorized IP to the device, do the following:
a. Select the 'Block Unauthorized IP' check box.
b. In the 'Maximum Number of Authentication Failures' field, enter the maximum
number of packets to authenticate before blocking the origin's IP address.
c. In the 'Block Period' field, enter the time frame during which the device drops
packets from an unauthorized IP address.

 Loading...
Loading...